- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Epicutaneous Application of Mannan Induces Psoriasis-like Inflammation in an Inbred Mouse Strain
表皮应用甘露聚糖可诱导近交系小鼠出现银屑病样炎症
发布: 2023年10月20日第13卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4845 浏览次数: 1860
评审: Komuraiah MyakalaKrishna NakuluriMichael David SchultzAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Mannan from yeast induces psoriasis-like inflammation in the skin of inbred mouse strains. Limitations of available models led us to develop a new psoriasis model with a rapid disease onset, severe disease course, short duration, and a simple and easy-to-induce protocol with much more practically convenient features and cost-benefits. Mannan-induced skin inflammation (MISI) is more severe than the classical imiquimod (IMQ)-induced skin inflammation (IISI), with characteristic features resembling human plaque psoriasis but with relatively fewer toxicity issues. Epicutaneous application of mannan (5 mg) in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant or Vaseline induces severe psoriasis in BALB/c female mice. Psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) and histological evaluation of the skin could help assess the disease development. MISI mimics natural environmental factors affecting the skin relatively more closely than IISI. This disease model can be used to dissect inflammatory pathways in the skin, identify genetic and environmental factors affecting psoriasis, and test potential pharmacological agents or new combinations of available drugs for treatment before designing clinical trials.
Key features
• S. cerevisiae mannan induces psoriasis-like skin inflammation(MISI) when applied on the skin of inbred mice.
• The MISI model has a rapid onset, severe disease, short duration, and simple and easy-to-induce protocol.
• MISI is more severe than imiquimod-induced skin inflammation (IISI).
• Female mice had a more severe disease than males in the MISI model, thereby allowing the study of sex-dependent disease mechanisms.
• The MISI model identifies skin inflammatory pathways and genetic/environmental factors affecting psoriasis.
• The MISI model can be used as a drug testing platform for potential pharmaceuticals to develop new therapeutics for psoriasis patients.
• The MISI model can be used to explore the relative contribution of different pattern recognition receptors in the development and severity of psoriasis.
Graphical overview
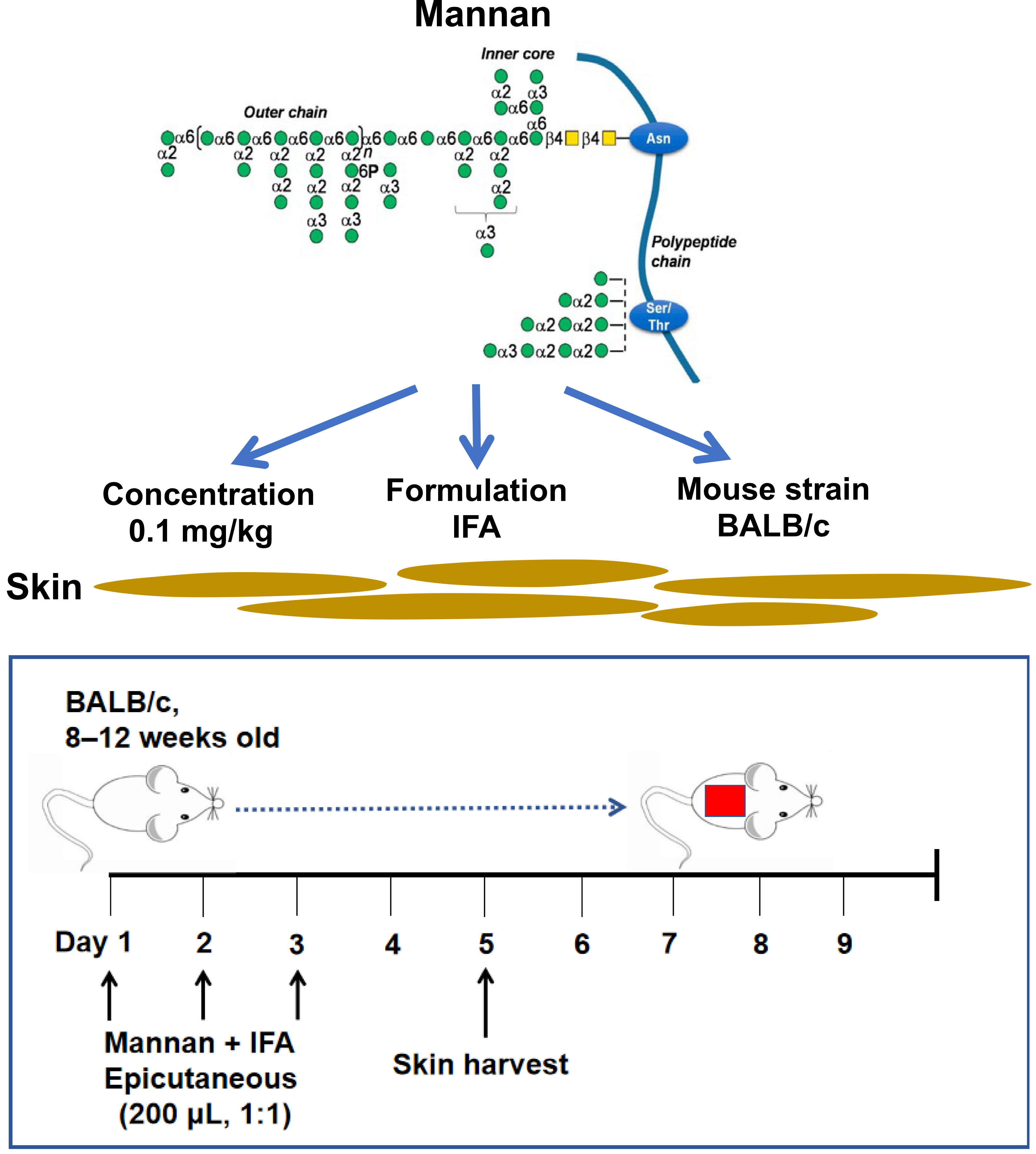
Background
Psoriasis is a skin inflammatory disease affecting 3% of the population (Girolomoni et al., 2017; Zhong et al., 2018). Psoriasis etiology is still unclear, but a strong association with human leukocyte antigens (HLA) was documented (Knight et al., 2012; Tsoi et al., 2012). Environmental factors like sex, stress, and smoking affect the clinical manifestations of psoriasis (Fry and Baker, 2007). Keratinocyte hyperproliferation, increased blood vessel formation, and infiltration of immune cells are common in psoriasis skin (Van der Fits et al., 2009). Innate and adaptive immune responses are indispensable for disease development (Villanova et al., 2014). Proinflammatory cytokines and the immune cells secreting them activate the effector cells present in the skin. For example, T cell–derived cytokines like IL-17A and IL-17F activate keratinocytes, which produce anti-microbial peptides and more cytokines and chemokines. These inflammatory factors shape psoriasis skin inflammation (Ando et al., 2015).
