- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolation and Enrichment of Major Primary Neuroglial Cells from Neonatal Mouse Brain
从新生小鼠脑中分离和富集主要原代神经胶质细胞
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2024年01月20日第14卷第2期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4921 浏览次数: 4294
评审: Xi FengAchira RoyNafisa M. Jadavji
Abstract
The central nervous system (CNS) relies on the complex interaction of neuroglial cells to carry out vital physiological functions. To comprehensively understand the structural and functional interplay between these neuroglial cells, it is essential to establish an appropriate in vitro system that can be utilized for thorough investigation. Traditional protocols for establishing primary neuronal and mixed glial cultures from prenatal mice or neural stem cells require sacrificing pregnant mice and have the drawback of yielding only specific types of cells. Our current protocol overcomes these drawbacks by utilizing the brain from day-0 pups to isolate CNS resident neuroglial cells including astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes [oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) and differentiated oligodendrocytes], and meningeal fibroblasts, as well as hippocampal neurons, avoiding sacrificing pregnant mice, which makes this procedure efficient and cost effective. Furthermore, through this protocol, we aim to provide step-by-step instructions for isolating and establishing different primary neuroglial cells and their characterization using cell-specific markers. This study presents an opportunity to isolate, culture, and establish all major CNS resident cells individually. These cells can be utilized in various cell-based and biochemical assays to comprehensively investigate the cell-specific roles and behaviors of brain resident cells in a reductionist approach.
Key features
• Efficient isolation of major neuroglial cells like meningeal fibroblasts, neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia from a single day-0 neonatal mouse pup’s brain.
• Circumvents the sacrifice of pregnant female mice.
• Acts as a bridging experimental method between secondary cell lines and in vivo systems.
• Isolated cells can be used for performing various cell-based and biochemical assays.
Graphical overview
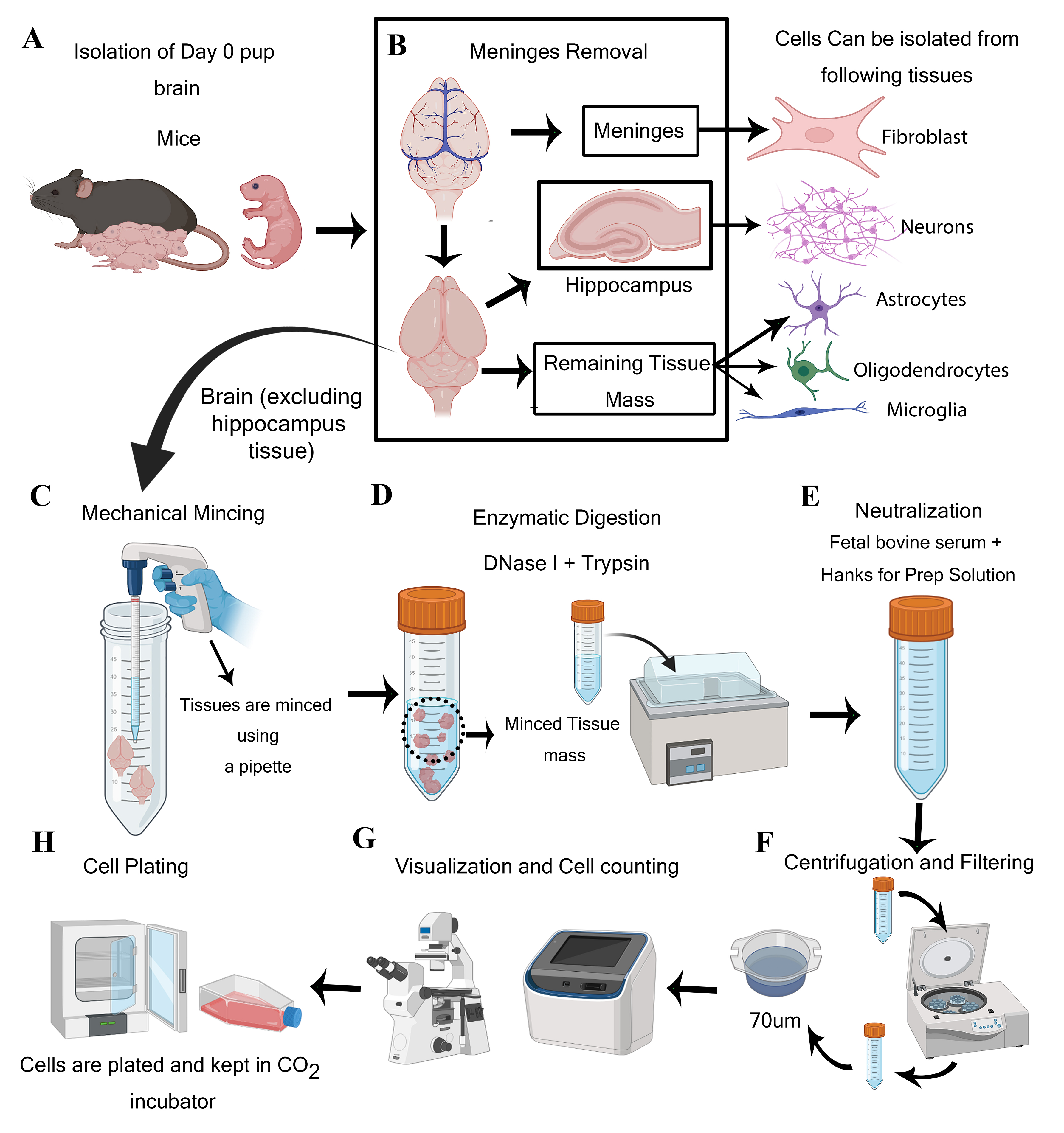
Steps for isolation of meningeal fibroblast and neuroglial cells from day 0 pups of mice (Created using BioRender.com)
Background
