- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Protocol for the High-quality Plasmid Isolation from Different Recalcitrant Bacterial Species: Agrobacterium spp., Rhizobium sp., and Bacillus thuringiensis
从不同难降解细菌中高质量分离质粒的方案:农杆菌、根瘤菌和苏云金芽孢杆菌
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2023年08月05日第13卷第15期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4788 浏览次数: 2547
评审: Hemant Kumar PrajapatiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
High yield of good quality plasmid DNA from gram -ve bacteria (Agrobacterium tumefaciens, A. rhizogenes, and Rhizobium sp.) and gram +ve bacterium (Bacillus thuringiensis) is difficult. The widely used plasmid extraction kits for Escherichia coli yield a low quantity of poor-quality plasmid DNA from these species. We have optimized an in-house modification of the QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit protocol of Qiagen, consisting of two extraction steps. In the first, the centrifugation after adding neutralization buffer is followed by ethanol (absolute) precipitation of plasmid DNA. In the second extraction step, the precipitated DNA is dissolved in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer, followed by an addition of 0.5 volumes of 5 M sodium chloride and 0.1 volumes of 20% (w/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate. After incubation at 65 °C for 15 min, the plasmid DNA is extracted with an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (CIA). RNase (20 mg/mL) is added to the upper phase retrieved after centrifugation and is incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. The extraction of the plasmid DNA with an equal volume of CIA is followed by centrifugation and is precipitated from the retrieved upper phase by adding an equal volume of absolute ethanol. The pellet obtained after centrifugation is washed twice with 70% (v/v) ethanol, air dried, dissolved in TE buffer, and quantified. This easy-to-perform protocol is free from phenol extraction, density gradient steps, and DNA binding columns, and yields high-quality plasmid DNA. The protocol opens an easy scale up to yield a large amount of high-quality plasmid DNA, useful for high-throughput downstream applications.
Key features
• The protocol is free from density gradient steps and use of phenol.
• The protocol is an extension of the QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit (Qiagen) and is applicable for plasmid DNA isolation from difficult-to-extract bacterial species.
• The protocol facilitates the direct transformation of the ligation product into Agrobacterium by skipping the step of E. coli transformation.
• The plasmids isolated are of sequencing grade and the method is useful for extracting plasmids for metagenomic studies.
Graphical overview
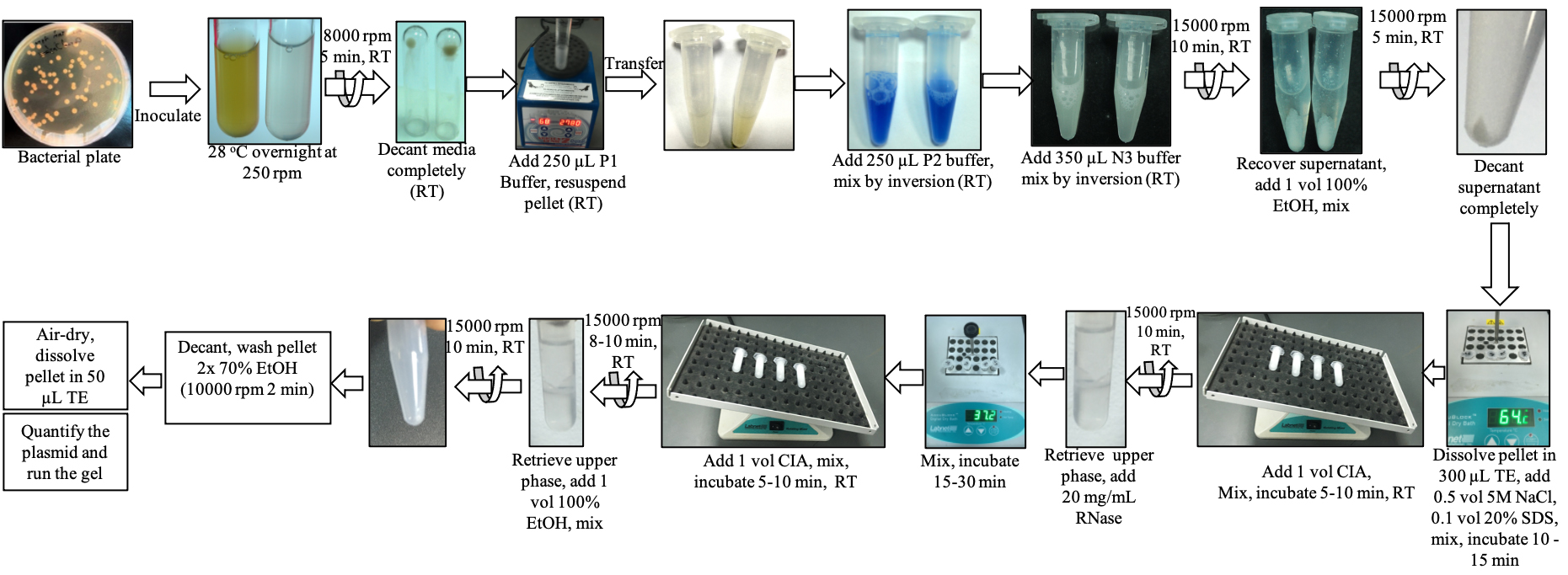
Overview of the plasmid isolation protocol (modified QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit) of the present study
Background
Plasmid isolation is an essential procedure in gene cloning, gene expression studies, sequencing, mutagenesis, and several downstream molecular processes. Easy-to-extract proprietary kits at different formats such as mini, midi, and maxi, and several published protocols are best suited for the plasmid extraction from widely used Escherichia coli strains. A simple and reliable method for isolating high-quality plasmid for downstream molecular applications from bacteria such as Agrobacterium tumefaciens, A. rhizogenes, Rhizobium sp., and Bacillus thuringiensis