- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Simple and Reproducible Stereomicroscopic Method to Assess Fungal Biofilms: Application to Antifungal Susceptibility Testing
评估真菌生物膜的简单和可重复的立体显微镜方法: 在抗真菌药敏试验中的应用
发布: 2023年07月05日第13卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4713 浏览次数: 1629
评审: Wenrong HeYe XuAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Candida albicans, a well-known opportunistic pathogen, is a major cause of human fungal infections. Biofilm formation is considered an important pathogenesis factor. Biofilms are less sensitive to antibiotics and immune responses, allowing them to colonize and persist in host niches. Biofilm screening is important in the identification of anti-biofilm drugs. However, developing nations, with limited financial resources, often do not have access to advanced scientific equipment. Here, we describe an in vitro, protocol using common materials and simple equipment to evaluate static microbial biofilms.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance (抗菌剂抗性)Background
Candida albicans, a commensal fungus, is a leading cause of human fungal infections. It becomes a very resilient pathogen under low host immunity, for example in neonates or patients with AIDS or transplants (Ostrosky-Zeichner et al., 2003). Biofilm formed by this pathogen plays important roles in both its virulence and antifungal resistance (Gulati and Nobile, 2016). Various microscopic methods are routinely used to evaluate Candida, including microscopic (atomic force, epifluorescence, laser scanning confocal, and scanning electron) assays. The simple technique described herein is more cost effective, in particular for biofilm screening projects.
The most common method to evaluate biofilm formation is the microplate assay (Azeredo et al., 2017). Here, we present a low-cost visual biofilm detection protocol that uses tissue culture plates and detection in brightfield that offers comparable results to standard assays (Shahina et al., 2022a and 2022b). This assay (Figure 1) is suitable for researchers in developing countries where there is a lack of access to high throughput microscopy and microplate readers.
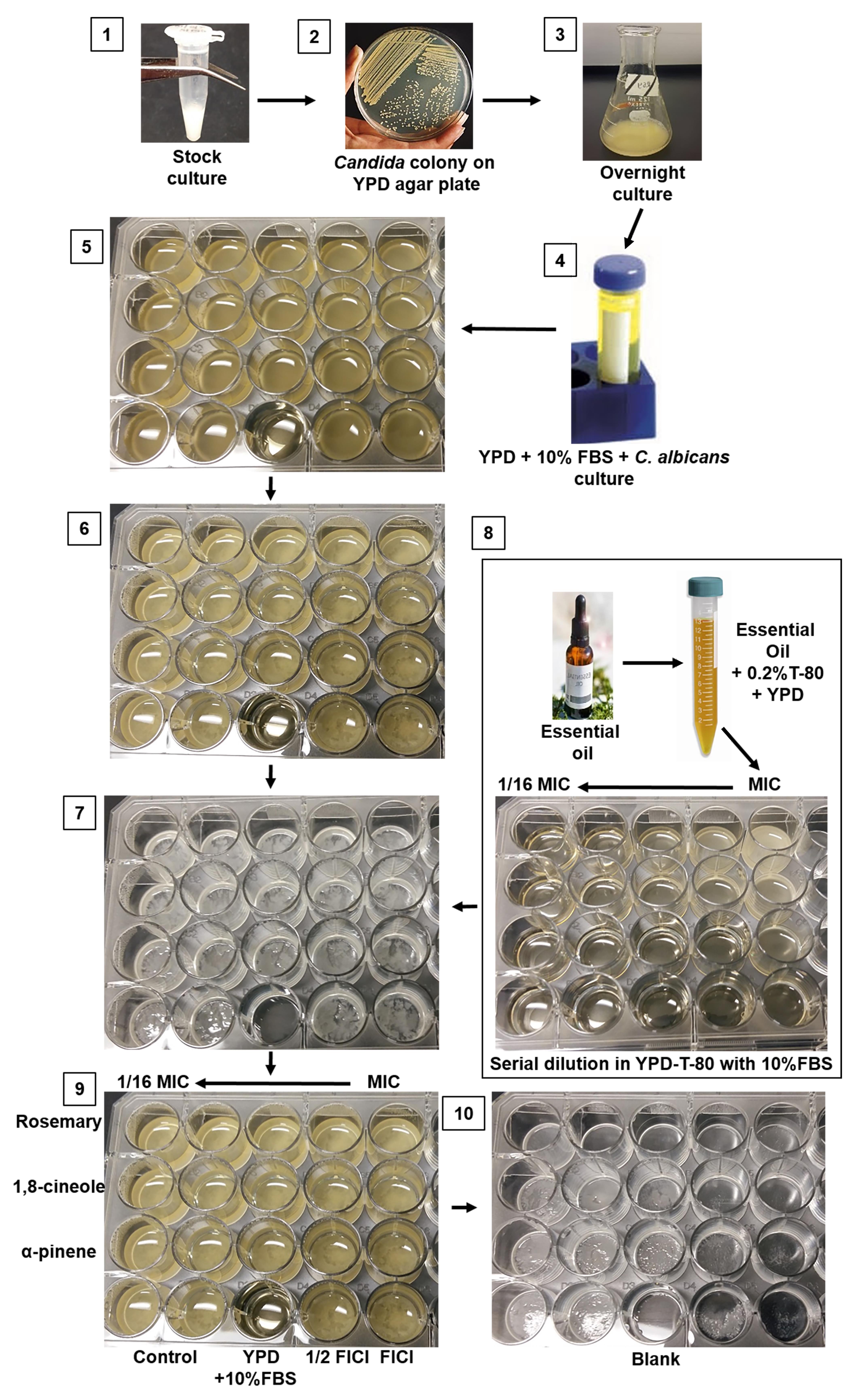
Figure 1. Schematic step-by-step protocol for visualizing C. albicans biofilm formation and inhibition. 1. C. albicans stock culture in 50% glycerol. 2. Colony formation on YPD media. 3. Overnight culture on YPD broth. 4. Sample in prewarmed 10% FBS with YPD diluted according to desired cell density. 5. Candida in 24-well plate (plate 1) in preparation for incubation at 37 °C for 24 h. 6. Sample plate after 24 h incubation. 7. Biofilm growth at the bottom of the 24-well plate following removal of the medium and planktonic cells. 8. Preparation of drugs/essential oils in a new plate (plate 2) and its transfer into the pre-formed biofilm (plate 1). 9. Biofilm with antifungal drugs (plate 1) is ready for incubation at 37 °C for 24 h. 10. After 24 h incubation (plate 1), the media is aspirated, and the plate is ready for stereomicroscopic imaging.
Materials and reagents
15 mL screw cap conical bottom tube (Sarstedt, catalog number: 50-809-221)
24-well tissue culture plates (Sarstedt, catalog number: 83.3922)
50 mL screw cap conical bottom tube (Sarstedt, catalog number: 50-809-218)