Intricate neuro-glial interactions, as an intertwined system of brain circuitry, play a vital role in various central nervous system (CNS) functions and in the maintenance of homeostasis [1, 2]. Contemporary research indicates that the role of glial cells is not limited to mere supportive cells for neurons; instead, glial cells carry out complex physiological functions such as recycling neurotransmitters, regulation of the blood–brain barrier, myelin sheath formation, immunological functions, and many more. Impairment or dysfunction of glial cell function frequently disrupts CNS cell communication, potentially leading to diverse pathological conditions [3–5]. To understand this complex cellular and molecular crosstalk in various pathological conditions, diverse experimental animal models have been developed [6, 7]. For instance, transgenic mice expressing mutated forms of amyloid protein precursor and presenilin-1 serve as a disease model for Alzheimer's [8], while transgenic mice overexpressing α-synuclein are widely employed to study Parkinson's disease [9]. Additionally, experimental autoimmune encephalitis and virus-induced demyelination models [mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) and Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus] have been extensively used to elucidate the etiology of multiple sclerosis [10, 11].
While in vivo models provide unique insights into neuropathological studies, investigating complex cellular interactions in an in vivo setup to emphasize the cell's individualistic role is an intricate process [12]. However, relying on secondary cell lines may be insufficient to understand the diverse functions of neuroglial cells, as they are transformed cells, and continuous cell divisions accumulate mutations [13, 14]. That is why a suitable in vitro primary culture system is necessary to elucidate the complex array of neuroglial crosstalk and, at the same time, overcome the limitations mentioned above. Existing primary neuroglial cell isolation procedures routinely involve using a certain developmental stage of pups to isolate a specific cell (8–12 pups), which can often be exhausting and time-consuming. Cells like astrocytes and meningeal fibroblasts are usually isolated from day-0 pups (P0) [15–17] whereas oligodendrocytes precursor cells’ (OPCs) isolation is done from 5–7-day-old pups [18]. However, neurons are terminally divided cells, and their isolation requires embryonic pups (E14–E15) [19], where the mice mother must be sacrificed.
