- EN - English
- CN - 中文
T-Cell-Based Platform for Functional Screening of T-Cell Receptors Identified in Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Sets of Tumor-Infiltrating T-Cells
基于 T 细胞的平台,用于对肿瘤浸润 T 细胞的单细胞 RNA 测序数据集中鉴定的 T 细胞受体进行功能筛选
发布: 2024年04月20日第14卷第8期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4972 浏览次数: 6370
评审: Mary Luz UribeAndrea GramaticaDavide PallucciMarco Di Gioia

相关实验方案

研究免疫调控血管功能的新实验方法:小鼠主动脉与T淋巴细胞或巨噬细胞的共培养
Taylor C. Kress [...] Eric J. Belin de Chantemèle
2025年09月05日 3522 阅读
Abstract
The advent of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) has enabled in-depth gene expression analysis of several thousand cells isolated from tissues. We recently reported the application of scRNAseq toward the dissection of the tumor-infiltrating T-cell repertoire in human pancreatic cancer samples. In this study, we demonstrated that combined whole transcriptome and T-cell receptor (TCR) sequencing provides an effective way to identify tumor-reactive TCR clonotypes on the basis of gene expression signatures. An important aspect in this respect was the experimental validation of TCR-mediated anti-tumor reactivity by means of an in vitro functional assay, which is the subject of the present protocol. This assay involves the transient transfection of mRNA gene constructs encoding TCRα/β pairs into a well-defined human T-cell line, followed by co-cultivation with the tumor cells of interest and detection of T-cell activation by flow cytometry. Due to the high transfectability and the low background reactivity of the mock-transfected T-cell line to a wide variety of tumor cells, this assay offers a highly robust and versatile platform for the functional screening of large numbers of TCR clonotypes as identified in scRNAseq data sets. Whereas the assay was initially developed to test TCRs of human origin, it was more recently also applied successfully for the screening of TCRs of murine origin.
Key features
• Efficient functional screening of—and discrimination between—TCRs isolated from tumor-reactive vs. bystander T-cell clones.
• Applicable to TCRs from CD8+ and CD4+ tumor-infiltrating T-cells originating from patient-derived tumor samples and syngeneic mouse tumor models.
• Rapid flow cytometric detection of T-cell activation by means of TNFα and CD107a expression after a 5 h T-cell/tumor cell co-cultivation.
Keywords: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞)Graphical overview
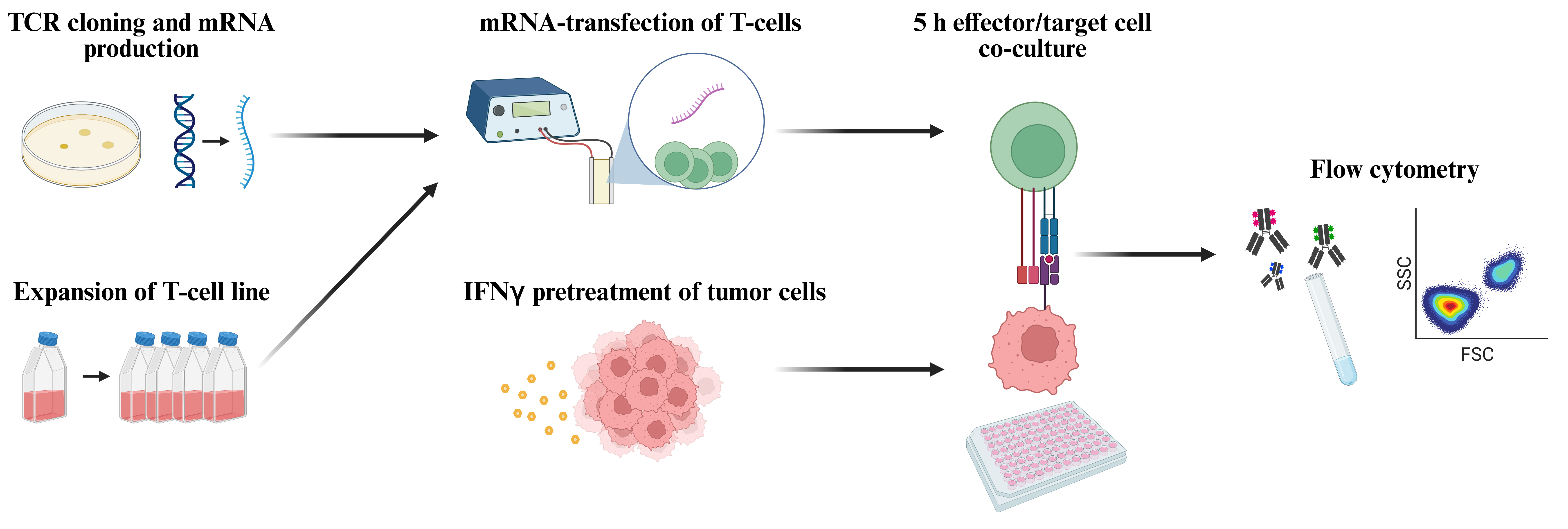
Workflow for functional screening of T-cell receptors (TCRs) as transiently expressed in human T-cells by means of mRNA transfection followed by co-culture with autologous tumor cells and analysis of T-cell reactivity by means of flow cytometric detection of TNFα and CD107a (figure created with BioRender.com).
Background
Crucial to the further improvement of T-cell cancer therapy is detailed information on the anti-tumor reactivity and antigen-specificity of the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) repertoire in large numbers of human tumor samples from different cancer types. In recent years, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) technology platforms have emerged to enable the identification of paired T-cell receptor (TCR)α/β sequences in the context of the complete transcriptome for thousands of tumor-infiltrating T-cells. Whereas initial studies primarily focused on discriminating between tumor-reactive and bystander