- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolation, Purification, and Culture of Embryonic Melanoblasts from Green Fluorescent Protein–expressing Reporter Mice
表达绿色荧光蛋白的报告小鼠胚胎黑素细胞的分离、纯化和培养
发布: 2023年09月05日第13卷第17期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4805 浏览次数: 1992
评审: Olga KopachPhilipp WörsdörferKrishna NakuluriSreejith Perinthottathil

相关实验方案

来自骨髓增生性肿瘤患者的造血祖细胞的血小板生成素不依赖性巨核细胞分化
Chloe A. L. Thompson-Peach [...] Daniel Thomas
2023年01月20日 2363 阅读
Abstract
In this article, we provide a method to isolate embryonic melanoblasts from reporter mouse strains. The mice from which these cells are isolated are bred into the ROSA26mT/mG reporter background, which results in green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in the targeted melanoblast population. These cells are isolated and purified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting using GFP fluorescence. We also provide a method to culture the purified melanoblasts for further analysis. This method yields > 99% purity melanoblasts specifically targeted, and can be used for a variety of studies, including gene expression, clonogenic experiments, and biological assays, such as viability, capacity for directional migration, or differentiation into melanin-producing melanocytic cells.
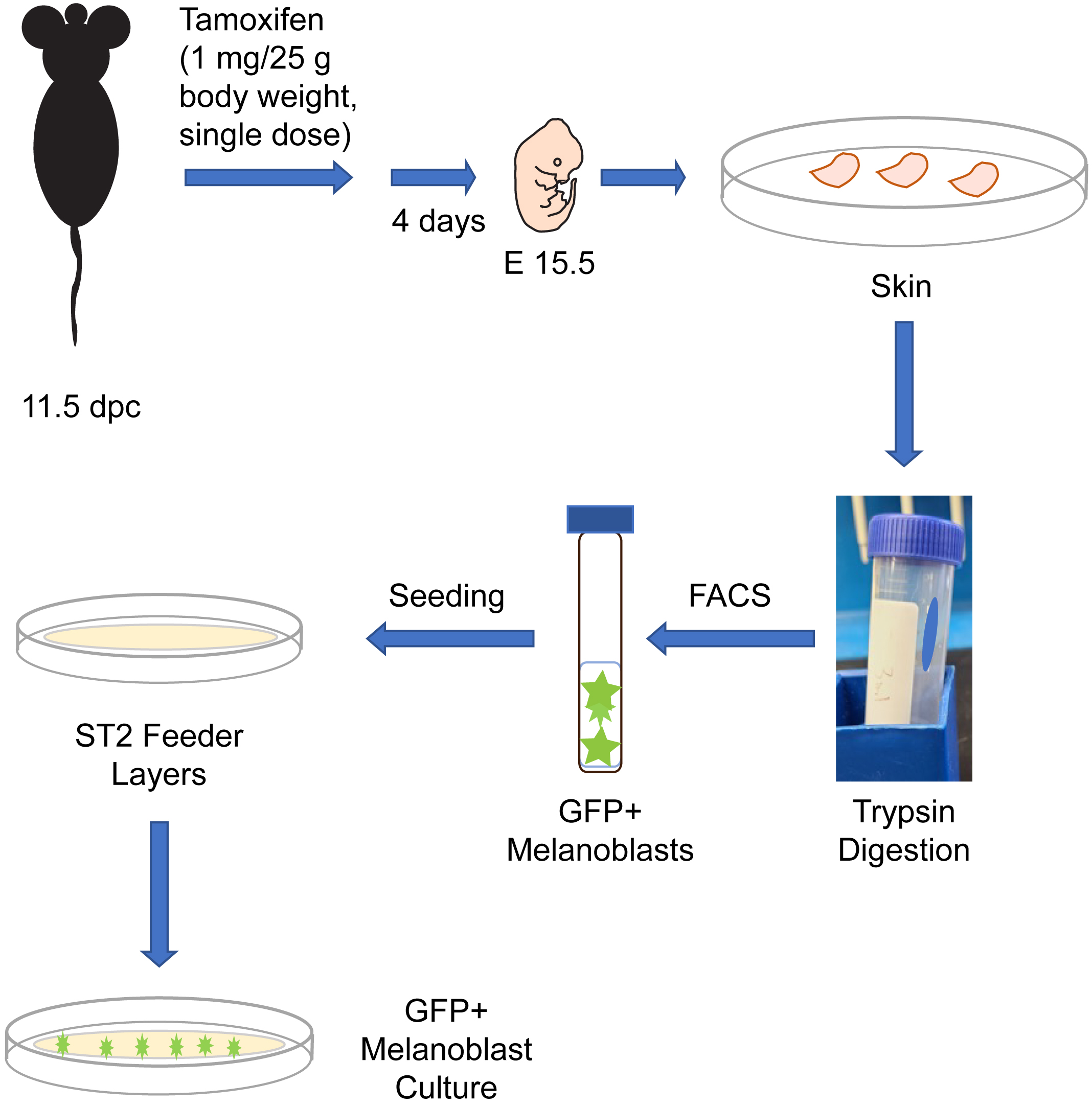
Graphical overview
Background
Melanocytes are melanin pigment–producing cells that are found in the skin, inner ear, nervous system, and in the heart (Li, 2014). Melanocytes and their precursor cells, melanoblasts, originate from neural crest cells. In mice, a subset of neural crest cells becomes specified as melanoblasts and begin their migration around embryonic day (E) 10.5 from the neural crest, to ultimately colonize the entire body (Mort et al., 2015). A second wave of melanoblast formation occurs around E14.5, when neural crest cells that migrated along a ventral path detach from nerve endings and differentiate into melanoblasts (Delmas et al., 2007; Adameyko et al., 2009). Melanoblasts proliferate, migrate, and interact with their surrounding environment to localize to specific sites in the body. By E16.5, melanoblasts from both waves will have homed to the basal layer of the epidermis, as well as the developing hair follicles (Mort et al., 2015). Understanding the ontogeny of melanocytic cells is a key area in developmental biology with significant implications for human health, as evidenced by the plethora of human diseases linked to defects in melanocytic lineage cells. In this protocol, we describe the isolation from reporter mice of embryonic melanoblasts which