- EN - English
- CN - 中文
MiniSOG2-mediated Specific Photoablation of Motor Neurons in Ascidian Embryos
MiniSOG2介导的海鞘胚胎运动神经元特异性光消融
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2022年10月20日第12卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4537 浏览次数: 1752
评审: Sunanda MarellaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
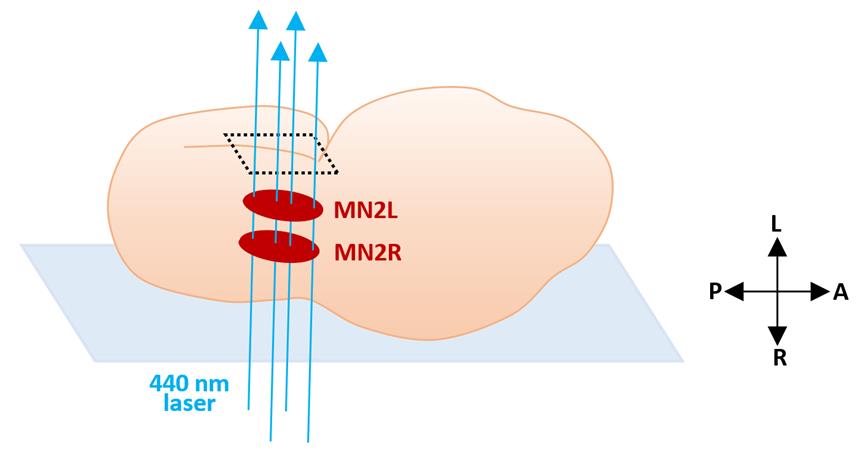
When understanding the neuronal function of a specific neural circuit, single-cell level photoablation of a targeted cell is one of the useful experimental approaches. This protocol describes a method to photoablate specific motor neurons via the mini singlet oxygen generator (miniSOG2), a light–oxygen–voltage (LOV)-based optogenetic tool used for ablating targeted cells in arbitrary areas. MiniSOG2 could induce the cell death pathway by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon blue light illumination. Photoablation of a specific cell using the miniSOG2 was performed to show that, in Ciona intestinalis type A (Ciona robusta), a single pair of motor neurons, MN2/A10.64, is necessary to drive their tail muscle contraction. The membrane targeted miniSOG2 combined with neuron-specific promoter (pSP-Neurog::miniSOG2-CAAX) was electroplated into the Ciona egg and transiently expressed at specific neurons of the embryo. MN2 labeled with pSP-Neurog:mCherry-CAAX was irradiated using a 440-nm laser from the lateral side for 10 min to ablate its neural function. The behavior of the embryo before and after the irradiation was recorded with a high-speed camera.
Graphical abstract:
Background
To understand neuronal function during development of specific neural circuits, several inhibitors of neurotransmitters or the knock-down/knock-out (KD/KO) of the neuron-specific gene have been used in previous ascidian research. However, inhibitors suppress the function of not only the targeted neuron but also the same types of other neurons, and the gene KD/KO method cannot artificially regulate the timing of inhibition. Therefore, specific ablation of the targeted neuron in the appropriate timeframe and area has been considered to be difficult. On the other hand, the mini singlet oxygen generator, or miniSOG2 (Makhijani et al., 2017), can be genetically introduced to the specific neurons and then ablate them at a given time using laser irradiation. Combined with the various tissue- and cell-specific promoters in Ciona (https://www.aniseed.cnrs.fr/aniseed/gene/?choice=find_cisreg) provides general information for ascidian-specific promoters), it was possible to ablate different neuron subtypes even at a single cell level. This method will be a strong tool for understanding not only the function of neurons but also the function of non-neuronal cells during ascidian development.
Materials and Reagents
Glass-based Petri dish (glass diameter ϕ12 mm or ϕ27 mm, IWAKI)
MiniSOG2 construct driven by your chosen promoter, e.g., pSP-Neurog::miniSOG2-CAAX. Plasmid coding miniSOG2 (pcDNA3.1_miniSOG2 T2A H2B-EGFP) (Addgene, catalog number: 87410). The DNA sequence of miniSOG2-CAAX is shown in Table 1.
Arbitrarily chosen fluorescent protein driven by the same promoter used for identifying miniSOG2 positive cells, such as pSP-Neurog::mCherry-CAAX. DNA sequence of mCherry-CAAX is shown in Table 1.
Egg and sperm dissected from Ciona matured adults
Natural sea water
Table 1. Sequences for miniSOG2-CAAX and mCherry-CAAX
Equipment
Confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM), inverted type (OLYMPUS, Olympus fv1000)
Optical power meter (HIOKI, optical power meter 3664)
Optical sensor (HIOKI, optical sensor 9742)
High-speed camera (WRAYMER, WRAYCAM-VEX230M)
Stereoscopic microscope (OLYMPUS, Olympus SZX12)
Software
Olympus fv1000 viewer (OLYMPUS)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Utsumi, M. K., Akahoshi, T., Oka, K. and Hotta, K. (2022). MiniSOG2-mediated Specific Photoablation of Motor Neurons in Ascidian Embryos. Bio-protocol 12(20): e4537. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4537.
- Akahoshi, T., Utsumi, M. K., Oonuma, K., Murakami, M., Horie, T., Kusakabe, T. G., Oka, K. and Hotta, K. (2021). A single motor neuron determines the rhythm of early motor behavior in Ciona. Sci Adv 7(50): eabl6053.
分类
神经科学 > 发育 > 电穿孔
发育生物学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











