- EN - English
- CN - 中文
In Vitro Analysis of Stalled Ribosomes using Puromycin Incorporation
利用嘌呤霉素结合对停滞的核糖体进行体外分析
发布: 2023年08月20日第13卷第16期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4744 浏览次数: 3337
评审: David PaulJingbo DaiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Ribosome footprint profiling has demonstrated that ribosomes can be slowed or stalled on select mRNAs, often due to the presence of rare codons, stalling motifs, or via a ribosome-binding protein (e.g., FMRP). Stalled ribosomes can act as physical roadblocks for trailing ribosomes and ultimately can cause ribosome collisions that stimulate no-go mRNA decay. Detecting stalled or slowed ribosomes in cells by ribosome footprint profiling or classic polysome profiling is laborious, technically challenging, and low throughput. Here, we present a protocol to assay for stalled ribosomes on in vitro–transcribed reporter mRNAs using a robust, commercially available mammalian in vitro translation lysate and an optimized low-speed sucrose cushion. In short, we take advantage of the ability of puromycin to incorporate into the nascent polypeptide and cause the ribosome to dissociate from the mRNA during active elongation, as well as the ability to selectively pellet ribosomes through a low-speed sucrose cushion due to their large molecular weight. Stalled ribosomes are not actively elongating and do not incorporate puromycin, allowing the ribosome-bound mRNA to pellet in the low-speed sucrose cushion. RT-qPCR is used to quantify the amount of ribosome-bound reporter mRNA in the pellet. This workflow allows for direct assessment of stalled ribosomes and is fully amendable to insertion of putative stalling motifs in the target mRNA, as well as supplementation with recombinant proteins or small molecule inhibitors that target translation elongation.
Key features
•This protocol is optimized for cap-dependent in vitro translation in the dynamic linear range.
•Details for generating capped reporter mRNA in one day are provided.
•Requires as little as one day to complete if starting with in vitro–transcribed mRNA.
•This protocol requires access to an ultracentrifuge and a real-time PCR system.
Graphical overview

Background
Upon initiating at a start codon, ribosomes proceed through elongation with repetitive cycles of decoding and translocation until they terminate at one of three stop codons (UAA, UAG, or UGA) (Dever et al., 2018). Elongating ribosomes may encounter a multitude of challenges, including rare codons, premature polyadenylation, truncated or damaged mRNA, proline-rich stalling motifs, strong or highly ordered mRNA structure, or mRNA- and ribosome-binding proteins (e.g., FMRP) (Kim and Zaher, 2022). These obstacles can stall ribosomes, which act as physical roadblocks for trailing ribosomes, resulting in ribosome collisions that stimulate the no-go mRNA decay pathway. In yeast, collided ribosomes are recognized by the E3 ligase Hel2 (ZNF598 in human and Caenorhabditis elegans) (Monem et al., 2023), which ubiquitinates ribosomal proteins eS10 and uS10 (Juszkiewicz et al., 2018). In yeast, ubiquitinated and collided ribosomes serve as a unique binding site for the endonuclease Cue2 (N4BP2 in humans, NONU1 in Caenorhabditis elegans) (D’Orazio et al., 2019). Subsequently, the new 5′ and 3′ ends are susceptible to degradation by Xrn1 and the exosome, respectively. Ribosome collisions also drive mRNA-specific feedback translation initiation inhibition to further prevent synthesis of deleterious truncated proteins (Juszkiewicz et al., 2020; Sinha et al., 2020). Upon large-scale ribosome collisions, global translation initiation is inhibited by activation of GCN2-mediated eIF2α phosphorylation (Wu et al., 2020).
Ribosome footprint profiling and classic polysome profiling can be used to detect stalled ribosomes; however, these approaches can be technically challenging, laborious, and rather low throughput. Additionally, ribosome profiling is not cost-effective when testing multiple specific mutations within reporter mRNAs or effector proteins. Here, we present a validated protocol that can be used to assess ribosome stalling in vitro that is medium-to-high throughput and can be performed in as little as one day if starting with in vitro–transcribed mRNA.
