- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Robust and Easy Protein Purification Method Using SpyDock-Modified Resin
一种使用 SpyDock 修饰树脂的稳定且简便的蛋白质纯化方法
发布: 2025年04月20日第15卷第8期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5270 浏览次数: 2035
评审: Alessandro DidonnaNuttavut KosemSneha Ray
Abstract
Protein purification is a critical step in both life sciences and biomanufacturing. Traditional affinity chromatography (AC) methods, including His-tag-based purification, provide high-purity proteins but are limited by the high cost of resins and the need for additional tag-removal steps. In this protocol, we present a reusable SpyDock-modified epoxy resin coupled with a pH-inducible self-cleaving intein for direct purification of proteins with authentic N-termini. This method enables efficient protein purification from cell lysates, achieving high purity (>90%) and yields comparable to the His-tag approach, without requiring tag removal. The SpyDock-modified resin protocol is robust, easy to implement, and cost-effective, making it suitable for both research and large-scale industrial applications.
Key features
• This protocol offers a robust and straightforward method for purifying proteins with authentic N-termini, eliminating the need for additional tag removal steps.
• The approach achieves higher purity and comparable yields to the commercial His-tag method.
• The SpyDock-modified epoxy resin is easy to prepare, cost-effective, and reusable.
Keywords: Protein purificationGraphical overview
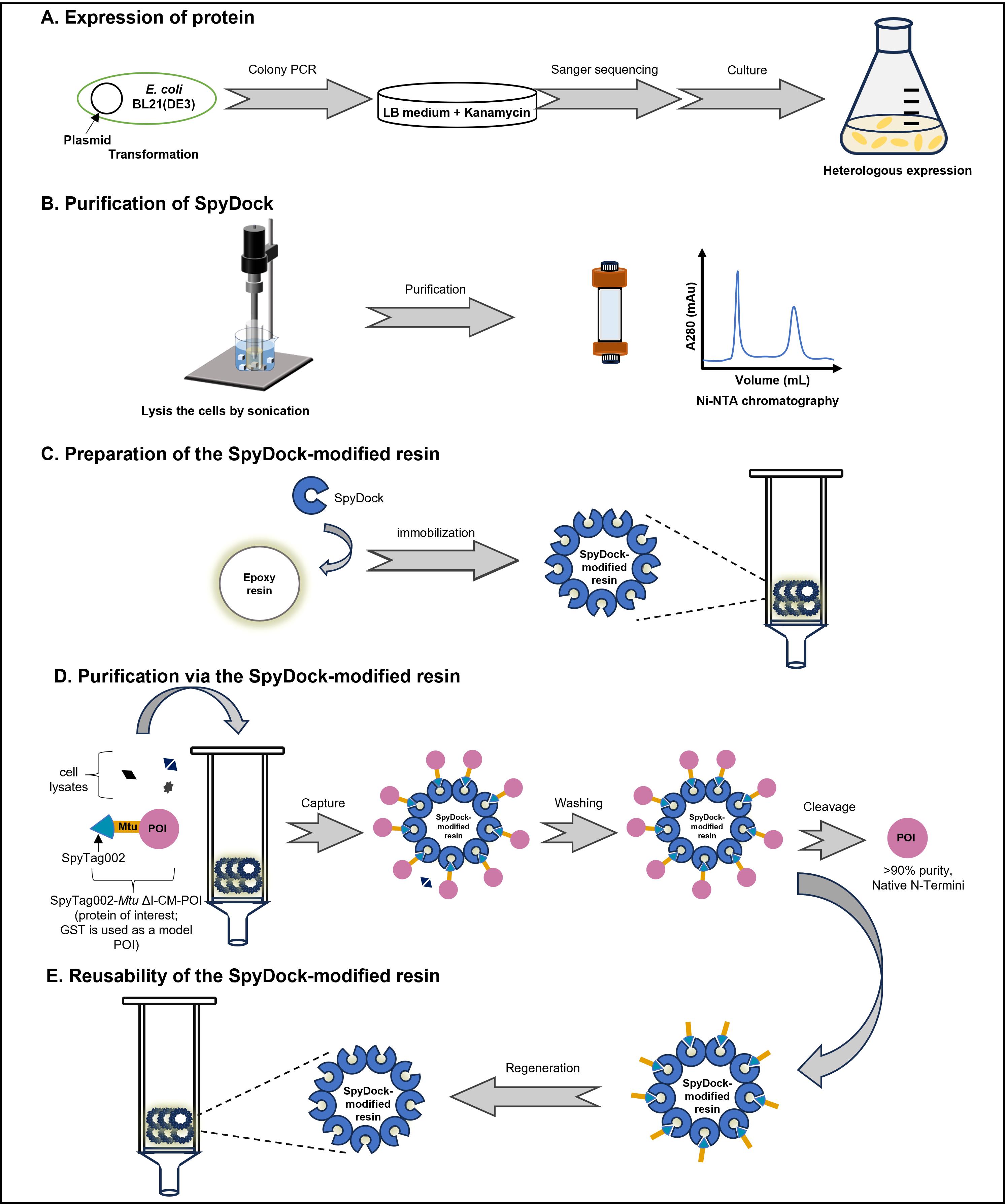
Background
Protein purification constitutes a foundational process in life sciences and biomanufacturing. It plays a pivotal role in producing high-quality proteins used in research, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications. Among the diverse array of available methods, affinity chromatography remains a dominant technology due to its high specificity and efficiency, which rely on specific interactions between target proteins and immobilized ligands [1]. However, the use of affinity tags, such as the His-tag, can present challenges, including potential disruptions to protein solubility, structure, and function, as well as complications from metal ion leakage and immunogenicity [2,3]. Moreover, the subsequent removal of tags via proteolysis can reduce yields and introduce additional costs [4]. These limitations have, in turn, prompted the development of more efficient, robust, and cost-effective purification strategies.
