- EN - English
- CN - 中文
An HPLC-based Assay to Study the Activity of Cyclic Diadenosine Monophosphate (C-di-AMP) Synthase DisA from Mycobacterium smegmatis
基于高效液相色谱法的史氏分枝杆菌DisA环二腺苷酸(C-di-AMP)合成酶活性研究
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2024年12月20日第14卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5138 浏览次数: 1789
评审: Ritu GuptaPrajita PandeySoumya Moonjely

相关实验方案

酸水解-高效液相色谱法测定集胞藻PCC 6803中聚3-羟基丁酸酯的含量
Janine Kaewbai-ngam [...] Tanakarn Monshupanee
2023年08月20日 1824 阅读
Abstract
Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is a recently discovered second messenger that modulates several signal transduction pathways in bacterial and host cells. Besides the bacterial system, c-di-AMP signaling is also connected with the host cytoplasmic surveillance pathways (CSP) that induce type-I IFN responses through STING-mediated pathways. Additionally, c-di-AMP demonstrates potent adjuvant properties, particularly when administered alongside the Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine through mucosal routes. Because of its pivotal role in bacterial signaling and host immune response, this molecule has garnered significant interest from the pharmaceutical industry. This protocol outlines the quantification of c-di-AMP by an HPLC-based assay to enumerate the activity of c-di-AMP synthase from Mycobacterium smegmatis. The following protocol is designed to be generic, enabling the study of c-di-AMP synthase activity from other bacterial species. However, modifications may be required depending on the specific activity of c-di-AMP synthase from different bacterial sources.
Key features
• Easy and time-saving HPLC-based quantification method for c-di-AMP.
• Quick and reliable method to study enzymatic activity/kinetics of DisA/DAC.
• Elimination of potentially hazardous radioactive substrates and products for c-di-AMP quantification.
Keywords: C-di-AMP (C-di-AMP)Graphical overview
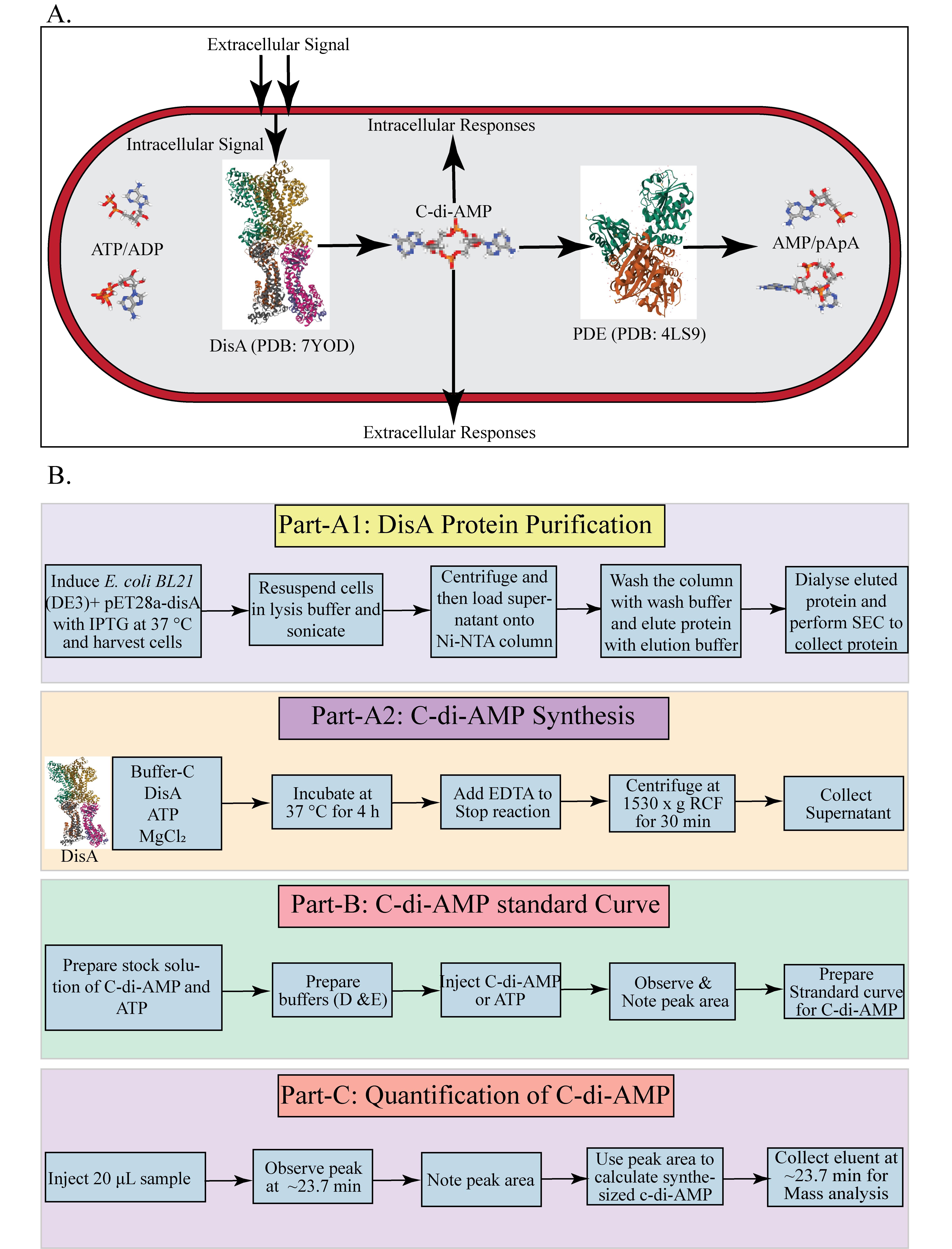
C-di-AMP homeostasis in mycobacteria and HPLC-based quantification process. A. Overview of c-di-AMP synthesis and hydrolysis in M. smegmatis. B. Overview of DisA protein purification, in vitro C-di-AMP synthesis, and HPLC-based quantification process.
Background
Cyclic di-adenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is an essential secondary messenger that plays a pivotal role in regulating various physiological processes, including osmoregulation, DNA integrity maintenance, sporulation, cell wall homeostasis, ion-channel regulation, antibiotic resistance, virulence gene expression, acid resistance, and carbon metabolism [1,2]. In the bacterial kingdom, c-di-AMP synthesis is catalyzed by di-adenylate cyclase (DAC) domain–containing