We take advantage of the selective nature of puromycin, an amino-acyl transfer RNA analog to incorporate into nascent polypeptides of only actively elongating ribosomes (Yarmolinsky and Haba, 1959). Puromycin incorporation results in ribosomes releasing both the nascent protein and the mRNA, resulting in the collapse of polysomes to monosomes (Yarmolinsky and Haba, 1959; Azzam and Algranati, 1973; Stefani et al., 2004; Sivan et al., 2007). Using an optimized low-speed sucrose cushion and subsequent RT-qPCR, we quantify ribosome-bound reporter mRNA to determine efficacy of puromycin to dissociate ribosomes. Ribosomes that are stalled during elongation do not actively incorporate puromycin; thus, these ribosomes are insensitive to puromycin and consistently pellet bound mRNA in the presence of puromycin. This protocol utilizes a commercially available mammalian translation lysate in conditions that allow for translation in the dynamic linear range and showcases cap and scanning dependency (Kearse et al., 2016). A key feature is an independent reporter that is translated and not treated with puromycin, which serves as a normalizing control for both the low-speed sucrose cushion and RT-qPCR. The low-speed sucrose cushion has been optimized so that only ribosome-bound mRNA is pelleted. Untranslated mRNA does not have sufficient molecular weight to pellet in these conditions. We have published this strategy and validated its efficacy using the Fragile X protein FMRP (an mRNA- and ribosome-binding protein that stalls ribosomes) (Darnell et al., 2011), along with FireFly Luciferase mRNA as the normalizing control reporter and nanoLuciferase mRNA as the experimental reporter (Figure 1) (Scarpitti et al., 2022).
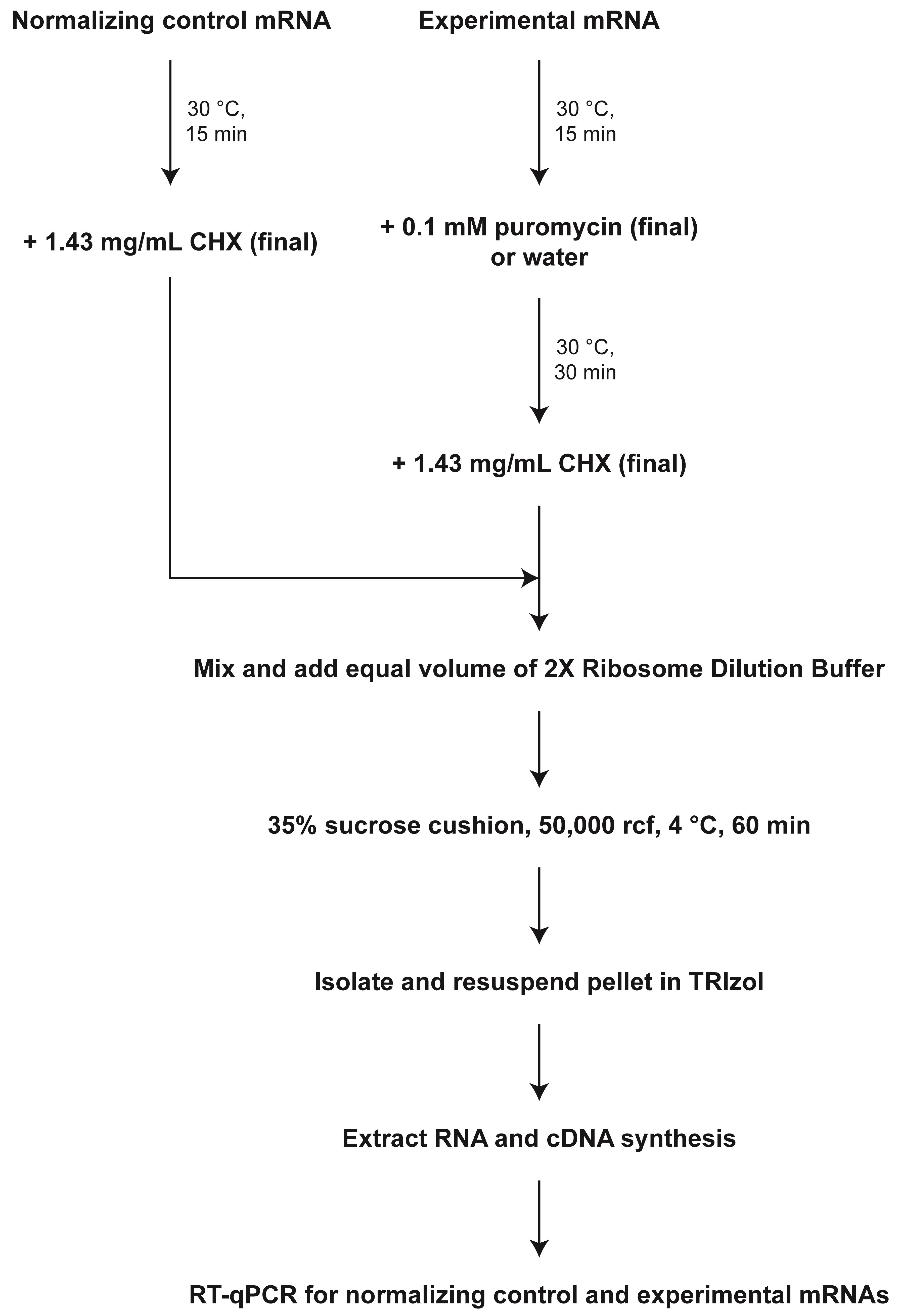
Figure 1. Schematic of overall strategy to assay for stalled ribosomes using puromycin incorporation and an optimized low-speed sucrose cushion.CHX = Cycloheximide.
Materials and reagents
Reagents
2-Propanol (isopropanol) (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: A416P-4)
3′-O-Me-m7G(5′)ppp(5′)G RNA Cap Structure Analog (anti-reverse cap analog; ARCA) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: S1411S)
Agarose LE, quick dissolve (Apex BioResearch Products, catalog number: 20-102QD)
Bromophenol blue (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610404)
Chloroform, ethanol stabilized (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: 67-66-3)
10× CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: B7204S)
Cycloheximide (CHX) (Sigma, catalog number: C1988)
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: MX1458-3)
Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 20290)
DNA Clean & Concentrator-25 kit (Zymo Research, catalog number: 11-305C)
DNase I (RNase-free) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0303L)
E. coli Poly(A) polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0276L)