express green fluorescent protein (GFP). These mice express in a Cre recombinase enzyme fused to a modified estrogen receptor (CreET2). In these animals, CreET2 expression is restricted to melanocytic lineage cells, as its transcription is under the control of the Tyrosinase promoter. Tamoxifen administration to these mice induces CreET2 nuclear translocation in melanoblasts, allowing activation of GFP expression. As a result, targeted melanoblasts can be identified through GFP fluorescence. This protocol can also be used to purify and characterize embryonic melanoblasts in which a gene of interest flanked by loxP sites can be inactivated by Cre recombinase (Crawford et al., 2017). In this protocol, we also describe methods to culture the embryonic melanoblasts using ST2 feeder layers. Specifically, seeding the purified melanoblasts onto a confluent monolayer of ST2 cells maintains their viability and supports their maturation into melanin-producing cells (Crawford et al., 2020). This system allows studies including single-cell analyses and whole-genome screens of melanoblasts. Under the conditions used in our cultures, melanoblasts remain viable for at least seven days and transition into melanin-producing cells.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Mice. The experiments we describe are conducted with mice generated by breeding the reporter strain Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo/J (hereafter termed ROSAmT/mG, The Jackson Laboratory, strain number 007676) (Muzumdar et al., 2007) with B6.Cg-Tg (Tyr-cre/ERT2)13Bos/J (hereafter termed Tyr::CreERT2, The Jackson Laboratory, strain number 012328) (Bosenberg et al., 2006). Our protocol uses melanoblasts isolated from timed-pregnant dams that are homozygous for the ROSAmT/mG allele and homozygous for Tyr::CreERT2. These reporter mice can be further bred into other backgrounds in which a gene of interest is flanked by loxP sites and can therefore be used to generate GFP-tagged melanocytic cells in which a gene of interest has also been inactivated upon administration of tamoxifen (Crawford et al., 2020). Non-targeted cells can be identified by their expression of mTomato fluorescent protein. These experiments require time-pregnant mice, which are first treated with tamoxifen at 11.5 days post-coitus (dpc; midday of the vaginal plug is considered 0.5 dpc), as described below in the procedure.
ST2 cells. Bone marrow stroma–derived cell line (Riken BioResource Research Center, catalog number: RCB0224). ST2 cells express collagens and fibroblast growth factors and support melanoblasts in culture (Abdallah et al., 2019).