TCR clonotypes on the basis of distinct transcriptomic gene signatures [1], more recent studies including our own encompassed experimental validation of the predicted tumor reactivity by means of molecular cloning of selected TCRα/β pairs and in vitro functional assays with TCR-transfected T-cells [2–7]. In the majority of cases, these screenings were based on the presumption that the immunodominant T-cell antigens in tumors are neoepitopes encoded by somatic mutations in the tumor genome, and therefore focused on TCR screening against libraries of potential neoepitopes. However, it is still an open question whether this class of epitopes truly represents the immunodominant antigens targeted by the natural anti-tumor T-cell response in human cancers.
In view of the latter, based on the low mutational burden of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) [8,9] and the notion that only a small fraction of nonsynonymous mutations is expected to encode immunogenic T-cell epitopes [10–13], we chose to perform an unbiased functional screening of tumor-derived TCRs against autologous tumor cells instead of mutanome-based candidate neoepitopes [7,14]. Evidently, this required a highly robust assay with a favorable signal-to-background ratio. Whereas Jurkat T-cells are commonly used in this respect, the readout for TCR-mediated activation is limited to interleukin-2 production and reporter gene construct expression. Instead, our TCR screening assay is based on a human T-cell line, subsequently referred to as T222, that originated from an ex vivo–expanded culture of tumor-infiltrating T-cells isolated from a human PDAC sample (PDA222). In the context of prior studies, we noticed that the TCR repertoire of this T-cell culture had drastically changed during expansion, leading to the loss of all dominant TCR clonotypes as detected in the tumor sample [15]. Upon further in vitro cultivation according to a well-established rapid expansion protocol [16], we found that this T-cell line grew indefinitely and consistently. Moreover, T222 lacked background reactivity as measured on the basis of multiple commonly applied T-cell activation parameters when co-cultivated with various human tumor cells, including multiple PDAC, colorectal cancer, and melanoma cell lines and cultures, rendering it a potentially suitable tool for the functional screening of TCRs as identified in scRNAseq data sets of tumor-infiltrating T-cell isolates. With respect to TCR gene transduction, we chose transient mRNA transfection, based on the superior results obtained with this technology by colleagues in the field [17]. We selected TNFα and CD107a as markers for T-cell activation, not only because these reflect key aspects of the effector T-cell response (cytokine production and cytolytic activity), but also because both markers can be optimally measured in the context of a 5 h assay. By means of mRNA-transfected T222 cells, we successfully screened > 150 TCRs derived from nine human PDAC samples for reactivity against autologous tumor cells in 5 h co-cultivation assays [7]. In subsequent studies, our assay was also used successfully for the screening of TCRs derived from tumor-reactive CD4+ T-cells and of > 100 TCRs derived from TIL scRNAseq data sets of murine PDAC tumors.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
T222 cell line as generated by in vitro expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of human PDAC sample PDA222 [7]