500 mM EDTA, pH 8.0 ULTROL grade (Millipore, catalog number: 324504)
Ethanol, 200 proof (Decon Laboratories, Inc., catalog number: 64-17-5)
10 mg/mL ethidium bromide (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 15585011)
Flexi Rabbit Reticulocyte Lysate System (Promega, catalog number: L4540)
37% (w/v) formaldehyde (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: F79-500)
Glycerol, biotechnology grade (Amresco, catalog number: 0854-4L)
Glycogen, molecular biology grade (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: R0561)
Hi-Di Formamide (Thermo Scientific, Applied Biosystems, catalog number: 4401457)
HiScribe T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis kit (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E2040S)
iScript Reverse Transcription Supermix (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1708841)
iTaq Universal SYBR Green Supermix, 5 mL (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1725124)
2 M KCl, pH 7.4 (MOLTOX, catalog number: 26-516.5)
1 M MgCl2 (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: AM9530G)
Millennium RNA size marker (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: AM7150)
10× MOPS buffer (KD Medical, catalog number: RGF-6170)
Nuclease-free water (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: AM9937)
Puromycin dihydrochloride (Sigma, catalog number: P8833)
6× purple gel loading dye (New England Biolabs, catalog number: B7024A)
Quick-Load Purple 1 kb Plus DNA ladder (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N0550S)
RNA Clean & Concentrator-25 kit (Zymo Research, catalog number: 11-353B)
RNase inhibitor, murine (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0314L)
Sucrose, Ultra-pure, RNase- & DNase-free (VWR, catalog number: 57-50-1)
10× TBE buffer (IBI Scientific, catalog number: IB70154)
1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 (Apex BioResearch Products, catalog number: 18-189)
TRIzol reagent (Ambion, catalog number: 15596018)
Xylene cyanol FF (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1610423)
pcDNA3.1(+)/nLuc-3XFLAG (Addgene, catalog number: 127299)
Dual promoter plasmid pCR II (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: K207040)
pGL4.13 (Promega, catalog number: E6681)
Solutions
100 mg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) (see Recipes)
10 mg/mL CHX (see Recipes)
5 mg/mL CHX (see Recipes)
1 M DTT, Cleland’s Reagent (see Recipes)
70% (v/v) ethanol (see Recipes)
1 mg/mL ethidium bromide (see Recipes)
10 mM GTP (see Recipes)
1× MOPS buffer (see Recipes)
10 mg/mL (~18 mM) puromycin (see Recipes)
0.6 mM puromycin (see Recipes)
2× ribosome dilution buffer (see Recipes)
RNA loading dye (see Recipes)
RNA sample buffer (see Recipes)
60% (w/v) sucrose (see Recipes)
35% (w/v) sucrose, buffered (see Recipes)
1× TBE buffer (see Recipes)
Recipes