Our current protocol overcomes these limitations by using day-0 pups to separate a variety of neuroglial cells. This procedure involves the collection of meninges and hippocampal tissue to isolate meningeal fibroblasts [16] and neurons [20], respectively. The remaining brain tissues (left after isolating meninges and hippocampus) can either be used to establish a mixed glial culture with subsequent isolation of enriched astrocytes [21] and microglia [22] or be used for OPCs culture, using serum-free oligodendrocyte-specific medium. OPCs can later be differentiated into mature oligodendrocytes using chemically defined differentiation medium [17]. In addition, this protocol avoids the sacrifice of female mice, as day-0 pups are used to harvest the cells. Astrocytes and fibroblasts isolated using this protocol can be passaged, whereas oligodendrocytes, neurons, and microglia should be seeded as per the experimental requirement. Therefore, if RNA or proteins from these cells are required, more pups are needed to obtain a larger number of these cells. Microglial cells isolated through this protocol can only be used for immunofluorescence experiments. For gene-level expression studies, it is advisable to use the CD11b microbeads–based magnetic cell sorting procedure to get a high yield of microglial cells [22].
The precision and handling can influence the yield of cells during the isolation process, which is discussed in detail in the procedure section. To mitigate such variability, it is essential that all steps be executed consistently and with the utmost care. This method allows for isolating all major CNS resident neuroglial cells without using fluorescence-activated cell sorting. These cells can be used to understand individual neuroglial cell–specific roles in CNS biology and pathology. This approach also increases the experimental opportunities for the scientific community more efficiently and cost effectively.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Animals
Mice: Day-0 mice pups, C57BL/6 (Strain #000664, common name B6) obtained from The Jackson Laboratory
Viruses: RSA59, an isogenic recombinant strain of murine beta corona virus (MHVA59) [23]
Reagents
Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS) (10×) (Gibco, catalog number: 14185-052)
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 (10×) (Gibco, catalog number: 70011-044)
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (7.5%) (Gibco, catalog number: 25080-094)
CAUTION: NaHCO3 is skin and eye irritant. Wear suitable gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (powder) (Gibco, catalog number: 12100-046)
Trypsin 0.25% (1×) (Gibco, catalog number: 15050-057)
L-Glutamine 200 mM (100×) (Gibco, catalog number: 25030-081)
0.5% Trypsin-EDTA (10×) (Gibco, catalog number: 15400-054)
CAUTION: Components containing Trypsin may produce an allergic reaction. EDTA may cause irritation to the eyes and skin. Use respiratory protection as well as protection for skin and eyes.
Heat inactivated horse serum (origin: New Zealand) (Gibco, catalog number: 26050-070)
Penicillin-streptomycin (Pen-Strep) (Gibco, catalog number: 15140-122)
Distilled water (Gibco, catalog number: 15230-147)
Sterile deionized H2O
F12 nutrient mixture (Ham) medium (Gibco, catalog number: 11765-054)
Heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 10082-147)
D-(+)-Glucose, Hybri-Max, ≥99.5% (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5146)
Trypsin from bovine pancreas (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9201-5G)
Laminin from Engelberth-holm swarm murine sarcoma basement membrane (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L2020-1MG)
MEM non-essential amino acids solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M7145)
HEPES buffer (1 M) (Gibco, catalog number: 15630-080)
CAUTION: It may cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and upper respiratory tract. Wear protective gloves, goggles, and mask.
Insulin from bovine pancreas (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I6634-50MG)
Poly-D-Lysine hydrobromide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7886-100MG)
Neurobasal medium (NB) (Gibco, catalog number: 21103-049)
Deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) from bovine pancreas (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5025-15KU)
CAUTION: May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled. Use protective clothing, gloves, and masks while using. Do not vortex, as DNase I is prone to physical denaturation.
B27 supplement 50× (Gibco, catalog number: 17504-044)
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2·6H2O) (SISCO Research Laboratories PVT LTD, catalog number: 1349130)
Calcium chloride (CaCl2·2H2O) (SRL, catalog number: 10035-04-8)
L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate (T4 thyroxine) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0397-1MG)
Apo-Transferrin human (transferrin) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-4382)
Putrescine dihydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5780-5G)
Progesterone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8783-5G)
Selenium dioxide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 325473)
CAUTION: Toxic if swallowed or inhaled. May cause damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure. Very toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. Use a face shield, safety glasses, gloves, and respiratory protectant.