is lacking, due to the recalcitrance of the bacterial strains to cell lysis. Besides, lysozyme in the cell lysis solution is required to circumvent the non-lysis of the cell wall (Marmur, 1961). The Agrobacterium cells are not sensitive to the lysozyme-EDTA-detergent lysis procedures (Marmur, 1961; Clewell and Helinski, 1969), necessitating a relatively long treatment with proteolytic enzymes (Zaenen et al., 1974). Further, it is challenging to isolate Ti-plasmid free of chromosomal DNA (Ledeboer et al., 1976). In the case of agrobacteria, which is used to develop genetically modified and genome-edited plants, if there is no stock culture of E. coli with the desired plasmid, it necessitates retransformation of the plasmid into E. coli and subsequent extraction of plasmids for restriction digestion verification (Wise et al., 2006) and other downstream applications, e.g., biolistic transformation. There is no reliable protocol to extract high-quality plasmid DNA in large amounts from agrobacteria to accomplish downstream applications directly, i.e., without E. coli retransformation. The protocols described for the extraction of plasmid DNA from Agrobacterium, Rhizobium, and Bacillus thuringiensis are relatively lengthy and consist of sucrose gradients, CsCl-dye buoyant density gradients, or ethidium bromide treatment followed by phenol extraction (Ledeboer et al., 1976; Adachi and Iyer, 1980; Zhang and Kerr, 1993; Reyes-Ramirez and Ibarra, 2008). Our attempts to isolate plasmid from the gram -ve bacteria (Agrobacterium tumefaciens, A. rhizogenes, Rhizobium sp., and gram +ve bacterium (Bacillus thuringiensis) using kits (QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit from Qiagen and PureLink Quick Plasmid Miniprep kit from Invitrogen) and the user-modified protocol of QIAprep plasmid kit (Weber et al. 1998; https://www.qiagen.com/no/resources/resourcedetail?id=95083ccb-9583-489e-b215-99bd91c0604e&lang=en) did not yield satisfactory results. Extracting and purifying plasmid DNA from these strains and diverse other bacterial strains, recalcitrant to quality plasmid isolation, warrant a simple, short, and reliable protocol. We believe that the present study’s high-yielding, high-quality plasmid DNA protocol will be useful for other bacterial strains resistant to cell lysis, especially for low-copy number plasmid strains.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105, AGL1, GV3101, and LBA4404 [all containing binary plasmid pCAMBIA 1201 harboring gusA gene under the control of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV) 35S promoter and bacterial selection marker chloramphenicol]
A. rhizogenes strains ATCC15834 and A4, containing binary plasmid harboring green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene under the control of 35S promoter and bacterial selection marker kanamycin
Rhizobium sp. (isolated from root nodules of desert tree legume, Prosopis cineraria)
Bacillus thuringiensis (received as a gift from a colleague, collected from the United Arab Emirates)
Reagents
Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (LB Miller Modification; PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: L475)
Tryptone (PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: T832)
Yeast extract (PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: Y892)
Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma, catalog number: S1679)
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate dibasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma, catalog number: P3786)
