- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Purification and Immunostaining of Mouse Ependymal Ciliary Shafts
小鼠室管膜纤毛干的纯化和免疫染色
发布: 2022年07月20日第12卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4467 浏览次数: 3160
评审: David PaulYoko BekkuNona Farbehi
Abstract
Cilia and flagella are microtubule-based hair-like organelles protruding from the surface of most eukaryotic cells, and play essential roles in cell locomotion, left-right asymmetry, embryo development, and tissue homeostasis. With isolated cilia and flagella, great progress has been made in understanding the composition, structure, and function of cilia. However, the current cilia/flagella isolation methods are deficient in the integrity or productivity of purified cilia when applied to mammalian motile cilia. Here, we describe a new protocol that isolates cilia shafts from mouse ependymal cells, by horizontal shear force and mild detergent. This method enables the production of virtually integral cilia with high yields and less cell body contamination. It is suitable for immunostaining, puromycin labeling assay, and proximity ligation assay of mammalian motile cilia.
Graphical abstract:
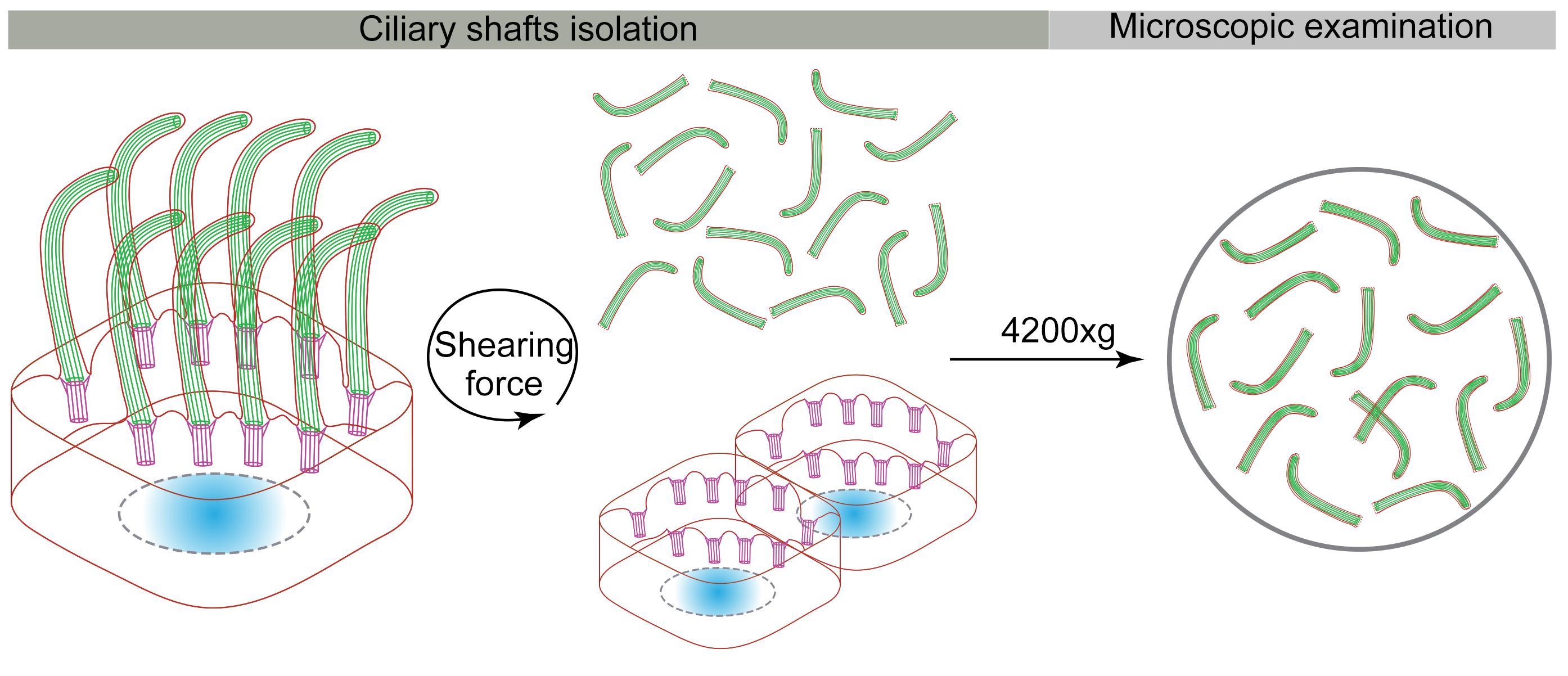
Background
Multiple cilia/flagella isolation methods, including pH-shock, calcium-shock, dibucaine treatment, and mechanical procedures (e.g., peel-off, and slide-pull), have been developed in various organisms (Witman et al., 1972, 1978, 1986; Adoutte et al., 1980; Mitchell et al., 2009). The pH- and calcium-shock methods were first created to purify cilia from Euglena and Tetrahymena, respectively (Gibbons, 1965; Rosenbaum and Child, 1967). Later, the two methods became the most used cilia/flagella purification methods in protozoa. In mammals, mechanical peel-off or slide-pull approaches have been used to isolate primary cilia from cultured cells, such as MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells, normal mouse cholangiocytes (NMCs), and normal rat cholangiocytes (NRCs) (Huang et al., 2006; Kiesel et al., 2020). The calcium-shock method combined with mechanical agitation is used to separate motile cilia from rabbit oviduct, pig trachea, and primary cultured mouse ependymal cells (mEPCs) (Anderson, 1974; Hastie et al., 1986; Zheng et al., 2019). It is also used to isolate primary cilia from rat olfactory cilia and inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD3) cells (Mayer et al., 2008; Ishikawa et al., 2012). The ciliary protein composition and high-resolution ciliary ultrastructure have been well studied using these methods in purified cilia/flagella. However, these procedures usually cause cilia membrane damage and ignore the physiological activity of isolated cilia, thus hindering further exploration of cilia biology.