100 mg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) (store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity CHX 100 mg/mL 1 g DMSO n/a To 10 mL Total n/a 10 mL 10 mg/mL CHX (working solution, aliquot into single-use vials and store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 100 mg/mL CHX 10 mg/mL 1 mL Milli-Q water n/a 9 mL Total n/a 10 mL 5 mg/mL CHX (working solution, aliquot into single-use vials and store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 10 mg/mL CHX 5 mg/mL 3 mL Milli-Q water n/a 3 mL Total n/a 6 mL 1 M DTT, Cleland’s Reagent (store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity DTT 1 M 1.542 g Milli-Q water n/a To 10 mL Total n/a 10 mL 70% (v/v) ethanol
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 100% Ethanol 70% (v/v) 35 mL Milli-Q water n/a 15 mL Total n/a 50 mL 1 mg/mL ethidium bromide
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 10 mg/mL ethidium bromide 1 mg/mL 100 μL Milli-Q water n/a 900 μL Total n/a 1 mL 10 mM GTP (store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 100 mM GTP (from HiScribe T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis kit) 10 mM 50 μL Nuclease-free water n/a 450 μL Total n/a 500 μL 1× MOPS buffer
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 10× MOPS buffer 1× 60 mL Milli-Q water n/a 540 mL Total n/a 600 mL 10 mg/mL (~18 mM) puromycin (store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Puromycin 10 mg/mL 1 g Milli-Q water n/a To 100 mL Total n/a 100 mL 0.6 mM puromycin (store at -20 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 18 mM puromycin 0.6 mM 66.67 μL Milli-Q water n/a 1.933 mL Total n/a 2 mL 2× ribosome dilution buffer (store at 4 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 40 mM 2 mL 2 M KCl 280 mM 7 mL 1 M MgCl2 20 mM 1 mL 100 mg/mL CHX 0.2 mg/mL 100 μL *Add day of use 1 M DTT 2 mM 100 μL *Add day of use Milli-Q water n/a 39.8 mL Total n/a 50 mL RNA loading dye
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Glycerol 50% (v/v) 5 mL 500 mM EDTA, pH 8.0 100 mM 2 mL Bromophenol blue 2.5 mg/mL 25 mg Xylene cyanol FF 2.5 mg/mL 25 mg Milli-Q water n/a 3 mL Total n/a 10 mL RNA sample buffer (make fresh day of use)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 37% (w/v) formaldehyde 9% (w/v) 35 μL Hi-Di formamide 69% (v/v) 100 μL 10× MOPS buffer 0.7× 10 μL Total n/a 145 μL 60% (w/v) sucrose
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Sucrose 60% (w/v) 300 g Milli-Q water n/a To 500 mL Total n/a 500 mL 35% (w/v) sucrose, buffered (store at 4 °C)
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 60% sucrose (w/v) 35% (w/v) 29.167 mL 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 20 mM 1 mL 2 M KCl 140 mM 3.5 mL 1 M MgCl2 10 mM 0.5 mL 100 mg/mL CHX 0.1 mg/mL 50 μL *Add day of use 1M DTT 1 mM 50 μL *Add day of use Milli-Q water n/a 15.733 mL Total n/a 50 mL 1× TBE buffer