Biotin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B-4501)
0.15 M Borate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6768-1KG)
99.9% Ethanol, absolute, analytical CSS reagent (Changshu song sheng fine chemicals, catalog number: GB678-90)
CAUTION: Highly flammable liquid may cause drowsiness and nausea.
Sodium chloride (NaCl) (SRL, catalog number: 7647-14-5)
Potassium chloride (KCl) (MERCK, catalog number: 7447-40-7)
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (MERCK, catalog number: 7558-79-4)
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (MERCK, catalog number: 7778-77-0)
Trypan Blue (0.4%) (Gibco, catalog number: 15250061)
Growth factors
Nerve growth factor (NGF) (Invitrogen, catalog number: 13257-019)
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) (R&D System, catalog number: 133-FB/CF)
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) (R&D System, catalog number: 221-AA)
Neurotrophin-3 (NT3) (PeproTech, catalog number: 450-03-10UG)
Reagents for immunofluorescence
Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787-100ml)
CAUTION: Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation and serious eye damage. Use skin and eye protectants.
Bovine serum albumin, for molecular biology (BSA) (HIMEDIA, catalog number: MB083-25G)
CAUTION: Causes skin and eye irritation; may cause an allergic response. Avoid contact with skin and eyes and wear respiratory protection, gloves, and goggles.
Antibodies
Primary antibodies against various cell markers are diluted with 0.1% BSA (prepared from 1% BSA) as per the given ratio (Table 1).
Table 1. Primary antibodies
Antibody name Dilution Cellular markers for Recommended storage condition Mouse anti-GFAP (Sigma, catalog number: G3893) 1:100 Astrocytes Stored at -20 °C freezer Rabbit anti-Vimentin (CST, catalog number: D21H3) 1:200 Meningeal fibroblasts Rabbit anti-Iba1 (SIGMA Wako, catalog number: 019-19741) 1:600 Microglia Mouse anti-NG2 (MERCK, catalog number: MAB5384-I) 1:50 OPCs Rabbit anti-MAP 2 (SIGMA, catalog number: M3696) 1:200 Neurons Mouse anti-NFM (SIGMA, catalog number: N5389) 1:100 Neurons Mouse anti-Gal C (H8H9) (Homemade) 1:20 Mature oligodendrocytes Mouse anti-A2B5 (Homemade) 1:20 OPCs Rabbit anti-Cx43 (SIGMA, catalog number: C6219) 1:1,000 a gap junction protein Fluorescently tagged secondary antibodies raised against mouse or rabbit are diluted in 0.1% BSA (prepared from 1% BSA) as per the given ratio (Table 2).