Tumor cell lines derived from primary tumor samples of PDAC patients [7]
Murine tumor cell lines PDA30364 and PDA30364-OVA [18]
Reagents
T7 mScript standard mRNA production system (Cellscript, catalog number: C-MSC100625)
RNA 6000 Nano Kit for 2100 Bioanalyzer Systems (Agilent, catalog number: 5067-1511)
pcDNATM 3.1(+) (Invitrogen, catalog number: V79020)
Anti-human HLA-A, B, C antibody APC, W6/32 (BioLegend, catalog number: 311410)
Anti-human HLA-DR Antibody PE, LN3 (BioLegend, catalog number: 327008)
X-VIVO 15 (Lonza, catalog number: BE02-060Q)
Human serum type AB (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H4522)
Gentamycin (Life Technologies, catalog number: 15750045)
Amphotericin B (Life Technologies, catalog number: 15290-026)
Human Interleukin-2 Proleukin® S (Clinigen Healthcare, catalog number: 17152.00.00)
Purified anti-human CD3 (Invitrogen, catalog number: 16-0037-85)
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2650)
Human albumin 20% (CSL Behring, catalog number: PZN: 1468366)
OptiMEM serum-reduced media (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 31985062)
Advanced DMEM/F12 (Gibco, catalog number: 12634010)
L-Glutamine, 200 mM (Gibco, catalog number: 25030-024)
Penicillin-Streptomycin, 10,000 IU/mL (Gibco, catalog number: 15140-122)
B-27 supplement, 50× (Gibco, catalog number: 17504044)
HEPES, 1 M, pH 7.0–7.6 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H0887)
Heparin sodium salt, grade I-A (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3149)
Glucose solution, 200 g/L (Gibco, catalog number: A24940-01)
RPMI 1640 (Gibco, catalog number: 52400-025)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Biowest, catalog number: S181B-500)
DMEM, high glucose (Gibco, catalog number: 41965-039)
Sodium pyruvate, 100 mM (Gibco, catalog number: 11360039)
Recombinant human/murine interferon gamma (IFNγ) (Immunotools, catalog number: 11343536/12343536)
MEKi, GDC-0623, mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor (Active Biochem, catalog number: A-1181)
Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8537)
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9418)
EDTA, UltraPure 0.5 M, pH 8.0 (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15575020)
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8139)
Ionomycin calcium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I0634)
Anti-human CD107a Antibody PE/APC, H4A3 (BioLegend, catalog number: 328608/328620)
GolgiStop, Protein Transport Inhibitor (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 554724)
GolgiPlug, Protein Transport Inhibitor (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 555029)
LIVE/DEAD Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain kit (DCM) (Life Technologies, catalog number: L34957)
Anti-mouse CD16/32, 93 (BioLegend, catalog number: 101320)
Anti-mouse CD16.2, 9E9 (BioLegend, catalog number: 149502)
Anti-human CD3 antibody Brilliant Violet 711, OKT3 (BioLegend, catalog number: 317328)
Anti-human CD4 antibody APC/Fire 750, SK3 (BioLegend, catalog number: 344638)
Anti-human CD8a antibody Alexa Fluor 700, HIT8a (BioLegend, catalog number: 300920)
Anti-mouse TCR beta chain antibody Brilliant Violet 421, H57-597 (BioLegend, catalog number: 109230)
Anti-mouse CD8a antibody PerCP, 53-6.7 (BioLegend, catalog number: 100732)
Anti-mouse CD8b antibody PE, YTS156.7.7 (BioLegend, catalog number: 126608)
Anti-mouse CD4 antibody PE, GK1.5 (BioLegend, catalog number: 100408)