The SpyTag‐SpyCatcher protein ligase system has recently emerged as a new tool for protein purification, owing to its unique capacity to form stable and highly specific covalent complexes [5]. While previous methods utilizing the SpyTag-SpyCatcher system have been described, they still face limitations, such as the need for chemical peptide synthesis and challenges related to the non-reusability of the covalent linkage [6]. More recently, the engineered SpyDock (13.6 kDa) has provided a non-reactive version of SpyCatcher immobilized on SulfoLink resin, which offers advantages. However, its application has been constrained by the need for an additional SpyTag in the protein of interest (POI), oxidation-sensitive thioether bonds, and high resin costs, limiting its scalability for industrial use [3].
Here, we present a robust and easy protein purification protocol utilizing SpyDock-modified resin to directly purify SpyTag-fusion proteins from crude cell lysates. This method achieves high purities (>90%) and comparable yields to the conventional His-tag method, with significant advantages, including the use of inexpensive epoxy resins, stable secondary amine bond formation between SpyDock and the resin, multiple reuse cycles, and the incorporation of a self-cleavable Mtu ∆I-CM intein to produce proteins with authentic N-termini. Mtu ∆I-CM is a pH-inducible C-terminal cleavage intein, in which C-terminal cleavage activity can be induced by a pH shift from weak alkaline to weak acid conditions [7]. It has been successfully used in several protein purification strategies for the removal of purification tags [8].
This approach provides a scalable and efficient solution for protein purification, with broad applicability in biotechnological and pharmaceutical industries. We demonstrate the success of this protocol with the purification of three model proteins: glutathione S-transferase (GST, 25.4 kDa), human growth hormone (hGH, 22.1 kDa), and the nanobody caplacizumab (27.9 kDa) [9].
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Plasmids available upon request
1. E. coli BL21(DE3) competent cells (TransGen Biotech, catalog number: CD901-02)
2. POI (protein of interest) construct in pET30a plasmid (Merck, Novagen®, catalog number: 69909). It contains residues 1-597 with an N-terminal SpyTag002-Mtu ∆I-CM
Reagents
1. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Newprobe, catalog number: PB10056)
2. Premixed protein marker (Takara, catalog number: 3595A)
3. 6× protein loading buffer (TransGen Biotech, catalog number: DL101-02)
4. Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, CAS number: P000967)
5. Tryptone (Oxoid, catalog number: LPOO24)
6. Yeast extract (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0021)
7. Kanamycin (Newprobe, catalog number: PB1093)
8. Isopropyl-β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A100487-0025)
9. Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: T2556)
10. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4) (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A501726)
11. Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A501727)
12. Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A600445)
13. Imidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900153)
14. Potassium chloride (KCl) (Aladdin, catalog number: P112134)
15. Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 238597)
16. Ethanolamine (Aladdin, catalog number: E103810)
17. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) pellets (Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, catalog number: P000880)
18. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Cologne Chemical Reagent Factory, catalog number: LC149502)
19. Acetic acid (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A501931)
20. Tris base (Biofroxx, catalog number: 1115GR500)
21. Phosphoric acid (Aladdin, catalog number: P112024)
22. Sodium azide (NaN3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S2002)
23. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA·Na2) (Macklin, catalog number: E909976)
24. Bis-Tris (Aladdin, catalog number: B105639)
25. Guanidine hydrochloride (GdnHCl) (Aladdin, catalog number: G108676)
26. Ethanol (EtOH) (Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, CAS number: 64-17-5)
27. YoungPAGE MES SDS running buffer, powder (GenScript, catalog number: M00677)
28. SOC medium (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: B540119)
Solutions
1. LB medium (see Recipes)
2. 50 mg/mL kanamycin stock (see Recipes)
3. 1 M IPTG (see Recipes)
4. Binding buffer (see Recipes)
5. Elution buffer (see Recipes)
6. 100 mM PBS (see Recipes)
7. 1 M NaH2PO4 (see Recipes)
8. 1 M Na2HPO4 (see Recipes)
9. Coupling buffer (see Recipes)
10. 1 M ethanolamine (see Recipes)
11. 0.1 M acetate buffer (see Recipes)
12. 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (see Recipes)
13. Tris-phosphate (TP) buffer (see Recipes)
14. Storage buffer stock (see Recipes)
15. Wash buffer WTP (see Recipes)
16. Cleavage buffer (see Recipes)
17. Wash buffer (see Recipes)
18. 6 M GdnHCl (see Recipes)
19. 0.1 M NaOH (see Recipes)
20. 20% ethanol (see Recipes)
Recipes
1. LB medium (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Tryptone | 10 g/L | 10 g |
| Yeast extract | 5 g/L | 5 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 1,000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1,000 mL |
Sterilize using an autoclave at 121 °C for 20 min.