proteins, which convert two ATP molecules into c-di-AMP in the presence of metal ions such as Mg and Mn. To date, five classes of DAC domain–containing proteins have been identified in bacteria: DNA integrity scanning protein A (DisA), c-di-AMP synthase A (CdaA), c-di-AMP synthase sporulation-specific (CdaS), c-di-AMP synthase N-terminal TM segment (CdaM), and c-di-AMP synthase Z (CdaZ) [3,4]. DisA, an octameric protein, has dual functions: it can bind to Holliday junction DNA or synthesize c-di-AMP [1]. Mycobacterium smegmatis is a non-pathogenic, rapidly growing bacterium from the genus Mycobacterium. It serves as a widely used model organism for studying mycobacteria, including pathogenic species like Mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) pathogens, such as Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium avium [5]. In M. smegmatis, the gene MSMEG_6080 encodes the c-di-AMP synthase DisA, which catalyzes c-di-AMP synthesis in the presence of Mg ions. DisA contains three main domains: the N-terminal DAC domain-1, the C-terminal DNA binding domain-3, and a linker domain (domain-2) that connects domain 1 and domain 2 [4,6]. The enzyme's active site is located at the interface of the DAC domains [1]. The cellular concentration of c-di-AMP is regulated by phosphodiesterases (PDEs), which are located in different operons and contain DHH-DHHA1 or HD (His-Asp) domains [7–9]. PDEs hydrolyze c-di-AMP into pApA or AMP. These enzymes typically feature a unique structural alignment, consisting of an N-terminal linked to a degenerate GGDEF domain and a C-terminal DHH-DHHA1 module, essential for c-di-AMP hydrolysis [9]. In Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the PDE (CnpB) has a core DHH-DHHA1 domain that hydrolyzes c-di-AMP first to linear 5'-pApA and then to two 5'-AMP molecules [8]. Similarly, the PDE in M. smegmatis (MSMEG_2630) contains a DHH-DHHA1 domain without additional regulatory domains found in the GdpP protein family of Bacillus subtilis. All types of PDEs require specific divalent metal ions (Mg, Mn, Co) for their activity [1,2,7]. The opposing activities of these enzymes maintain the homeostasis of c-di-AMP within bacterial cells. Herein, we describe an HPLC-based protocol to study the c-di-AMP synthesis by DisA protein from M. smegmatis. This protocol outlines a straightforward method for quantifying c-di-AMP synthesized by mycobacterial DisA. The method is adapted from protocols by Bai et al., Christen et al., and Ryjenkov et al., with necessary modifications [10–13]. This HPLC-based method allows quick, easy, and quantitative estimation of synthesized c-di-AMP by DisA, avoiding the utilization of potentially hazardous radioactive substrates and products.
