- EN - English
- CN - 中文
β-lactamase (Bla) Reporter-based System to Study Flagellar Type 3 Secretion in Salmonella
基于β-内酰胺酶(Bla)报告子的系统研究沙门氏菌鞭毛3型分泌
发布: 2023年06月20日第13卷第12期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4696 浏览次数: 1774
评审: David A. CisnerosSrujana Samhita YadavalliAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

酸水解-高效液相色谱法测定集胞藻PCC 6803中聚3-羟基丁酸酯的含量
Janine Kaewbai-ngam [...] Tanakarn Monshupanee
2023年08月20日 1824 阅读

基于高效液相色谱法的史氏分枝杆菌DisA环二腺苷酸(C-di-AMP)合成酶活性研究
Avisek Mahapa [...] Dipankar Chatterji
2024年12月20日 1789 阅读
Abstract
Export of type 3 secretion (T3S) substrates is traditionally evaluated using trichloroacetic acid (TCA) precipitation of cultured cell supernatants followed by western blot analysis of the secreted substrates. In our lab, we have developed β-lactamase (Bla), lacking its Sec secretion signal, as a reporter for the export of flagellar proteins into the periplasm via the flagellar T3S system. Bla is normally exported into the periplasm through the SecYEG translocon. Bla must be secreted into the periplasm in order to fold into an active conformation, where it acts to cleave β-lactams (such as ampicillin) to confer ampicillin resistance (ApR) to the cell. The use of Bla as a reporter for flagellar T3S allows the relative comparison of translocation efficiency of a particular fusion protein in different genetic backgrounds. In addition, it can also be used as a positive selection for secretion.
Graphical overview
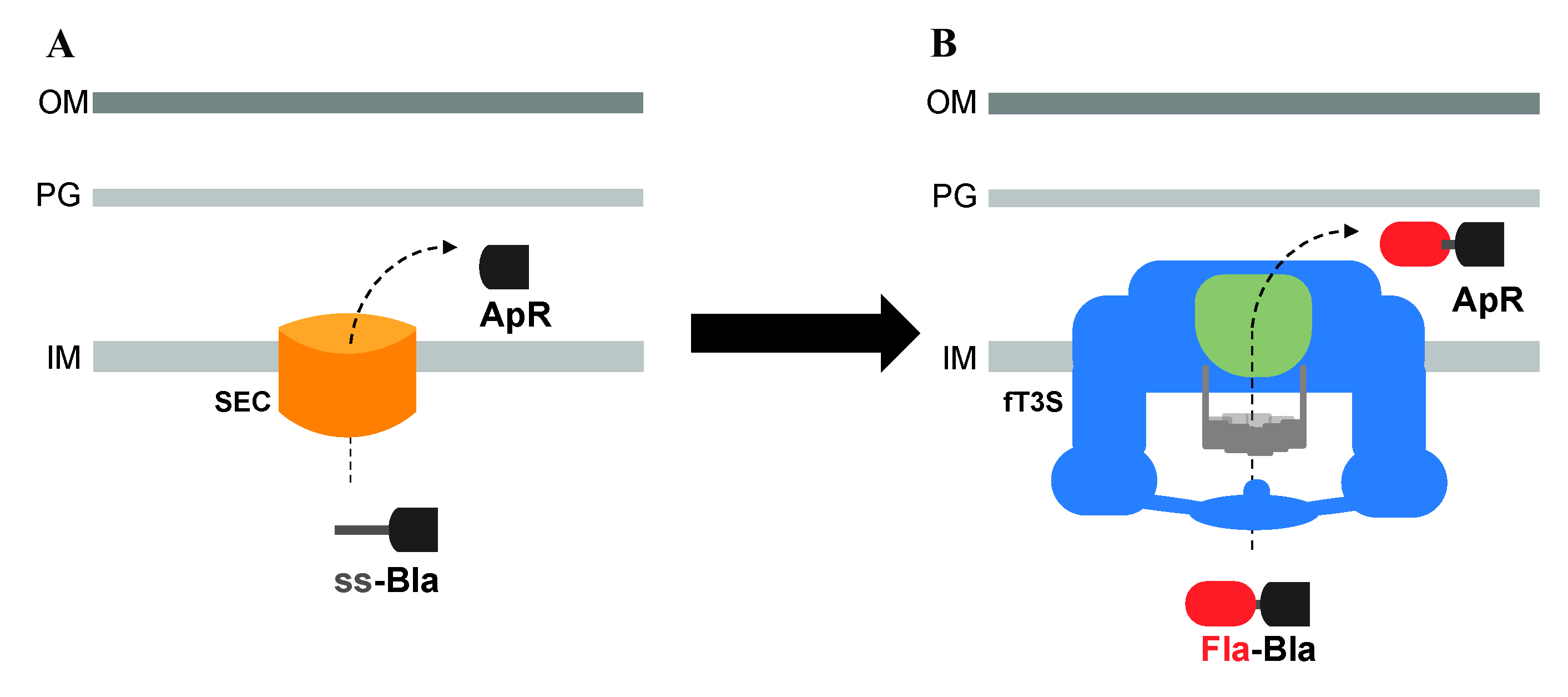
Utilization of β-lactamase (Bla) lacking its Sec secretion signal and fused to flagellar proteins to assay the secretion of exported flagellar substrates, into the periplasm, through the flagellar T3S system. A. Bla is normally transported into the periplasm space through the Sec secretion pathway, where it folds into an active conformation and allows resistance to ampicillin (ApR). B. Bla, lacking its Sec secretion signal, is fused to flagellar proteins to assay the secretion of exported flagellar proteins into the periplasm through the flagellar T3S system.
Background
Flagella are helical, corkscrew-like appendages that, depending on their clockwise or counterclockwise rotation, push or pull bacterial cells. They act like tiny propellers allowing bacteria to move through liquids or across hydrated surfaces. For the assembly of the bacterial flagellum, a flagellar type 3 secretion (T3S) system initially exports early component substrates that build the hook-basal body (HBB) structure, which is the main component making up the flagellar motor. Upon HBB completion, the flagellar T3S system undergoes a secretion substrate specificity switch, resulting in an export selectivity for late substrate proteins, which include flagellin that assembles into the long external filament that acts as the propeller of the flagellum.