Mannan is present in nearly all fungi species. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans mannans are pathogenic factors in psoriasis (Picciani et al., 2013). An intraperitoneal injection of mannan extracted from Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall was shown to induce psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis symptoms in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-deficient, Ncf1-gene-mutated mice that are available only in specific labs (Khmaladze et al., 2014). On the other hand, an epicutaneous application of imiquimod (IMQ) for 5–7 days leads to the development of an acute psoriasis phenotype. However, the disease developed in IMQ-induced psoriasis is often accompanied by severe weight loss in BALB/c mice (Swindell et al., 2017). Herein, we describe an induction protocol for plaque psoriasis-like inflammation in an inbred mouse strain (BALB/c) by epicutaneous application of mannan (Figure 1). A local (epicutaneous) instead of the intraperitoneal application of mannan could mimic a more natural way of skin exposure to environmental triggers for skin disease induction. Induced skin inflammation resembles human plaque psoriasis. Redness covered with white scales and skin thickness in the lesion area in mannan-exposed skin is more straightforward, making this model simpler for visually observing most manifestations of the disease.
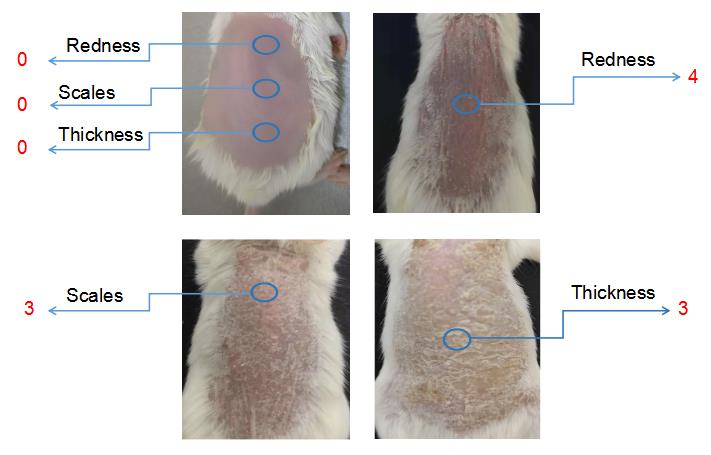
Figure 1. Clinical scoring for psoriasis inflammation. A representative psoriasis inflammation scoring method is given. PASI scores for the above skin conditions are as follows: redness: 4; scales: 3; thickness: 3. Each group contains 10 mice. BALB/cfemale mice were used for experiments. Left column pictures were reproduced from Figure 1A of the published paper (Wu et al., 2023).
Moreover, the proliferation of keratinocytes and innate immune cells, the infiltration of T lymphocytes in the skin, and an increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines were induced after epicutaneous mannan application (Wu et al., 2023). The activation of TLR7 and TLR8, mainly expressed in the immune cells, mediates the effects of IMQ (Bong et al., 2002). In contrast, mannan is a ligand for mannose receptors and is the primary trigger of IL-17 pathways in the host (Jiang et al., 2017). In addition, a higher-level expression of TLR2, TLR4, CD206, Dectin-2, Mincle, and DC-SIGN receptors was found in mannan-induced skin inflammation (MISI) (Wu et al., 2023). Thus, this disease model differs from IMQ-induced psoriasis-like inflammation, mainly in terms of the health status of the animals. Unlike the IMQ model, the body weight loss in MISI is negligible.