Materials and reagents
Reagents
Purified DisA protein (Origin: M. smegmatis)
ATP (Sigma, catalog number: A2383)
C-di-AMP (Jena Bioscience, catalog number: NU-954S)
Tris base (Sigma, catalog number: 10708976001)
EDTA (Sigma, catalog number: E4884)
Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma, catalog number: S9888)
Tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate (Sigma, catalog number: 15583)
Methanol (HPLC grade) (Sigma, catalog number: 34860)
Double-distilled water (Milli-Q Ultrapure Water Systems)
KH2PO4 (Sigma, catalog number: P5655)
MgCl2 (Sigma, catalog number: M8266)
Tris-Cl (Sigma, catalog number: 10812846001)
Luria Bertani Broth, Miller (HIMEDIA, catalog number: M1245)
IPTG (Sigma, catalog number I6758)
Dialysis membrane (Sigma, catalog number: D9527)
Pipette tips (Tarsons, catalog numbers: 521000, 521010, 521020)
1.5 mL reaction tubes (Tarsons, catalog number: 500010)
Membrane filter, 0.22 μm pore size (Merck, catalog number: GSWP04700)
Protein purification buffers: lysis buffer, wash buffer, and elution buffer (see Recipes)
DisA dialysis buffer (buffer A) (see Recipes)
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) (buffer B) (see Recipes)
Buffer C for c-di-AMP synthesis reaction (see Recipes)
Buffer D (see Recipes)
Buffer E (see Recipes)
Protein Purification buffers
Lysis buffer
50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.9), 300 mM NaCl, and 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)
Wash buffer
50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.9), 300 mM NaCl, and 40 mM imidazole
Elution buffer
50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.9), 300 mM NaCl, and 300 mM imidazole
DisA dialysis buffer (buffer A)
50 mM Tris-Cl buffer at pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) (buffer B)
50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.9), 300 mM NaCl
Buffer C for c-di-AMP synthesis reaction
50 mM Tris (pH 9.4), 300 mM NaCl
Buffer D
100 mM KHPO, 4 mM tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate, pH 5.9
Buffer E
75% (v/v) buffer D, 25% (v/v) methanol
Equipment
Micropipettes with varying capacity (T-2, T-10, T-20, T-100, T-200, T-1000) (Tarsons, catalog numbers: 030000, 030010, 030020, 030030, 030040, 03005)
Spectrophotometer (Eppendorf, model: BioSpectrometer®)
HPLC system: Agilent 1200 HPLC (Agilent Technologies, model: Agilent 1200 HPLC) equipped with quaternary pump, autosampler, thermostated column compartment, with a UV detector
Äkta (Cytiva, former GE Health care, model: 29707638)
C-18 column (4.6 × 150 mm) (Agilent, model: Eclipse XDB-C-18)
Superose 12 10/300 Column (Cytiva, catalog number: GE17-5173-01)
Dry bath (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1660563)
Refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: centrifuge 5430)
Vortex shaker (Tarsons, model: SPINIXTM)
Biological safety cabinet (Thermo Scientific, model: 1300 Series Class II, Type A2)
Vacuum pump and assembly (Tarsons, model: ROCKYVACTM Vacuum Pump with assembly)
Water purification system (Millipore, model: Ultra-Pure Water Purification System)
Software and datasets
HPLC system software LC/CE Agilent ChemStation (B.04.02 SP1, 4/2010)
Graph Pad Prism 5.01 (5.01, 9/2007)
Procedure
文章信息
稿件历史记录
提交日期: Jul 30, 2024
接收日期: Oct 4, 2024
在线发布日期: Nov 4, 2024
出版日期: Dec 20, 2024
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Mahapa, A., Gautam, S., Rathore, A. and Chatterji, D. (2024). An HPLC-based Assay to Study the Activity of Cyclic Diadenosine Monophosphate (C-di-AMP) Synthase DisA from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Bio-protocol 14(24): e5138. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5138.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 其它化合物
生物化学 > 其它化合物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