The export of T3S substrates is traditionally evaluated using trichloroacetic acid (TCA) precipitation of the supernatant of cultured cells, followed by western blot analysis of the secreted substrates. This technique is very useful at assessing protein translocation but is limited to the study of substrates that are translocated outside the cells. We have developed a reporter assay using β-lactamase (Bla), lacking its Sec secretion signal, for the secretion of flagellar proteins into the periplasm through the flagellar T3S system. Bla is an enzyme that cleaves and inactivates β-lactam antibiotics, such as ampicillin (Ap), through hydrolysis of the peptide bond of the characteristic four-membered β-lactam ring. The inactivation of the antibiotic provides Ap-resistance (ApR) to the bacterium; for that, Bla needs to be transported into the periplasm where it folds into an active conformation. Such translocation into the periplasm occurs through the Sec-secretion pathway. Secreted proteins through the Sec-dependent pathway are readily recognized by an N-terminal signal sequence, which is cleaved during the process of secretion into the periplasm to yield a mature protein. Flagellar proteins are exported through the T3S pathway. Fusing Bla without its N-terminal signal sequence to the C-terminal of flagellar proteins results in the transport of the Fla-Bla fusions into the periplasm, where Bla is active and confers ApR (Lee and Hughes, 2006; Hirano et al., 2009; Erhardt and Hughes, 2010; Singer et al., 2014; Hendriksen et al., 2021; Qu et al., 2022). In cells expressing intact flagellar structures, Fla-Bla fusions are secreted into the periplasm transiently after completion of the flagellar core T3S system until outer membrane penetration. Once the flagellar structure penetrates the outer membrane, the Fla-Bla fusions are secreted into the extracellular medium. Mutants defective in rod assembly continuously secrete Fla-Bla fusion into the periplasm, which results in higher levels of ApR. By using assays to assess minimum inhibitory concentrations of ampicillin, we can estimate how much of the Fla-Bla fusion is exported and provide a quick estimate of secreted flagellar substrate levels. The use of Bla as a reporter for the flagellar T3S substrates also provides a positive selection for secretion. Using this technique, we were able, for example, to localize important sites of recognition in an early substrate’s secretion signal by the flagellar T3S apparatus located at the cytoplasmic base of flagellum (Qu et al., 2022). This system is not specific to Salmonella; Bla fusions to T3S proteins have been used in other Gram-negative pathogens, such as enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and Yersinia enterocolitica (Charpentier and Oswald, 2004; Diepold et al. 2015). In these systems, Bla fusions were used to measure the translocation of effector proteins in living host cells and in the extracellular medium, using a fluorescent β-lactamase substrate. Thus, fusion to Bla can be used to measure translocation of proteins either into the periplasm or the extracellular medium. We use secretion of Bla fusions in the periplasm because of the powerful selection of ApR. Here, we describe in detail the protocol used to assay the minimum inhibitory concentration to ampicillin for the assessment of the translocation efficiency of protein fusions in the periplasm and for positive selections using this system.
