- EN - English
- CN - 中文
In-house Extraction and Purification of Pfu-Sso7d, a High-processivity DNA Polymerase
内部提取和纯化Pfu-Sso7d:一种高持续性的DNA聚合酶
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2024年04月05日第14卷第7期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4967 浏览次数: 2672
评审: Marcelo S. da SilvaRitu GuptaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an extensively used technique to quickly and accurately make many copies of a specific segment of DNA. In addition to naturally existing DNA polymerases, PCR utilizes a range of genetically modified recombinant DNA polymerases, each characterized by varying levels of processivity and fidelity. Pfu-Sso7d, a fusion DNA polymerase, is obtained by the fusion of Sso7d, a small DNA-binding protein, with Pfu DNA polymerase. Pfu-Sso7d is known for its high processivity, efficiency, and fidelity but is sold at a sumptuously high price under various trade names and commercial variants. We recently reported a quick and easy purification protocol that utilizes ethanol or acetone to precipitate Pfu-Sso7d from heat-cleared lysates. We also optimized a PCR buffer solution that outperforms commercial buffers when used with Pfu-Sso7d. Here, we provide a step-by-step guide on how to purify recombinant Pfu-Sso7d. This purification protocol and the buffer system will offer researchers cost-efficient access to fusion polymerase.
Key features
• We detail a precipitation-based protocol utilizing ethanol and acetone for purifying Pfu-Sso7d.
• Despite ethanol and acetone displaying effective precipitation efficiency, acetone is preferred for its superior performance.
• Furthermore, we present a PCR buffer that outperforms commercially available PCR buffers.
• The Pfu-Sso7d purified in-house and the described PCR buffer exhibit excellent performance in PCR applications.
Background
DNA polymerases are extensively used in PCR to exponentially amplify DNA and generate a substantial quantity from a minimal initial DNA template. An efficient PCR amplification necessitates a DNA polymerase that is not only thermostable but also has excellent fidelity and processivity. These essential DNA polymerase characteristics shorten extension times and enable error-free amplification of lengthy DNA templates. A variety of approaches are utilized to enhance the processivity of the DNA polymerase. One such approach is using fusion DNA polymerases, created by the covalent fusion of a tiny DNA-binding protein to the polymerase domain of the enzyme. Pfu-Sso7d fusion DNA polymerase, for instance, is produced by the fusion of Pfu DNA polymerase with Sso7d, a tiny 7 kDa protein derived from Sulfobulus solfataricus, and binds to dsDNA in a sequence-independent manner [1,2]. This fusion significantly increases processivity by preventing the Pfu-Sso7d from frequently dissociating from the template.
Recombinant DNA polymerases are typically purified through a time-consuming, cost-intensive, two-step affinity purification followed by dialysis [3,4]. We recently reported a straightforward, economical, and time-saving method for expressing and purifying the Pfu-Sso7d fusion DNA polymerase. This involves heat denaturation and DNase I treatment of bacterial lysate to recover thermostable DNA polymerase (Figure 1). The heat-cleared and DNase I–treated lysates are then precipitated using ethanol or acetone [5]. We also reported an in-house PCR buffer system that outperforms commercially available alternatives for PCR amplification of various DNA templates. Laboratories dealing with a large number of PCRs and constrained resources can greatly benefit from the in-house purification of thermostable polymerases and the preparation of in-house buffer solutions.