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Sigma, catalog number: M2773)
Mannitol (Sigma, catalog number: M1902)
Bacto-agar (Himedia, catalog number: GRMO26)
Kanamycin sulfate (PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: K378)
Rifampicin (PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: R7382)
Formamide (Sigma, catalog number: 47671)
Chloramphenicol (PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: C1919)
QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 27109)
PureLink Quick Plasmid Miniprep kit (Invitrogen, catalog number: K210011)
Resuspension solution P1 with RNase and Blue lysate (Qiagen, catalog number: 19051)
Resuspension buffer R3 (Invitrogen, catalog number: K2100-14)
Lysis solution P2 (Qiagen, catalog number: 19052)
Lysis buffer L7 (Invitrogen, catalog number: K2100-14)
Neutralizing solution N3 (Qiagen, catalog number: 19064)
Precipitation buffer N4 (Invitrogen, catalog number: K2100-14)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Sigma, catalog number: L3771)
RNase (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: EN0531)
Ethanol absolute (Sigma, catalog number: NC1971050)
Disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate (Na2EDTA·2H2O) (Sigma, catalog number: E6760)
Tris-base (Sigma, catalog number: T1503)
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma, catalog number: 07102)
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Sigma, catalog number: 06203)
Chloroform (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C2432)
Glacial acetic acid (VWR, catalog number: VWRC20104.334)
Isoamyl alcohol (Sigma, catalog number: 19392)
Methanol ChromasolvTM (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 34860-2.5L-R)
NcoI-HF (NEB, catalog number: R3193M), storage at -20 °C
BstEII-HF (NEB, catalog number: R3162M), storage at -20 °C
HotStar Taq DNA Polymerase PCR kit (Qiagen, catalog number: 203205)
PCR primers (Macrogen, South Korea)
Agarose D1 Low CE (Conda Lab, catalog number: 8010.00)
HydragreenTM Safe DNA Dye (20,000×) (ACTGene, catalog number: ACT-IDMG04)
6× DNA loading dye (NEB, catalog number: B7024A)
GeneRuler 1 kb Plus DNA ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SM1333)
Lambda DNA/EcoRI Plus HindIII marker (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SM0191)
Solutions
1 N HCl
1 N NaOH
LB Agrobacterium medium (see Recipes)
Yeast Mannitol medium (see Recipes)
Tris-EDTA (TE; see Recipes)
Tris (see Recipes)
Na2EDTA (see Recipes)
Kanamycin (see Recipes)
Rifampicin (see Recipes)
Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE, see Recipes)
Chloramphenicol (see Recipes)
5 M Sodium chloride (see Recipes)
20% (w/v) SDS (see Recipes)
Chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (CIA) (see Recipes)
Ethanol (70%, v/v) (see Recipes)
Media components (1 L) for the bacterial culture (see Recipes)
Antibiotics preparation (see Recipes)
Stock solutions (see Recipes)
Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer (100 mL) (see Recipes)
10× Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE) (see Recipes)
Agarose gel (0.8%, w/v) preparation (see Recipes)
Recipes
Media components (1 L) for the bacterial culture
Components LB Agrobacterium (g/L) LB (g/L) YM (g/L) Tryptone 10 (5 g for LBA4404 strain) 10 Yeast extract 5 5 0.1 NaCl 5 10 0.2 KH2PO4 10 MgCl2·7H2O 0.2 Mannitol 10 Dissolve the components in 800 mL of MilliQ water and adjust to 1 L using MilliQ water. Transfer into a Duran bottle. Adjust the pH to 7.0 using 1 N HCl/1 N NaOH.