2. 50 mg/mL kanamycin stock (10 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Kanamycin | 50 mg/mL | 0.5 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 10 mL |
| Total | n/a | 10 mL |
a. Sterilize by filtering with a 0.22 μm syringe filter.
b. Store in 1 mL aliquots at -20 °C.
3. 1 M IPTG (10 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| IPTG | 1 M | 2.38 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 10 mL |
| Total | n/a | 10 mL |
a. Sterilize by filtering with a 0.22 μm syringe filter.
b. Store in 1 mL aliquots at -20 °C.
4. Binding buffer (pH 7.4) (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | 15.6 mM | 2.22 g |
| KH2PO4 | 4.4 mM | 0.6 g |
| NaCl | 500 mM | 29.22 g |
| Imidazole | 30 mM | 2.04 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 1,000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1,000 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 7.4 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
5. Elution buffer (pH 7.4) (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | 15.6 mM | 2.22 g |
| KH2PO4 | 4.4 mM | 0.6 g |
| NaCl | 500 mM | 29.22 g |
| Imidazole | 500 mM | 34.04 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 1,000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1,000 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 7.4 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
6. 100 mM PBS (pH 7.0) (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | 94.7 mM | 13.44 g |
| KH2PO4 | 5.3 mM | 0.72 g |
| NaCl | 137 mM | 8 g |
| KCl | 2.7 mM | 0.2 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 1,000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1,000 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 7.0 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
7. 1 M NaH2PO4 (500 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaH2PO4 | 1 M | 59.99 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 500 mL |
8. 1 M Na2HPO4 (500 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | 1 M | 70.98 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 500 mL |
9. Coupling buffer (pH 10.0) (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2SO4 | 250 mM | 35.51 g |
| 1 M NaH2PO4 | 6.8 mM | 6.8 mL |
| 1 M Na2HPO4 | 93.2 mM | 93.2 mL |
| H2O | n/a | To 1,000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1,000 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 8.0 with extra 1 M Na2HPO4.
b. Adjust pH from 8.0 to 10.0 with 1 M NaOH.
c. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
10. 1 M ethanolamine (pH 8.0) (200 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanolamine | 1 M | 12.1 mL |
| H2O | n/a | To 200 mL |
| Total | n/a | 200 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 8.0 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
11. 0.1 M acetate buffer (pH 4.0) (100 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid | 0.1 M | 571.9 μL |
| NaCl | 0.5 M | 2.922 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 100 mL |
| Total | n/a | 100 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 4.0 with 1 M NaOH.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
12. 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) (100 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Tris base | 0.1 M | 1.2114 g |
| NaCl | 0.5 M | 2.922 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 100 mL |
| Total | n/a | 100 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 8.0 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
13. Tris-phosphate (TP) buffer (pH 7.0) (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphoric acid | 25 mM | 0.86 mL |
| H2O | n/a | To 1000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1000 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 7.0 with Tris base.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
14. Storage buffer stock (50 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaN3 | 20% (w/v) | 0.01 g |
| TP buffer | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 50 mL |
a. Sterilize by filtering with a 0.2 μm syringe filter.
b. Store at -20 °C.
c. Dilute 400-fold with TP buffer before use.