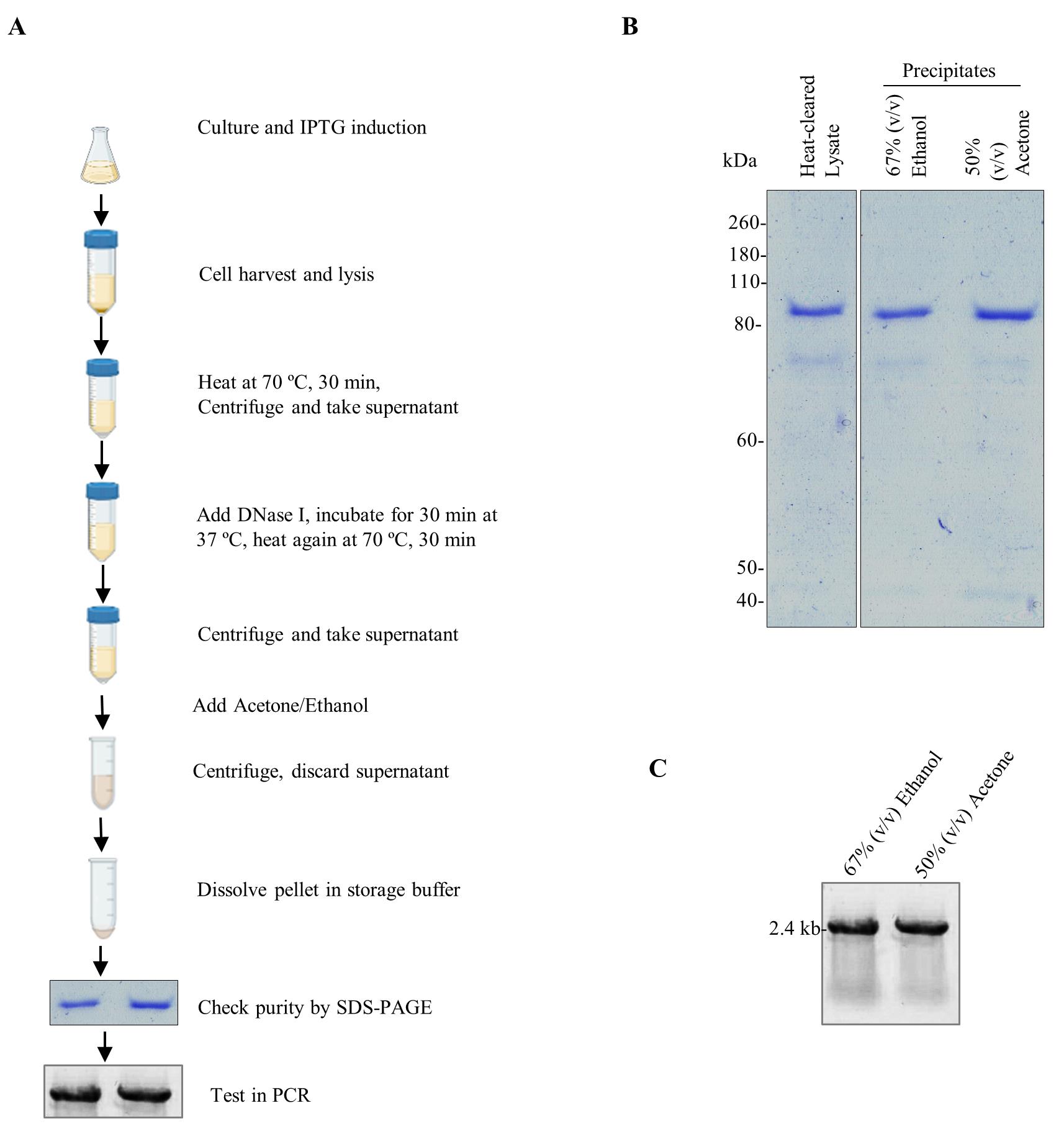
Figure 1. Precipitation-based protocol for the purification of Pfu-Sso7d fusion DNA polymerase. A. Schematic representation showing the extraction and purification of Pfu-Sso7d from the IPTG-induced bacterial culture. Briefly, a colony of BL21 (DE3) pLysS transformed with pET-28b-Pfu-Sso7d expression plasmid was cultured and induced with IPTG. Bacterial cells were harvested and lysed using a lysis buffer containing lysozyme. Heat-cleared and DNase I–treated lysates were then precipitated using acetone or ethanol and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and PCR. B. SDS-PAGE analysis of the Pfu-Sso7d in heat-cleared and DNase I–treated cell lysate and of the precipitates obtained with 67% (v/v) ethanol or 50% (v/v) acetone. C. The precipitated Pfu-Sso7d was tested in the PCR amplification of a 2.4 kb fragment from the plasmid template.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
BL21 (DE3) pLysS cells for protein expression (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C606010)
pET-28b-Pfu-Sso7d plasmid (a gift from Dr. Alexander Klenov, York University, Canada) (Sequence can be downloaded from https://barricklab.org/twiki/pub/Lab/ProtocolsReagentsPfuSso7d/6his-pfu-sso7d-pET28.gbk)
Reagents
Tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane, Tromethamine, Tris base (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 71033)
Luria broth (LB) (Himedia, catalog number: M575)
Agar (Himedia, catalog number: GRM026)
Super optimal catabolite (SOC) (Himedia, catalog number: G015)
Kanamycin (Himedia, catalog number: A008)
Chloramphenicol (Himedia, catalog number: CMS218)
Deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 14464)
Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Himedia, catalog number: MB072)
Phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 87606)
Lysozyme (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 45822)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 1948101)
Acrylamide 1× crystal (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 89314)
Bis-acrylamide (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 38516)
Ammonium persulfate (APS) (Himedia, catalog number: MB003)
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl ethylenediamine (TEMED) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 84666)
β-mercaptoethanol (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 83759)
Sodium phosphate monobasic (NaH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71505-250)
Glycerol (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 59991)
Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 17315)
Bromophenol blue (Himedia, catalog number: GRM914)
Pair of specific primers (Integrated DNA Technology)
Deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) (Invitrogen, catalog number: AM2222)
Agarose (Himedia, catalog number: MB002)
Betaine solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B0300)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Qualigens, catalog number: Q18455)
Ethanol, absolute 99.9% (any brand)
Acetone (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 31566)
Tween 20 (Merck, catalog number: SB3S630097)
Triton X-100 (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 64518)
Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 76945)
Glycine (Merck, catalog number: MA7M562461)
Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 93473)
Sodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate (Na2HPO4·2H2O) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 83417)
Potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate extra pure AR, 99.5% (KH2PO4) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 50451)
Nonidet P-40 (NP-40) (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: 28324)
Bovine serum albumin solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A8412)
Acetic acid (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 85801)
Ammonium sulphate [(NH4)2SO4] (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 88064)
Magnesium sulphate (MgSO4) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 50014)
Potassium chloride extra pure AR, 99.5% (KCl) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 38630)
Hydrochloric acid, 6N aqueous solution (HCl) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 17560)
Ethidium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E7637)
Magnesium chloride anhydrous extra pure, 98% (MgCl2) (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 31196)
Solutions
Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
Storage buffer (see Recipes)
100 mM IPTG (see Recipes)
1 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 (see Recipes)
1.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8 (see Recipes)
4× SDS dye (see Recipes)
10× Tris-Glycine-SDS buffer (see Recipes)
Staining solution (see Recipes)
De-staining solution (see Recipes)
10× PCR buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
PBS (100 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Na2HPO4·2H2O 100 mM 1.779 g KH2PO4 18 mM 0.244 g NaCl 137 mM 0.8 g KCl 2.7 mM 0.02 g Adjust pH to 7.4 with HCl/NaOH Double-distilled water n/a up to 100 mL Autoclave and store at 4 °C.
Lysis buffer (50 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity NaCl (5 M) 300 mM 3 mL NaH2PO4 (1 M, pH 8.0) 50 mM 2.5 mL Glycerol (100%) 10% (v/v) 5 mL Triton-X 100 (10%) 0.1% (v/v) 0.5 mL Double-distilled water n/a up to 50 mL Store at 4 °C. Add 0.5 mM PMSF and 2 mg/mL lysozyme just before use.