For solid media, add bacto-agar 15 g/L after adjusting the pH.
Autoclave at 121 °C (15 psi) for 15 min and store at room temperature (RT) for two months.Antibiotics preparation
Antibiotics Preparation and storage Working concentration Kanamycin Weigh 50 mg in a 1.5 mL Eppendorf, add 1 mL of sterile water, dissolve, and store at 4 °C for one week. 50 mg/L Chloramphenicol Weigh 25 mg in a 1.5 mL Eppendorf, add 1 mL of absolute ethanol, dissolve, and store at 4 °C for one week. 25 mg/L Rifampicin Weigh 20 mg in a 1.5 mL Eppendorf, add 1 mL of formamide*, dissolve and warp with aluminum foil, and store at 4 °C for one week. 20 mg/L *Methanol is an alternative solvent.
Stock solutions
Stock Preparation and storage 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) Dissolve 121.1 g of Tris-base in 800 mL of MilliQ water. Adjust the pH to 8.0 by adding concentrated HCl. Adjust to 1 L using MilliQ water. Transfer into a 1 L Duran bottle. Autoclave at 121 °C (15 psi) for 15 min. Store at RT for six months. 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) Weigh 93 g of disodium EDTA·2H2O in ~400 mL of MilliQ. Stir vigorously on a magnetic stirrer with a stir bar. Adjust the pH to 8.0 with NaOH (~10 g of NaOH pellets). Adjust to 500 mL using MilliQ water. Transfer into a 500 mL Duran bottle. Autoclave at 121 °C (15 psi) for 15 min. Store at RT for six months. 5 M NaCl Dissolve 29.2 g of NaCl in 80 mL of MilliQ water and adjust to 100 mL using MilliQ water. Transfer into a 100 mL Duran bottle. Autoclave at 121 °C (15 psi) for 15 min. Store in a Duran bottle at RT for six months. SDS (20%, w/v) Weigh 20 g of SDS, dissolve it in MilliQ water, and adjust to 100 mL using MilliQ water. Transfer into a 100 mL Duran bottle. Autoclave at 121 °C (15 psi) for 15 min. Store at RT for six months. Caution: use face masks during preparation. Chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) (CIA) Add 2 mL of isoamyl alcohol in a 50 mL sterile Falcon tube and adjust to 50 mL by adding chloroform. Mix well and cover with aluminum foil. Store at RT for two weeks. Caution: prepare in a fume hood. 70% (v/v) ethanol Measure 35 mL of absolute ethanol in a 50 mL sterile Falcon tube, add 15 mL MilliQ water, and mix well. Store at RT for six months. Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer (100 mL)
Components Volume (mL) Final concentration Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) 1.0 10 mM Na2EDTA (pH 8.0) 0.2 1 mM MilliQ water 98.8 Autoclave in a 100 mL Duran bottle at 121 °C (15 psi) for 15 min and store at RT for six months. 10× Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE)
Components Amount Concentration 1× 1× preparation Tris-base 48.5 g 40 mM Mix 10 mL of 10× with 90 mL Na2EDTA (pH 8.0) 20 mL 1 mM MilliQ water Glacial acetic acid 11.4 mL 20 mM Dissolve tris-base in approximately 800 mL of MilliQ water. Add acetic acid and EDTA. Adjust to 1 L. Transfer into 1 L Duran bottle. Store at RT for six months. Agarose gel (0.8%, w/v) preparation
Weigh 0.48 g of agarose and add into 60 mL of 1× TAE buffer in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Microwave for 2 min, cool to 50 °C, add 6 μL of Hydragreen, and cast in the gel tray with 15 wells combs.