Reagent Final concentration Quantity 10× TBE buffer 1× 100 mL Milli-Q water n/a 900 mL Total n/a 1 L
Laboratory supplies
0.2 mL, open-top thick wall polycarbonate tube, 7 mm × 20 mm (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 343775)
1.7 mL microcentrifuge tube, clear (Olympus Plastics, catalog number: 24-282)
500 mL Erlenmeyer flask
8-strip PCR tubes (Olympus Plastics, catalog number: 27-125UA)
Hard-shell PCR plates, 96-well, thin-well (Bio-Rad, catalog number: HSP9601)
Ice
Ice buckets
Light-dry tissue wipes (VWR, catalog number: 82003-820)
Microseal ‘B’ seals (Bio-Rad, catalog number: MSB1001)
Nitrile gloves
P10, P20, P200, and P1000 calibrated pipettes
P10, P20, P200, and P1000 pipette tips (VWR, catalog numbers: 76323-388, 76323-390, and 76323-456)
Parafilm
Plastic wrap
Tube racks
Equipment
-80 °C freezer
-20 °C freezer
4 °C refrigerator
Aspirator
CFX Connect Real-Time System (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1855201)
Eppendorf centrifuge 5430 (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022620509)
Fume hood
GelDoc Go Gel imaging system with Image Lab Touch software (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 12009077)
Microwave
MilliporeSigma Synergy ultrapure water purification system (Fischer Scientific, catalog number: SYNS0HFUS)
NanoDrop One Microvolume UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: ND-ONE-W)
OWL EasyCast B1 Mini Gel electrophoresis system (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: B1-BP)
OWL EasyCast B1A Mini Gel electrophoresis system (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 09-528-110)
Paper towels
Plate centrifuge, PerfectSpin P (VWR Peqlab, catalog number: PEQL91-PSPIN-P)
Pointed tweezers
S100-AT3 fixed angle rotor (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 45585)
Sorvall Discovery M120 SE micro-ultracentrifuge (Hitachi)
T100 thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 1861096)
Vortex mixer (Benchmark, catalog number: BV1000)
Software and datasets
Bio-Rad CFX Maestro
Microsoft Excel
Prism GraphPad Molarity Calculator (https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/molarityform/)
Oligo Calc: Oligonucleotide Properties Calculator (http://biotools.nubic.northwestern.edu/OligoCalc.html)
Transcription and Translation Tool (https://biomodel.uah.es/en/lab/cybertory/analysis/trans.htm)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Scarpitti, M. R. and Kearse, M. G. (2023). In Vitro Analysis of Stalled Ribosomes using Puromycin Incorporation. Bio-protocol 13(16): e4744. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4744.
- Scarpitti, M. R., Warrick, J. E., Yoder, E. L., and Kearse, M. G. (2022). A noncanonical RNA-binding domain of the fragile X protein, FMRP, elicits translational repression independent of mRNA G-quadruplexes. J Biol Chem 298(12): 102660.
分类
分子生物学 > RNA > mRNA 转译
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link