Materials and reagents
96-well culture plates (Olympus plastic, catalog number: 25-104)
Test tubes (borosilicate glass 13 × 100 mm) (FisherBrand, catalog number: 14-961-27)
Petri dishes (9 cm diameter)
Microcentrifuge tubes (1.5 mL)
Conical centrifuge tubes (50 mL)
Millipore water, sterilized
Ampicillin sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9518-100G)
Bacto peptone (Gibco, catalog number: 211677)
Difco bile salts No. 3 (BD, catalog number: BD 213020)
Bacto proteose peptone (Gibco, catalog number: 211684)
Agar, powdered (Apex, catalog number: 20-273)
Sodium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9888-1KG)
Yeast extract (Apex, catalog number: 20-254)
Tryptone, powdered (Apex, catalog number: 20-251)
Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate (Na2HPO4·7H2O) (Fisher, catalog number: S373-500)
Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Fisher, catalog number: P285-3)
Aluminum foil
Strains to be tested and containing fusions to β-lactamase (see Notes)
Lysogeny Broth-Lennox (LB) media (see Recipes)
PPBS plates (see Recipes)
10× phosphate buffer (see Recipes)
Buffered saline (see Recipes)
Ampicillin solution stocks (see Recipes)
Lysogeny Broth-Lennox (LB) plates (see Recipes)
Notes:
We routinely use Salmonella typhimurium LT2, strain TH437 (S. typhimurium LT2 wild type) as a negative control (MIC 1.5) and strain TH15737 (flgM-bla ΔflgHI fljBenxvh2 Δflk) as a positive control (MIC 100). These strains are available upon request.
We insert the Bla fusion without its signal sequence (amino acids 24–286 of Bla) just before the stop codon of the gene of interest, in the chromosome, using the lambda red recombination technique. We routinely do not add linkers, but we see no reason they could not be added. Confirm that the DNA sequence of any construct made is correct and that the protein expression is unaffected by the fusion before conducting assays.
Equipment
Conventional autoclave
-20 °C freezer
Vortex mixer
Temperature-controlled environmental shaker (set at 37 °C)
Temperature-controlled shaking water bath (set at 37 °C)
Standard micropipettes as well as matching tips
2,000 μL electronic pipette repeater (Rainin EDP3-Plus LTS 0.2–2 mL)
20 μL electronic pipette repeater (Rainin EDP3-Plus LTS 2–20 μL)
25 mL glass pipettes, sterilized
10 mL glass pipettes, sterilized
Note: Multichannel pipettes can be used instead of pipette repeaters.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
如何引用
Chevance, F. F. V. and Hughes, K. T. (2023). β-lactamase (Bla) Reporter-based System to Study Flagellar Type 3 Secretion in Salmonella. Bio-protocol 13(12): e4696. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4696.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 其它化合物
生物科学 > 微生物学
分子生物学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link