Laboratory supplies
90 mm Petri dish (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: F611001)
Safe-lock tubes (2.0 and 1.5 mL) (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030 120.094)
Pipettes (1,000, 200, 100, 20, and 10 μL) (Rainin, catalog number: L1000XLS+, L200XLS+, L100XLS+, L20XLS+, and L10XLS+, respectively)
Duran bottle [DURAN® ORIGINAL GL 45, catalog number: 10113399 (1,000 mL) and 10108298 (500 mL)]
Beakers (0.6 and 1 L) (Nalgene, catalog number: 1201-0600 and 1201-1000, respectively)
PYREX® 250 mL narrow mouth Erlenmeyer flask (Corning, catalog number: 4980-250)
Graduated cylinders (0.5 and 1 L) (Nalgene, catalog number: 3662-0500 and 3662-1000, respectively)
Pipette tips (1,000, 250, and 20 μL) (Rainin, catalog number: 30389294, 30389301, and 30389297, respectively)
Magnetic stirrer (Corning®, model: PC-620D, catalog number: 6796-620D)
Stir bars (PhytoTech Labs, catalog number: B011)
Tube racks (Globe Scientific, catalog number: 456350B)
Kimwipes (KIMTECH, catalog number: 34120)
14 mL sterile Falcon bacterial culture tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 352057)
Disposable gloves (Kimberly-Clark, catalog number: 52816)
Inoculation loops (VWR, catalog number: 10806-354)
Wide Mini-Sub Cell GT Horizontal Electrophoresis System, 15 cm × 7 cm tray, with gel caster and casting gates (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1704469)
Weigh dish (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 3846D19)
Weigh paper (Thomas Scientific, catalog number: 9885G50)
Spatula (PhytoTech Labs, KS, USA, catalog number: S798)
Face mask (Euromed, China, catalog number: EM1834)
Disposable cuvettes (BrandTech, catalog number: 759075D)
Equipment
Autoclave (Tomy, model number: SX-700)
Weighing scale (Mettler Toledo®, model: MS603S/01)
Refrigerator (4 and -20 °C) (Evermed, model: BLCRF-370W)
pH meter (Thermo Fisher, model: Fisherbrand Accumet AB150, catalog number: 13636AB150B)
Laminar air flow cabinet (Esco, Horizontal Laminar Flow Cabinet, Gen 3, model: LHG-3AG-F8, catalog number: 2120387)
Bead sterilizer (PhytotTech Labs, model: ErgoSteri VT glass bead sterilizer, catalog number: S7520)
Shaker incubator (Eppendorf, model: New Brunswick Innova® 42, catalog number: M-1335-0004)
UV-Visible spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, model: Evolution 201, catalog number: 840-210600)
Centrifuge (Tomy, model: MX-307)
Vortexer (Scientific industries, model: Vortex-GenieTM 2T mixer, catalog number: SI-T266)
Heating block (Labnet International, AccuBlock, Digital dry bath, model: Labnet International D1100, catalog number: D1100-230V)
Fume hood (Esco, AscentTM Max Ductless Fume Hood, model: ADC-4BI, catalog number: 2040042)
Nutating Mixer (Labnet International, model: Labnet GyroMiniTM Nutating 3-D Mixer with dimpled mat, 120 V, catalog number: S0500)
NanoDropTM (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: ND2000C)
Microwave (Samsung, model: ME733K)
MilliQ water purification system (MilliQ, model: Elix integral 10)
Gel DocTM EZ imager (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 170-8270)
PowerPacTM Basic (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 164-5050)
Electrophoresis unit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1704405)
Desktop (Dell, model: Optoplex 9020)
Thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: T100)
Software and datasets
NanoDrop 2000 (version 1.6, free, Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Image Lab 6.0 (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
Insight2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 837-002700)
Microsoft Excel for Mac (v16.69.1, 2022)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Kodackattumannil, P., Sasi, S., Krishnan, S., Lekshmi, G., Kottackal, M. and Amiri, K. M. A. (2023). Protocol for the High-quality Plasmid Isolation from Different Recalcitrant Bacterial Species: Agrobacterium spp., Rhizobium sp., and Bacillus thuringiensis. Bio-protocol 13(15): e4788. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4788.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物遗传学 > 质粒
分子生物学 > DNA > DNA 提取
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