Table 2. Secondary antibodies
Antibody name Dilution Recommended storage condition Donkey anti-Rabbit Alexa Fluor 568 (Invitrogen, catalog number: A10042) 1:1,000 Stored at 4 °C Goat anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen, catalog number: A11001) 1:1,000 Goat anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 546 (Invitrogen, catalog number: A11003) 1:1,000
Solutions
DMEM solution (see Recipes)
Astrocyte-specific medium (see Recipes)
Hanks for prep solution (see Recipes)
Serum for prep solution (see Recipes)
1× PBS (see Recipes)
HBSS solution (see Recipes)
NB/B27 medium (see Recipes)
Oligodendrocytes-specific media (see Recipes)
Neuron-specific media (see Recipes)
DM supplement (see Recipes)
T4 thyroxine (see Recipes)
30% glucose (1.66 M) (see Recipes)
Insulin (see Recipes)
Biotin (see Recipes)
Oligodendrocyte differentiation media (see Recipes)
DMEM Minus (-) (see Recipes)
DMEM Plus (+) (see Recipes)
HBSS (+) or 1% glucose HBSS solution (see Recipes)
DNase I solution (see Recipes)
Trypsin (see Recipes)
Poly-D-Lysine (PDL) coating (see Recipes)
Wash buffer (see Recipes)
Blocking serum (1% BSA) (see Recipes)
Recipes
DMEM solution
Prepare by dissolving DMEM powder in 1 L of double-autoclaved Milli Q water; then, add NaHCO3. Follow the table below for preparation. Mix properly (so that no clumps remain) and then adjust the pH to 7.2–7.4. Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper. The solution can be stored at 4 °C for up to one month.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition DMEM powder 1 pouch 13.4 g/L 4 °C NaHCO3 3.7 g/L 44.04 mM Room temperature (20–25 °C) Double-autoclaved Milli Q H2O 1 L NA Room temperature Final volume 1 L 4 °C Astrocyte-specific medium
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper. Always prepare fresh; the solution can be stored for approximately one month at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition FBS 10 mL 10% (v/v) -20 °C Pen-Strep 1 mL 1% (v/v) -20 °C L-Glutamine 0.1 mL 0.2 mM -20 °C DMEM solution 89.9 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 100 mL 4 °C Hanks for prep solution
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper before use. The solution can be stored at 4 °C for up to 1–2 weeks.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition HBSS (10×) 10 mL 10% (v/v) 4 °C 1 M HEPES buffer 2.5 mL 25 mM 4 °C 7.5% NaHCO3 1 mL 1% (v/v) 4 °C Pen-Strep 1 mL 1% (v/v) -20 °C Double-autoclaved Milli Q H2O 85.5 mL NA Room temperature Final volume 100 mL 4 °C Serum for prep solution
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper before use. The solution can be stored at 4 °C for up to one week.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition Heat-inactivated FBS 10 mL 10% (v/v) -20 °C Non-essential amino acid solution 1 mL 1% (v/v) 4 °C L-Glutamine 1 mL 2 mM -20 °C Pen-Strep 1 mL 1% (v/v) -20 °C DMEM 87 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 100 mL 4 °C 1× PBS
Dissolve the following reagents as per the given quantities in 800 mL of distilled water and adjust the pH to 7.2–7.4; then, make up the volume up to 1 L and filter sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition NaCl 8 g 137 mM Room temperature KCl 0.2 g 2.7 mM Room temperature Na2HPO4 0.24 g 10 mM Room temperature KH2PO4 1.44 g 1.8 mM Room temperature Distilled water 1 L NA Room temperature Final volume 1 L 4 °C HBSS solution
100× Ca2+ (90 mM)
Dissolve 1.324 g of CaCl2·2H2O in 100 mL of distilled water.
100× Mg2+ (104.8 mM)
Dissolve 2.13 g of MgCl2·6H2O in 100 mL of distilled water.
HBSS with Ca2+ and Mg2+
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper. This solution can be stored for up to 1–2 months at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition HBSS (10×) 10 mL 10% (v/v) 4 °C Ca2+ (100×) 1 mL 0.9 mM 4 °C Mg2+ (100×) 1 mL 1.05 mM 4 °C Double-autoclaved Milli Q H2O 88 mL NA Room temperature Final volume 100 mL 1% (v/v) 4 °C NB/B27 medium
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper. Always prepare fresh and do not store the solution for more than two weeks.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition B27 Supplement 50× 2 mL 2% (v/v) 4 °C Pen-Strep 2.5 mL 2.5% (v/v) -20 °C L-glutamine 2.5 mL 5 mM -20 °C NB 93 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 100 mL 4 °C Oligodendrocytes-specific media
Always prepare fresh and use it according to your experimental planning.
Critical step: Do not filter the growth factors. Always add the growth factors instantly in the NB/B27 incomplete media just before use for your experiments and put growth factors back in the -20 °C freezer without any delay.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition PDGF (1 µg/mL) 100 µL 2 ng/mL -20 °C FGF (10 µg/mL) 50 µL 10 ng/mL -20 °C NT3 (1 µg/mL) 50 µL 1 ng/mL -20 °C NB/B27 medium 50 µL NA 4 °C Final volume 50 µL 4 °C Neuron-specific media
Always prepare the solution fresh just before the experiment.
