- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Determination of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Content in Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Using Acid Hydrolysis Followed by High-performance Liquid Chromatography
酸水解-高效液相色谱法测定集胞藻PCC 6803中聚3-羟基丁酸酯的含量
发布: 2023年08月20日第13卷第16期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4790 浏览次数: 1824
评审: Dennis J NürnbergAmberley D. StephensAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

基于高效液相色谱法的史氏分枝杆菌DisA环二腺苷酸(C-di-AMP)合成酶活性研究
Avisek Mahapa [...] Dipankar Chatterji
2024年12月20日 1789 阅读
Abstract
Various photoautotrophic cyanobacteria accumulate intracellular poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) granules. This protocol can be used for determining the PHB contents of the cells as % PHB weight per dry cell weight using acid hydrolysis followed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This HPLC analysis is rapid, with a running time of approximately 5 min per sample. The technique can accurately determine PHB concentrations in the range of 2–1,000 μg/mL PHB. However, this technique is not applicable for determining the contents of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) in cyanobacteria.
Keywords: Cyanobacteria (蓝藻)Background
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) is a common biopolymer accumulated in various heterotrophic bacteria and autophototrophic cyanobacteria as a storage for carbon and energy (Amadu et al., 2021; Yashavanth et al., 2021). PHB can be used as biodegradable plastic and scaffold for tissue engineering (Bhati et al., 2010; Monshupanee et al., 2016; Tarawat et al., 2020). In the well-studied cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (hereafter, Synechocystis), cells have low PHB contents 0.4%–5% under a normal growth condition but, under nitrogen or phosphorus deprivation, PHB accumulation is significantly increased, up to 5%–13% w/w dry weight (Wu et al., 2001; Panda and Mallick, 2007; Monshupanee and Incharoensakdi, 2014; Koch et al., 2019). In Synechocystis, PHB biosynthesis is catalyzed by three enzymes (Figure 1). First, two acetyl-CoA are combined into acetoacetyl-CoA by 3-ketothiolase (PhaA). Second, acetoacetyl-CoA is reduced to 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA by acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (PhaB). Finally, PHA synthase (PhaEC) polymerizes 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA to form PHB (Taroncher-Oldenburg et al., 2000).
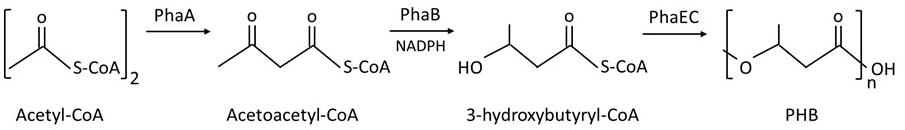
Figure 1. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) biosynthesis in Synechocystis according to Taroncher-Oldenburg et al. (2000)
Various cyanobacteria accumulate PHB in the absence of essential nutrients including nitrogen or phosphorus (Drosg et al., 2015; Koller and Maršálek, 2015; Kaewbai-ngam et al., 2016). The previous reports on Synechocystis suggested that PHB serves as a carbon and energy reserve for growth recovery under nitrogen repletion (Koch et al., 2019; Kaewbai-ngam et al., 2022).
The common method for quantifying PHB content in microbes is the depolymerization of PHB by methanolysis in acid, with subsequent analysis by gas chromatography (GC) (Juengert et al., 2018). Another alternative method is the alkaline lysis of PHB, followed by the enzymatic assay method using 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (Zilliges and Damrow, 2017). However, the GC method is time consuming, and the enzymatic assay requires enzyme preparation, which is costly. Here, we describe a rapid quantification of PHB content in cyanobacterial cells using acid hydrolysis followed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This technique takes only 5 min of HPLC operation per sample and can be used to determine PHB contents in 135 evolutionarily diverged cyanobacterial species (Kaewbai-ngam et al., 2016). Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) is the co-polymer, which comprises 3-hydroxybutyrate (HB) and 3-hydroxyvalerate (HV) monomers (Verlinden et al., 2007; Balaji et al., 2013). PHBV changes material properties upon altering mole ratio (mol %) of the two monomers: 3-hydroxybutyrate (HB) and 3-hydroxyvalerate (HV) (Tarawat et al., 2020). We are reporting here a detailed protocol of PHB content determination that summarizes the steps for converting PHB to crotonic acid by acid hydrolysis, followed by the determination of crotonic acid contents using HPLC. We also show that this protocol cannot be used to determine PHBV content.