Storage buffer (50 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity EDTA (0.5 M) 0.1 mM 0.01 mL Tris-HCl (1 M, pH 8.0) 25 mM 1.25 mL NaCl (5 M) 250 mM 2.5 mL NP-40 (100%) 0.2% (v/v) 0.1 mL Glycerol (100%) 50% (v/v) 25 mL Tween 20 (100%) 0.2% (v/v) 0.1 mL Double-distilled water n/a up to 50 mL Filter sterilize, aliquot, and store at -20 °C. Add 2 mM DTT just before use.
100 mM IPTG (10 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity IPTG 100 mM 0.238 g Double-distilled water n/a up to 10 mL Filter sterilize, aliquot, and store at -20 °C.
1 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 (100 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Tris base 1 M 12.1 g Adjust pH to 8.8 with HCl/NaOH Double-distilled water n/a up to 100 mL Autoclave and store at 4 °C.
1.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8 (100 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Tris base 1.5 M 18.1 g Adjust pH to 8.8 with HCl/NaOH Double-distilled water n/a up to 100 mL Autoclave and store at 4 °C.
4× SDS dye (5 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Tris-HCl (1 M, pH 6.8) 200 mM 1 mL Glycerol (100%) 40% (v/v) 2 mL SDS (10%) 4% (w/v) 2 mL Bromophenol blue 0.08% (w/v) 0.004 mL Double-distilled water n/a up to 5 mL Aliquot and store at -20 °C. Add β-mercaptoethanol to 5% (v/v) just before use.
10× Tris-Glycine-SDS buffer (100 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Tris base 250 mM 3.03 g SDS 35 mM 1 g Glycine 1.92 M 14.4 g Double-distilled water n/a up to 100 mL Store at room temperature.
Staining solution (500 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Methanol (100%) 40% (v/v) 200 mL Acetic acid (100%) 8% (v/v) 40 mL Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 0.1% (w/v) 0.5 g Double-distilled water n/a up to 500 mL Store at room temperature.
De-staining solution (500 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Methanol (100%) 40% (v/v) 200 mL Acetic acid (100%) 8% (v/v) 40 mL Double-distilled water n/a up to 500 mL Store at room temperature.
10× PCR buffer (25 mL)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Tris-HCl (1.5 M, pH 8.8) 200 mM 3.3 mL KCl (1 M) 100 mM 2.5 mL (NH4)2SO4 (1 M) 100 mM 2.5 mL MgSO4 (1 M) 20 mM 0.5 mL Triton X-100 (10%) 1% (v/v) 2.5 mL Nuclease-free BSA (100 mg/mL) 1 mg/mL 0.25 mL Double-distilled water n/a up to 25 mL Filter sterilize, aliquot, and store at -20 °C.
Laboratory supplies
100 mm cell culture dishes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z755923-150EA)
50 mL tubes (Abdos, catalog number: P10424)
1.5 mL tubes (Abdos, catalog number: P10202)
Equipment
Micropipettes 10, 100, 200, and 1,000 μL (any brand)
Orbital shaker (any brand)
Vortex mixer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 128101)
Water bath (MAC Serological water bath, catalog number: MSW-273)
Incubator (any brand)
Centrifuge (any brand)
Biosafety cabinet (MAC Horizontal laminar flow bench, catalog number: MSW-161)
PCR machine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: VeritiTM 96-well fast thermal cycler)
Agarose gel apparatus (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1703940)
Protein electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad, model: Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra cell, catalog number: 1658005EDU)
Visible spectrophotometer (Labman, model: LMSP-V320)
Autoclave (any brand)
UV transilluminator (any brand)
Quantus fluorometer (Promega, catalog number: E6150)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Mahboob, A., Fatma, N. and Husain, A. (2024). In-house Extraction and Purification of Pfu-Sso7d, a High-processivity DNA Polymerase. Bio-protocol 14(7): e4967. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4967.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 表达
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