Reagents
Tamoxifen (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: T-5648)
Absolute ethanol (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 493511)
70% ethanol (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 63350-M)
Bovine serum albumin fraction V (Wisent, catalog number: 800-095-EG)
Cremophore/Kolliphor EL (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: C5135)
MGM-4 basal medium (Lonza, catalog number: CC-3250)
MGM-4 SingleQuot kit with supplements & growth factors (Lonza, catalog number: CC-4435)
Endothelin 3, lyophilized (ET3) (Lonza, catalog number: CC-4510)
2.5% trypsin (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15090046)
Trypsin neutralizing solution (Life Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R-002-100)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco, catalog number: 26140079)
0.25% trypsin/EDTA (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25200072)
7-Amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: A9400)
Paraformaldehyde (PFA) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 158127)
Sterile RPMI medium (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: R8758)
NaCl (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: S5150)
KCl (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: P5405)
Na2HPO4 (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: S7907)
KH2PO4 (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: P5655)
NaOH (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: S8045)
Triton X-100 (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: X100-100ML)
Mouse Anti-TRP1 antibody (Abcam, catalog number: 3312)
Goat anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor® 594 Conjugate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A-11032)
Mounting medium with DAPI (ibidi, catalog number: 50011)
Solutions
Tamoxifen stock solution (50 mg/mL) (see Recipes)
Melanoblast culture medium (see Recipes)
ST2 culture medium (see Recipes)
Sterile Ca2+- and Mg2+-free phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4 (see Recipes)
FACS buffer: sterile Ca2+- and Mg2+-free PBS containing 2% FBS (see Recipes)
7-Amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) stock solution (see Recipes)
7-Amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) working staining solution (see Recipes)
1 N NaOH solution (see Recipes)
4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) (see Recipes)
Recipes
Tamoxifen stock solution (store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Tamoxifen 50 mg/mL 25 mg Absolute ethanol 50% 250 μL Cremophore/Kolliphor 50% 250 μL Total n/a 500 μL Melanoblast culture medium (store at 4 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity MGM-4 basal medium n/a 500 mL MGM-4 SingleQuot Kit n/a 1 kit (9 mL) ET3 255 ng/mL 130 μg Total n/a 509 mL ST2 cell culture medium (store at 4 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity RPMI medium 90% 450 mL FBS 10% 50 mL Total n/a 500 mL Ca2+- and Mg2+-free phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, store at 4 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity NaCl 137 mM 8 g KCl 2.7 mM 0.2 g Na2HPO4 10 mM 1.44 g KH2PO4 1.8 mM 0.24 g Total n/a to 1,000 mL Autoclave to sterilize.
FACS buffer (store at 4 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Sterile Ca2+- and Mg2+-free PBS 98% 98 mL FBS 2% 2 mL Total n/a 100 mL Keep sterile.
7-Amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) stock solution (store at -20 °C, protected from light)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 7-AAD 1 mg/mL 1 mg Methanol 5% 50 μL Sterile Ca2+- and Mg2+-free PBS 950 μL Total n/a 1 mL 7-Amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) working staining solution (freshly prepared)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 7-AAD stock solution 1% 100 μL FACS buffer 99% to 10 mL Total n/a 10 mL 1 N NaOH solution
Reagent Final concentration Quantity NaOH 1 N 40 g H2O n/a to 1,000 mL Total n/a 1,000 mL 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) solution
Reagent Final concentration Quantity PFA 4% 0.4 g Ca2+- and Mg2+-free PBS n/a to 10 mL Total n/a 10 mL Prepare just prior to use.
Laboratory supplies
Bacterial grade 100 mm Petri dishes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: FB0875713A)
Surgical scissors (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 14002-12)
Two sets of forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11000-12)
Scalpel (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 10003-12)
Scalpel blades (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 10011-00)
Sterile 15 mL conical tubes (Sarstedt, catalog number: 62.554.502)
Sterile 50 mL conical tubes (Sarstedt, catalog number: 62.547.205)
2 mL microcentrifuge tubes (VWR, catalog number: 20170-098)
Sterile 10 mL disposable plastic syringes (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 302995)
Sterile 21 G needles for syringe (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 305165)
Sterile 5 mL round-bottom snap cap tubes (BD Falcon, catalog number: 52054)
Sterile 40 μm nylon cell strainers (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-771-1)
Neubauer hemocytometer (Hausser Scientific, catalog number: 15170-173)
BioLite T25 flasks, cell culture treated (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 130189)
35 mm μ-dishes with a 4-well insert (ibidi, catalog number: 80466)
Pipet-aid (Thermo Fisher Scientific, S1 Pipet Filler, catalog number: 9521)
Micropipettes (Eppendorf Research plus, P20, P200, P2000)
12 mm glass coverslips (Mandel Scientific, catalog number: NEU-GG-12)
Equipment
Stereomicroscope (Leica Stereo Zoom GZ6E)
Phase contrast and fluorescence inverted microscope with camera and humidified CO2 37 °C chamber for time-lapse videomicroscopy (Leica DMIRBE or equivalent)
Becton Dickinson FACSAria III cell sorter (BD Biosciences)
Becton Dickinson FACSCanto flow cytometer (BD Biosciences)
Centrifuge (Eppendorf 5810R)
Biosafety cabinet (Microzone BK-2-4)
CO2 cell culture incubator (VWR, catalog number: 10710-944)
Water bath (PolyScience, catalog number: WBE05A11B)
Rocking platform (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 166709 or equivalent)
Software
FACSDiva Software (v. 8.0.1) or equivalent
Volocity software for cellular imaging and analysis (PerkinElmer), or equivalent
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Crawford, M., Barr, K. and Dagnino, L. (2023). Isolation, Purification, and Culture of Embryonic Melanoblasts from Green Fluorescent Protein–expressing Reporter Mice. Bio-protocol 13(17): e4805. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4805.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离 > 流式细胞术
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 荧光
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link