Materials and reagents
Organism: wildtype Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (Pasteur Culture Collection, France)
Pipette tips 5,000 μL (Biohit, catalog number: 780 300)
Pipette tips 1,000 μL (Labcon, catalog number: 1046-800-000-9)
Pipette tips 200 μL (Labcon, catalog number: 1165-800-000)
Pipette tips 10 μL (Labcon, catalog number: 1161-800-000)
Plastic cuvette for spectrophotometer (Brand, catalog number: 7591 50)
50 mL tubes (Axygen Scientific, catalog number: SCT-50ml-25-S)
10 mL glass tubes with screw cap (Pyrex, catalog number: 9825)
2 mL HPLC glass vials with septum cap (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: CHSV9-10P)
1.5 mL reaction tubes (Labcon, catalog number: 3016-870-000)
3 mL disposable syringes (Nipro, catalog number: 20B20/FEB2020)
Sterile syringe polypropylene filter, 0.22 μm (Filtep-bio, catalog number: 20220516002)
Polypropylene membrane, 0.45 μm (Filtrex, catalog number: FTM-PP47045-010)
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 363502)
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 403121)
Crotonic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 113018)
Adipic acid (Fluka Analytical, catalog number: 09582)
Distilled water
Acetonitrile, HPLC grade (Honeywell, catalog number: AHO15-4A)
Methanol, HPLC grade (VWR chemicals, catalog number: 67-56-1)
Absolute ethanol (Merck, catalog number: 100983)
Citric acid (BDH, catalog number: 08D150022)
Sodium hydroxide (Merck, catalog number: 1310-73-2)
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (Merck, catalog number: 104873)
Ortho-phosphoric acid (H3PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7664-38-2)
Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Merck, catalog number: 102382)
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (Na2EDTA·2H2O) (Merck, catalog number: 108418)
Iron (III) chloride (FeCl3) (Ajax Finechem, catalog number: AF608291)
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Merck, catalog number: 105886)
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) (Carlo Erba Reagenti, catalog number: 7783-20-2)
Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) (Ajax Finechem, catalog number: 1502523945)
(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid)-NaOH (HEPES-NaOH) (OmniPur, catalog number: 7365-45-9)
Boric acid (H3BO3) (Scharlau, catalog number: 10043-35-3)
Manganese (II) chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O) (Kemaus, catalog number: 13446-34-9)
Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O) (Ajax Finechem, catalog number: 0707330)
Sodium molybdate dihydrate (Na2MoO4·2H2O) (Kemaus, catalog number: 10102-40-6)
Copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O) (BDH, catalog number: 100915R)
Cobalt (II) nitrate hexahydrate (Co(NO3)2·6H2O) (Carlo Erba Reagenti, catalog number: 10026-22-9)
Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (K2HPO4) (Carlo Erba Reagenti, catalog number: 7758-11-4)
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) (Merck, catalog number: 100731)
BG11 media (see Recipes)
Standard sulfuric acid solution (see Recipes)
Standard adipic acid solution (see Recipes)
Standard crotonic acid solution (see Recipes)
Premix solution used in Table 1 (see Recipes)
Mobile phase for HPLC analysis (see Recipes)
Equipment
Micro pipettes (Gilson: 20–1,000 μL)
Micro pipettes (Boeco, model: SA series ADJ 500–5,000 μL)
Glass pipettes (Qualicolor: 1–10 mL) and rubber pipette bulbs
Wide-neck 250 mL Erlenmeyer glass flasks (Duran)
Laboratory glass bottles (Duran)
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Note: This should be worn at all times when working with concentrated acids.
Safety glasses
Lab coat
Gloves, purple nitrile (Kimtech, catalog number: SM0182ZZZ_37AX)
Autoclave (Hirayama manufacturing corporation, model: HA-30)
Laminar flow bench (Boss tech, model: HBV120)
Fume hood (HYSC LAB, model: FH-120)
Spectrophotometer (Jenway, model: UV/VIS 6400)
Culture shaker [Sac Science, model: Sling shaker (120–150 rpm), 3 levels]
Centrifuge (Hettich zentrifugen, model: Mikro 220/220 R)
Microcentrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5417C)
Analytical balance (Mettler Toledo, model: PJ360)
Water bath (Hangzhou Bioer technology, model: N series)
Oven (Contherm, model: 2050)
Vortex shaker (Scientific industries, model: K-550-GE)
pH meter (Mettler Toledo, model: FiveEasy F20)
Filtration equipment (Pyrex, model: 33980-1L)
HPLC machine (Shimadzu, model: Shimadzu-02-1060)
HPLC UV/Vis detector (Shimadzu, model: SPD-10A)
HPLC pump (Shimadzu, model: LC-10AD)
HPLC auto-injector (Shimadzu, model: SIL-10AD VP)
HPLC column oven (Shimadzu, model: CTO-10A VP)
HPLC column (GL Sciences, model: InertSustain C18, 4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm)
Conventional guard column (GL Sciences, model: InertSustain C18, 4.0 mm × 10 mm, 5 μm)
Software
Shimadzu HPLC LGE system, Japan
Excel, Microsoft, USA
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Kaewbai-ngam, J., Incharoensakdi, A. and Monshupanee, T. (2023). Determination of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Content in Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Using Acid Hydrolysis Followed by High-performance Liquid Chromatography. Bio-protocol 13(16): e4790. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4790.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 其它化合物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