Critical step: Do not filter the growth factors. Caution should be followed as aforesaid for oligodendrocytes-specific medium.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition NGF (100 µg/mL) 7 µL 50 ng/mL -20 °C NB/B27 medium 15 mL NA 4 °C Final volume mL 4 °C DM supplement
Filter sterilize the mixture after combining all components using a 0.2 µm filter. Store 1 mL aliquots at -20 °C for approximately two months.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition Transferrin 5 mL 250 mg/5 mL DMEM -20 °C Putrescine 5 mL 26.85 mg/5 mL DMEM (33.3 mM) Room temperature Progesterone 10 mL 3 mg/5 mL [of 95% EtOH (1.908 mM)] (dilute 25 µL of this in 10 mL DMEM) Room temperature Selenium dioxide 5 mL 3.3 mg/10 mL DMEM (2.974 mM) (dilute 40 µL of this in 5 mL DMEM) Room temperature Final volume 25 mL -20 °C T4 thyroxine
Aliquot and store at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition T4 thyroxine 1 mg 22.5 µM -20 °C DMEM 50 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 50 mL 4 °C 30% glucose (1.66 M)
Dissolve 30 g of glucose in 100 mL of sterile ddH2O. Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper and store at 4 °C.
Insulin
Mix the provided quantity of insulin in DMEM and then add 1 N HCl dropwise until the cloudy solution clears. Filter sterilize the solution and store 1 mL aliquots at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition Insulin 25 mg 4.36 µM -20 °C DMEM 10 mL NA 4 °C 1 N HCl NA NA Room temperature Final volume 10 mL 4 °C Biotin
Dissolve biotin in doubled-distilled water (ddH2O) (5 mg in 100 mL of ddH2O) to make a stock of 204.65 µM. Then, prepare a working stock of 40.93 µM as per the instructions below and sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 µm filter paper; store at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition Biotin 20 mL 40.93 µM 4 °C DD H2O 80 mL NA Room temperature Final volume 100 mL 4 °C Oligodendrocyte differentiation media
Mix all the given components and store the solution at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition T4 thyroxine 4 mL 0.9 µM -20 °C 30% glucose 2 mL 33.4 mM 4 °C L-Glutamine 2 mL 4 mM -20 °C Pen-Strep 2 mL 2% v/v -20 °C Insulin 1 mL 4.36 µM 4 °C DM supplement 1 mL 1% v/v -20 °C Biotin 200 µL 81.86 µM 4 °C DMEM 94 mL NA 4 °C F12 medium 94 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 200 mL 4 °C DMEM Minus (-)
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper.
Critical: Always prepare fresh and store at 4 °C for no more than 1–2 weeks.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition 1 M HEPES buffer 1 mL 10 mM 4 °C Pen-Strep (100×) 1 mL 1% (v/v) -20 °C Non-essential amino acid solution 1 mL 1% (v/v) 4 °C DMEM 97 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 100 mL 4 °C DMEM Plus (+)
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper.
Critical: Prepare fresh and store at 4 °C refrigerator for not more than 1–2 weeks. FBS and HS should be filtered first to prevent the clogging of filter paper.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition 1 M HEPES buffer 1 mL 10 mM 4 °C Pen-Strep (100×) 1 mL 1% (v/v) -20 °C Non-essential amino acid solution 1 mL 1% (v/v) 4 °C Heat inactivated FBS 5 mL 5% (v/v) -20 °C Heat inactivated horse serum 5 mL 5% (v/v) -20 °C DMEM 87 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 100 mL 4 °C HBSS (+) or 1% glucose HBSS solution
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.22 µm filter paper. The solution can be stored for up to one month at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition HBSS (1×) 100 mL NA 4 °C Glucose 1 g (w/v) 55.5 mM Room temperature Final volume 100 mL 4 °C DNase I solution
DNase I enzyme is commercially available as a powder. Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 µm filter paper before use. Aliquot the solution to 2 mL tubes and store at -20 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition DNase I 3 mg 0.1 mg/mL -20 °C 1× PBS 30 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 30 mL -20 °C Trypsin
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 µm filter before use. Aliquot the solution in 2 mL tubes and store at -20 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition Trypsin from bovine pancreas 300 mg 10 mg/mL -20 °C 1× PBS 30 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 30 mL -20 °C Poly-D-Lysine (PDL) coating
Dissolve 5 mg of PDL in 100 mL of distilled water, then add 400 mL of distilled water to make up the volume.
Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 µm filter paper. Store at 4 °C.
To coat:
Add 1 mL of 0.15 M borate (in 0.15 M NaOH, pH 8.4) per 100 mL of PDL solution and filter coat flasks with the PDL-borate for at least 2 h at room temperature.
Suction the liquid off the plastic and dry at 37 °C overnight.
Reagent setup for immunofluorescence
Wash buffer
Critical: Always prepare fresh just before using and store at 4 °C.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition 1× PBS 49 mL NA 4 °C Ca2+ (100×) 0.5 mL 0.9 mM 4 °C Mg2+ (100×) 0.5 mL 1.04 mM 4 °C Final volume 50 mL 4 °C Blocking serum (1% BSA)
Mix properly using the vortex and keep the solution for some time to settle the frothing.
Critical: Do not vortex for a long period, otherwise it will cause too much frothing in the solution.
Instead of BSA, goat serum can also be used for the preparation of blocking serum and antibody diluents.
Components Quantity Final concentration Recommended storage condition BSA 1 g 1% (w/v) 4 °C Wash buffer 100 mL NA 4 °C Final volume 100 mL 4 °C
Laboratory supplies
Cell strainer (70 and 100 μm) (Falcon, catalog numbers: 352350 and 352360)
15 mL centrifuge tubes (Tarsons, catalog number: 546021)
50 mL centrifuge tubes (Tarsons, catalog number: 546041)
Serological pipette (5 mL and 10 mL) (Thermo scientific Nunc, catalog numbers: 170355N and 7128)
6-well plate (Nunc Thermo, catalog number: 140675)
35 mm disc (Nunc Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 150460)
60 mm disc (Nunc Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 150288)
100 mm disc (Nunc Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 150350)
Bacterial Petri dish (Tarson, catalog number: 460095)
Pipette controller (Gilson, catalog number: 101300)
Syringes (Dispo Van, Hindustan Syringes and Medical devices, catalog number: 840054SM1)
Pipette tips [Tarson, catalog numbers: 521020 (200–1,000 µL), 521010 (2–200 µL), 521000 (0.2–10 µL)]
0.22 µm filter (Merck, Life Sciences, catalog number: B20345)
4 chambers (mounted on permanox) slides (Nunc, catalog number: 120075LE 1007)
Equipment
Biosafety hood (Thermo Scientific, Heraguard, catalog number: 41237696)
Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5702R, catalog number: 5703YH207703)
CO2 incubator (Thermo Scientific, model: Heracell 150i, catalog number: G-3168)
Dissection microscope (Nikon SMZ 745 Model C-LEDS, catalog number: 226763)
Microscope (Nikon, model: Eclipse Ts2, catalog number: 137714)
Analytical balance (Sartorius PRACTUM213-10IN, catalog number: S/N 003670729)
Shaker incubator (ZHICHENG, catalog number: G-1377 ZHWY-103B)
Water bath with shaker (Jio Tech, catalog number: G-3179)
Forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 00649-11)
Fine forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog numbers: 11251-33, 11252-40, 11252-30)
Software and datasets
For image processing
ImageJ (NIH, USA)
Zen 2010 software (Carl Zeiss, Germany)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2024 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Kumar Samal, S., Sharma, M. and Das Sarma, J. (2024). Isolation and Enrichment of Major Primary Neuroglial Cells from Neonatal Mouse Brain. Bio-protocol 14(2): e4921. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4921.
分类
神经科学 > 细胞机理 > 细胞分离和培养
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 单层培养
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












