- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Evaluation of Caspase-1 Activation and IL-1β Production in A Kainic Acid Microdyalisis Brain Injury Model
在红藻氨酸损伤透析模型中评估半胱天冬酶1的活化和IL-1β的产生
发布: 2013年04月20日第3卷第8期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.433 浏览次数: 10661
Abstract
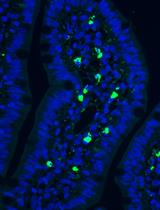
Intracerebral infusion of kainic acid (KA) by a microdialysis probe induces a focal swelling in the brain-perfused area which promotes inflammation (Compan et al., 2012; Oprica et al., 2003). The microdialysis technique allows the local in vivo perfusion of KA and the simultaneous collection of inflammatory mediators, and other neuroactive substances, released in the injured brain. This protocol also allows the perfusion of different solutions in each cerebral hemisphere at the same time. By perfusing KA in isotonic solution of Krebs-Ringer Bicarbonate (KRB) (280-290 mOsm) in one hippocampus and KA in hypertonic KRB solution (1,400-1,500 mOsm) in the contralateral side, we can evaluate in vivo the efficiency of hypertonic solutions in preventing inflammation induced by swelling after KA infusion. Once the inflammatory response has been induced, it is possible to infuse through the microdialysis probe a biotinylated specific inhibitor of caspase-1 allowing the detection of the brain regions and cells involved in IL-1 production in response to the injury (Oprica et al., 2003).
Keywords: ELISA (ELISA)Materials and Reagents
- Female Sprague-Dawley rats* of 200-220 g body weight
- Isoflurane (Baxter S. L, catalog number: 691477H )
- Local analgesic Bupivacaine 0.25% (Braun Medical S. A, catalog number: 671065 )
- Betadine (Meda Farma Sau, catalog number: 644625.6 )
- Ocular lubricant (Lab Pérez Giménez, catalog number: 973370 )
- Sorbitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6021 )
- Albumin from rat serum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A6414 )
- Kainic Acid 100 mM (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K0250 )
- Biotinylated Caspase Inhibitor 100 mM biotinyl-YVAD-CMK (AnaSpec, USA)
- Capillary Gap microscope slides (Dako REAL, catalog number: K8020 )
- Fluorescein-streptavidin conjugate (BD Pharmingen, PharmingenTM, catalog number: 554060 A-2001 )
- NeuN (Chemicon International, catalog number: MAB377 )
- Goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody Alexa Fluor-568 (Life Technologies, Molecular Probes®, catalog number: A11031 )
- Hoechst 33342 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B2261 )
- Paraformaldehyde
- KH2PO4
- MgSO4
- NaHCO3
- CaCl2
- KCl
- Isotonic Krebs Ringer Bicarbonate (see Recipes)
- Hypertonic KRB (see Recipes)
- Isotonic Krebs Ringer Bicarbonate (KRB) (see Recipes)
- Hypertonic KRB (see Recipes)
- Sacrifice anesthesia solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Small-animal sterotaxic apparatus (David Kopf, catalog number: 962 )
- Perfusion pumps (Bas, catalog number: MD-1001 )
- 1 ml syringes (Bas, catalog number: MD-000 )
- Dental drill and # 1 burrs
- Scalpel
- Anesthesia Isoflurane vaporizer (Parkland Scientific, catalog number: V3000PK )
- Rat ear bars (David Kopf, catalog number: 957 )
- Rat anesthesia mask (David Kopf, catalog number: 1929-B )
- Hypodermic needle (25 G)
- Microdialysis pumps (BAS, catalog number: MD-1001 Babe Bee)
- Microdialysis probes, Cut-off 100.000 Daltons CMA-12 14/02 PES, (CMA, USA)
- Liquid Switch Valve (Univentor, Zejtun ZTN08, catalog number: 8401405 )
- Tygon tubing R3603; 0.38 mm ID (Cole Parmer Instruments Co. USA)
Experimental set-up
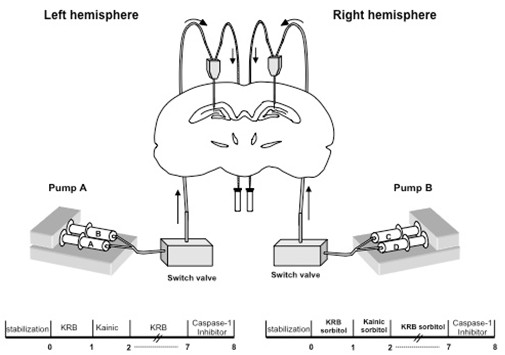
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Herranz, A. S., Bazán, E., Reimers, D., Montero-Vega, M. T., Jménez-Escrig, A. and Pelegrín, P. (2013). Evaluation of Caspase-1 Activation and IL-1β Production in A Kainic Acid Microdyalisis Brain Injury Model. Bio-protocol 3(8): e433. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.433.
分类
免疫学 > 动物模型 > 大鼠
生物化学 > 其它化合物 > 酸
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link