96-well, flat base, PS, transparent plate (Sarstedt, catalog number: 82.1581001)
Syringe filter, Filtropur S, 0.2 μm (Sarstedt, catalog number: 83.1826.001)
Test tube racks (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-809-62) or any standard test tube racks
Agar (VWR, catalog number: 97064-336)
Antifungal agent; amphotericin B (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 1397-89-3)
BactoTM peptone (Becton Dickinson, catalog number: 211677)
D-(+)-Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8270)
Essential oils:
RM (Aroma force, catalog number: 6658117001)
1,8-cineole, 99% (Acros organics, catalog number: 470-82-6)
(+)–α-pinene ≥ 99% (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 268070)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 12483-020)
Parafilm (Amcor, catalog number: PM996)
Yeast extract (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 70161)
TWEEN® 80, polysorbate 80 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 9005-65-6)
Yeast extract peptone (YPD) plate containing freshly revive C. albicans colonies
YPD agar medium (per liter) (see Recipes)
YPD broth (per liter) (see Recipes)
YPD broth containing 10% FBS (see Recipes)
Equipment
-20 °C freezer (General Electrics)
-80 °C freezer (Revco, catalog number: ULT2586-4-A)
Autoclave (Steris Scientific, AMSCO® C series small steam sterilizer) or any standard autoclave
Balance (Mettler Toledo NewClassic MF Precision Balance, catalog number: ML303E/03)
Benchtop shaking incubator (CorningTM LSETM, catalog number: CLS6791)
Inoculating loop (FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 131045)
Laminar flow workstation (MicroZone Corporation, model: V4-MN-99-030) or any standard equipment with similar features
Microbiological benchtop laboratory incubator (Thelco, Model 4)
Micropipette 100–1,000 μL (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000063)
Micropipette 20–200 μL (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000055)
Micropipette 100–1,000 μL tips (VWR International, catalog number: 83007-376)
Micropipette 20–200 μL tips (Sarstedt, catalog number: 70.3030)
Micropipette 500–5,000 μL tips (Sarstedt, catalog number: 70.1183.002)
Petri dish, 92 mm × 16 mm (Sarstedt, catalog number: 82.1473.001)
Pipette, 500–5,000 μL (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3123000071)
Plate reader for OD determination (BioTek Instruments, Epoch- Microplate Spectrophotometer)
Note: The plate reader was used for verification of this method; a standard spectrophotometer (supplier model T, A, C. Detector: Silicon Photodiode or Thermo ScientificTM GENESYSTM Visible and UV-Visible Spectrophotometers) can be used to measure OD.
PYREX glass erlenmeyer flask, 125 mL (Corning, catalog number: 4980-125)
Stereomicroscope (Nikon’s SMZ 1500) equipped with a 2× and 4× objective and a digital camera or eyepieces for use of a mobile phone camera
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Shahina, Z. and Dahms, T. E. S. (2023). A Simple and Reproducible Stereomicroscopic Method to Assess Fungal Biofilms: Application to Antifungal Susceptibility Testing. Bio-protocol 13(13): e4713. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4713.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物膜 > 杀伤试验
生物科学 > 生物技术 > 微生物技术
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