15. Wash buffer WTP (pH 7.0) (500 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphoric acid | 25 mM | 0.86 mL |
| Imidazole | 0.5 M | 3.47 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 500 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 7.0 with Tris base.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
16. Cleavage buffer (pH 6.2) (200 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | 10.2 mM | 0.288 |
| KH2PO4 | 1.8 mM | 0.048 |
| NaCl | 137 mM | 1.6 g |
| KCl | 2.7 mM | 0.04 g |
| Bis-Tris | 20 mM | 0.839 g |
| EDTA·Na2 | 2 mM | 0.1489 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 200 mL |
| Total | n/a | 200 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 6.2 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
17. Wash buffer (pH 7) (500 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphoric acid | 25 mM | 0.86 mL |
| Imidazole | 4 M | 138.94 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 500 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 7 with Tris base.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
18. 6 M GdnHCl (pH 2.0) (500 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Guanidine hydrochloride | 6 M | 289.5 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 500 mL |
a. Adjust pH to 2.0 with 12 M HCl.
b. Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
19. 0.1 M NaOH (500 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| NaOH | 0.1 M | 2 g |
| H2O | n/a | To 500 mL |
| Total | n/a | 500 mL |
Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
20. 20% ethanol (1,000 mL)
| Reagent | Final concentration | Quantity or Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | 20% (v/v) | 200 mL |
| H2O | n/a | To 1,000 mL |
| Total | n/a | 1,000 mL |
Filter through a 0.22 μm hydrophilic membrane.
Laboratory supplies
1. HisTrapTM HP column (Cytiva, catalog number: 17524802)
2. Epoxy Activated Sepharose® 6B (Cytiva, catalog number: 17048001)
3. Empty spin columns (Biocomma, catalog number: 007400)
4. 0.2 mL PCR tubes (Axygen, catalog number: PCR-2CP-RT-C)
5. 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Axygen, catalog number: MCT-150-C)
6. 2 mL microcentrifuge tubes (Axygen, catalog number: MCT-200-C)
7. 15 mL centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430791)
8. 50 mL centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430829)
9. 1 L conical flask (Northglass, catalog number: HX-1121-01-11)
10. Sterile spreader (Baroque, catalog number: P003277)
11. 0.22 μm syringe filters (Pall Corporation, catalog number: 4652)
12. Syringes 20 mL, sterile, disposable (Double-dove, catalog number: HX-SLZSQ-SG-20ML/16)
13. Hydrophilic membrane filter, 0.22 μm, 47 mm, disposable (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: GSWP04700)
14. Amicon Ultra centrifugal filter units (3 K MWCO) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: UFC900396)
15. 4%–20% YoungPAGE® Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE gel (GenScript, catalog number: M00928)
16. SnakeSkinTM dialysis tubing, 3.5 K MWCO (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 88244)
Equipment
1. Pipetting system (Gilson, model: PIPETMAN Classic Starter Kit)
2. Shaking incubator (New Brunswick Scientific, model: Innova44)
3. Biochemical incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: IMH100-S)
4. Spectrophotometer (Youke Instrument, model: UV755B)
5. Electronic analytical balance (Mettler Toledo, model: MS204TS)
6. Autoclave (Hirayama, model: HVE-50)
7. -80 °C freezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 995)
8. Clean bench (Donglian, model: DL-CJ-2NDII)
9. Ultrasonic crasher (Scientz, model: JY92-II)
10. Centrifuge for 15 and 50 mL tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5810R)
11. Centrifuge for 1 and 2 mL tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5425R)
12. Electrophoresis equipment (Bio-Rad, model: Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Cell Systems)
13. pH meter (Mettler Toledo, model: FE28-standard)
14. Mini rotator (Gilson, model: Roto-MiNi Plus)
15. AKTA Purifier chromatography system (GE Healthcare, model: AKTA Purifier 10)
16. Protein staining instrument (GenScript, model: eStain L1)
17. Vacuum filtration system (Ilmvac GmbH, model: 120788)
18. Dry bath incubator (Coyote, model: H2O3-100C)
19. Magnetic stirrer (IKA, model: RTC-basic)
Software and datasets
1. SnapGene® (SnapGene, https://www.snapgene.com/)
2. ImageJ (National Institutes of Health DNA, https://imagej.net/ij/)
3. Prism (GraphPad, https://www.graphpad.com/)
4. Compute pI/Mw tool (https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/)
5. Unicorn for AKTA purifier (GE Healthcare, https://www.cytivalifesciences.com/en/us/shop/chromatography/software/unicorn-7-p-05649)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jan 6, 2025
接收日期: Mar 11, 2025
在线发布日期: Mar 24, 2025
出版日期: Apr 20, 2025
版权信息
© 2025 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Yang, X., Lin, Z., Xiang, Y., Chen, B. and Lao, Z. (2025). A Robust and Easy Protein Purification Method Using SpyDock-Modified Resin. Bio-protocol 15(8): e5270. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5270.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