Cytofix/Cytoperm Fixation/Permeabilization kit (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 554714)
Perm/Wash buffer, included in Fixation/Permeabilization kit (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 51-2091KZ)
Anti-human TNF alpha antibody Alexa Fluor 488, MAb11 (BioLegend, catalog number: 502915)
Solutions
T-cell expansion medium (see Recipes)
Freezing medium (see Recipes)
T-cell medium (see Recipes)
Tumor cell medium I: human (see Recipes)
Tumor cell medium II: mouse (see Recipes)
FACS buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
T-cell expansion medium
X-VIVO 15 supplemented with 2% human serum type AB, 100 IU/mL penicillin-streptomycin, 20 µg/mL gentamycin, 2.5 µg/mL amphotericin B, and 30 ng/mL purified anti-human CD3
Freezing medium
FBS supplemented with 10% DMSO
T-cell medium
X-VIVO 15 supplemented with 2% human albumin
Tumor cell medium I: human
DMEM/F12+ supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 IU/mL penicillin-streptomycin, 2% B27 supplement (50×), 5 mM HEPES, 12 mg/mL heparin, and 6 g/L glucose
Tumor cell medium II: mouse
DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 IU/mL penicillin-streptomycin, and 1 mM sodium pyruvate
FACS buffer
PBS supplemented with 0.5% BSA and 5 mM EDTA
Laboratory supplies
T25 tissue culture flask (TPP, catalog number: TPP90026)
Cuvette, 0.4 cm gap Gene Pulser/MicroPulser Electroporation (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1652088)
24-well plate, flat bottom, TC-treated (VWR, catalog number: 734-2325)
96-well U-bottom plate, round bottom, TC-treated (Avantor, catalog number: 734-2328)
96-well plate, flat bottom, polystyrene (TPP, catalog number: TPP92096)
96-well V-bottom plate, conical bottom, non treated, no lid (Costar, catalog number: 3897)
Pasteur pipette, glass 230 mm, no filter (WU Mainz, catalog number: 200763)
15 mL tube conical bottom (Greiner, catalog number: 188271-N)
50 mL tube conical bottom, polypropylene (Falcon, catalog number: 352070)
Equipment
2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent)
Incubator Heracell 240i (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 51032875)
Centrifuge 5810R refrigerated (Eppendorf, catalog number: EPP-022628187)
Electroporator, Gene Pulser Xcell Systems with ShockPod cuvette chamber (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1652660)
LSRFortessaTM cell analyzer (BD Biosciences)
Software
FlowJo v10.9.0 (FlowJo LLC, Ashland, OR, USA)
Bio Render (https://www.biorender.com/)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Ehrenfried, A. R., Zens, S., Steffens, L. K., Kehm, H., Paul, A., Lauenstein, C., Volkmar, M., Poschke, I., Meng, Z. and Offringa, R. (2024). T-Cell-Based Platform for Functional Screening of T-Cell Receptors Identified in Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Sets of Tumor-Infiltrating T-Cells. Bio-protocol 14(8): e4972. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4972.
- Meng, Z., Rodriguez Ehrenfried, A., Tan, C. L., Steffens, L. K., Kehm, H., Zens, S., Lauenstein, C., Paul, A., Schwab, M., Förster, J. D., et al. (2023). Transcriptome-based identification of tumor-reactive and bystander CD8+ T cell receptor clonotypes in human pancreatic cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 15(722): eadh9562.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫细胞功能 > 淋巴细胞
免疫学 > 免疫机理
细胞生物学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link