Furthermore, mannan had a shorter exposure time (3 days) to induce the disease than IMQ (5–7 days), demonstrating more cost-effective and convenient features. A response to dexamethasone in MISI has shown its usefulness in testing and validating various anti-psoriatic drugs for future treatments in psoriasis patients. Many autoimmune diseases show sexual dimorphism during disease development, and this plaque psoriasis-like skin inflammation induced by mannan also showed strong female preponderance, demonstrating its use in exploring sex-dependent mechanisms (Wu et al., 2022). Although mannan-induced skin inflammation results in acute and relapsing disease symptoms after repeated exposure, like other induced acute psoriasis mouse models, this model can also not completely mimic the relapsing and chronic characteristic features of human plaque psoriasis.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
8–12-week-old BALB/c female mice maintained in a pathogen-free animal house were purchased from Southern Medical University and Guangdong Medical Animal Experiment Center. Each group contains 5–12 mice. All animal experiments were performed per the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 8023) and approved by the ethics committee of Southern Medical University (l2018183). Mice were kept in cages in a climate-controlled environment having 12:12 h light/dark cycles and given food and water ad libitum. Southern Medical University Animal Care and Use Committee, Guangzhou, China, approved all the procedures.
BALB/c is among the most popular inbred mouse strains in many international research laboratories. The IMQ-induced psoriasis mouse model is commonly induced in these mice for drug evaluation. Skin redness can be more easily observed in this white mouse. BALB/c female mice were used in all the experiments described below.
Reagents
S. cerevisiae mannan (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M7504) was dissolved (100 mg/mL solution) in sterile phosphate buffered saline, PBS (Gibco, catalog number: 14190-094).
Incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (IFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F5506-10)
Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F5674)
Isoflurane (Healthcare, catalog number: 676544)
Phenobarbital (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 57-30-7)
Imiquimod cream (AldaraTM, catalog number: 678432)
Hair removal cream (Nair, catalog number: 657789)
Paraffin (Leica, catalog number: 3960l095)
4% Paraformaldehyde (Leagene, catalog number: DF0135)
Hematoxylin solution (Mayer) (Beyotime, catalog number: C0105)
0.2% Eosin solution in PBS (Mayer) (Beyotime, catalog number: C0105)
Xylene solution (Beyotime, catalog number: C0105)
Neutral gum (Solarbio, catalog number: G8590)
Vaseline (Yuanye, catalog number: 8009-03-8)
Liquid Paraffin oil (Yuanye, catalog number: 67552)
Ethanol (absolute) (Mackline, catalog number: E821482)
Plus-loaded slides (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 6885)
Xylene-based mounting medium (HistoLab, catalog number: 00801)
Solutions
Different concentrations of ethanol (see Recipes)
Mannan-PBS solution (see Recipes)
Phenobarbital-normal saline solution (see Recipes)
Preparation of mixture (see Recipes)
Recipes
Different concentrations of ethanol
Reagent Ethanol (absolute) H2O 95% ethanol 950 mL 50 mL 90% ethanol 900 mL 100 mL 80% ethanol 800 mL 200 mL 70% ethanol 700 mL 300 mL 50% ethanol 500 mL 500 mL Mannan-PBS solution
Solution 100 mg/mL mannan-PBS solution PBS 50 mg/mL mannan-PBS solution 50 μL 50 μL Phenobarbital-normal saline solution
Solution Phenobarbital powder Normal saline 80 mg/mL phenobarbital-saline solution (5 mL) 400 mg 5 mL Preparation of mixture
Mixture Mannan-PBS solution (50 mg/mL) IFA Mannan + IFA 100 μL 100 μL
Equipment
Small animal weighing device (CHIKO, model: ZK-DST)
Digital vernier caliper (Yasuwang, catalog number: ASO-1-894-01)
Mouse skin shaver (Riward, catalog number: CP-5200)
Tissue processing/embedding cassettes with lid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z672122)
Brush (Asone, catalog number: CC-5667-04)
Vacuum tissue processor (Leica, model: ASP300S)
Embedding machine (Tissue-Tek; Sakura)
Microtome (Leica, model: RM2255)
Eclipse upright optical microscope (Nikon, model: Ci-E)
Software and datasets
Image-pro plus 6.0 software (Nikon; Ci-E)
GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Prism; version 5)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Wu, H. and Nandakumar, K. S. (2023). Epicutaneous Application of Mannan Induces Psoriasis-like Inflammation in an Inbred Mouse Strain. Bio-protocol 13(20): e4845. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4845.
分类
免疫学 > 动物模型 > 小鼠
医学 > 发炎
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link