Here, we report a protocol of cilia isolation, which is improved from the calcium-shock combined mechanical agitation method. To maintain the integrity of isolated cilia and reduce cytoplasmic contamination, we decreased the detergent concentration in the deciliation buffer and replaced the vortex with horizontal shear force. With this method, we obtained a sufficient yield of motile cilia for immunostaining, puromycin labeling, and proximity ligation assays. As an example of its application, we applied this procedure to purify mouse ependymal cilia to verify ciliary RNA local translation. In addition, this method can also be used to purify motile cilia from mouse brain lateral ventricle.
Materials and Reagents
0.22 μm filter (Millipore, catalog number: SLGPR33RB)
75 cm2 Flask (Corning, catalog number: 430641)
15 mL tube (Falcon, catalog number: 352095)
12 mm diameter circle coverslips (Marienfeld, catalog number: MAR0111520)
Glass slides (Premiere, catalog number: 9308W)
24-well plate (Costar, catalog number: 3524)
15 cm Petri dish (Corning, catalog number: 430599)
Filter paper (GE, catalog number: 10311611)
Parafilm (Bemis, catalog number: PM-996)
Milli-Q water
Fibronectin (1 mg/mL) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: FC010), store at 4°C
Papain (Worthington Biochemical Corporation, LS003126), store at 4°C
DMEM (ThermoFisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number:12430054), store at 4°C
Primocin (50 mg/mL) (InvivoGen, ant-pm-2), store at -20°C
Fetal bovine serum (Ausbian, VS500T), store at -20°C
Poly-L-lysine hydrobromide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P1399), store the powder at -20°C.
Note: Sterilize the stock solution (100 mg/mL Poly-L-lysine in Milli-Q water) with a 0.22 μm filter, and store it in aliquots at -20°C.
Trition X-100 (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A110694)
Tween 20 (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: A100777)
Paraformaldehyde (PFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6148), store the powder at 4°C
Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A3912), store the powder at 4°C
Mouse anti-Acetylated Tubulin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6793), store at 4°C
Rabbit anti-Cep290 (home-made) (Zhao et al., 2021), store at -20°C
Guinea pig anti-Odf2 (home-made) (Zhao et al., 2019), store at -20°C
Donkey anti-mouse IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: A-21202), long-term storage at -80°C, short-term storage at 4°C
Donkey anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with Cy3 (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 711-165-152), long-term storage at -80°C, short-term storage at 4°C
Donkey anti-guinea pig IgG conjugated with Alexa Fluor 647 (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 706-605-148), long-term storage at -80°C, short-term storage at 4°C
ProLong Diamond Antifade Mountant (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: P36970), store at 4°C
Immersion oil (Lecia microsystem, catalog number: 12847995)
PBS (see Recipes), store at 4°C
Dissection buffer (see Recipes), store at 4°C
Enzymatic digestion buffer (see Recipes), freshly prepared
mEPC culture medium (see Recipes), store at 4°C
Starvation culture medium (see Recipes), store at 4°C
Deciliation buffer (see Recipes), store at 4°C
4% PFA (see Recipes)
TBST (10×) (see Recipes)
Blocking buffer (see Recipes), stored in aliquots at -20°C
Equipment
Milli-Q (Millipore, model: Advantage A10)
Sharp tweezer (Dumont, catalog number: 0208-5/45-PO)
Tweezer (Dumont, catalog number: 0203-5/15-PO)
Horizontal shaker (Zhichu, model: ZQZY-AS9)
Superspeed centrifuge (ThermoFisher Scientific, model: Sorvall LYNX 6000, catalog number:75006590)
Swinging bucket rotor (ThermoFisher Scientific, model: BIOFlexTM HC, catalog number: 75003000)
Confocal microscopy (Leica, model: TCS SP8 WLL system equipped with a 63×/1.4 oil immersion objective)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Hao, K., Zhu, X. and Yan, X. (2022). Purification and Immunostaining of Mouse Ependymal Ciliary Shafts. Bio-protocol 12(14): e4467. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4467.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞器分离
分子生物学 > RNA > mRNA 转译
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link














