- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Simple Technique for Direct Immobilization of Target Enzymes from Cell Lysates Based on the SpyTag/SpyCatcher Spontaneous Reaction
基于 SpyTag/SpyCatcher 自发反应从细胞裂解物中直接固定目标酶的简单技术
发布: 2022年01月05日第12卷第1期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4282 浏览次数: 3846
评审: Alessandro DidonnaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Many of the current methods for enzyme purification and immobilization suffer from several drawbacks, such as requiring tedious multistep procedures or long preparation, and being environmentally unfriendly, due to the chemicals and conditions involved. Thus, a simple technique for direct purification and immobilization of target enzymes from cell lysates was proposed. The elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs)-SpyCatcher chimera could mediate the formation of silica carriers within seconds and the target enzymes were then covalently immobilized on silica carriers via SpyCatcher/SpyTag spontaneous reaction. These tailor-made carriers were easily prepared, with precisely controlled morphology and size, as well as none-consuming surface modification needed, which could specifically immobilize the SpyTag-fused target enzymes from the cell lysate without pre-purification.
Background
Enzymes are green biocatalysts with high activity in industrial manufacture. However, enzymes suffer from some problems which may hinder their industrial applications. Firstly, the process of enzyme purification is long and tedious, while in other cases it just includes one chromatographic step (Lin et al., 2020). Meanwhile, enzymes are soluble and thus need to be immobilized, for further reutilization. Hence, we propose a novel and simple technique that could directly purify and immobilize target enzymes from cell lysates (Figure 1). Briefly, new ELPs [K5V4F-40] were fused to the N-terminal of SpyCatcher (K5-C), and the K5-C chimera was purified by the inverse transition cycling (ITC) method. Then, the purified K5-C was self-encapsulated to form the K5-C modified silica NPs (K5-C@SiO2), via ELPs-mediated biomimetic silicification. On the other hand, the target enzyme was fused to the N-terminal of SpyTag and the SpyTag-fused enzymes could be directly purified and immobilized from cell lysate via the covalent bonds between the SpyCatcher and SpyTag. To verify the feasibility of this technique, we immobilized β-1,3-xylanase on K5-C@SiO2, with high activity recovery, good immobilization efficiency, and excellent reusability.
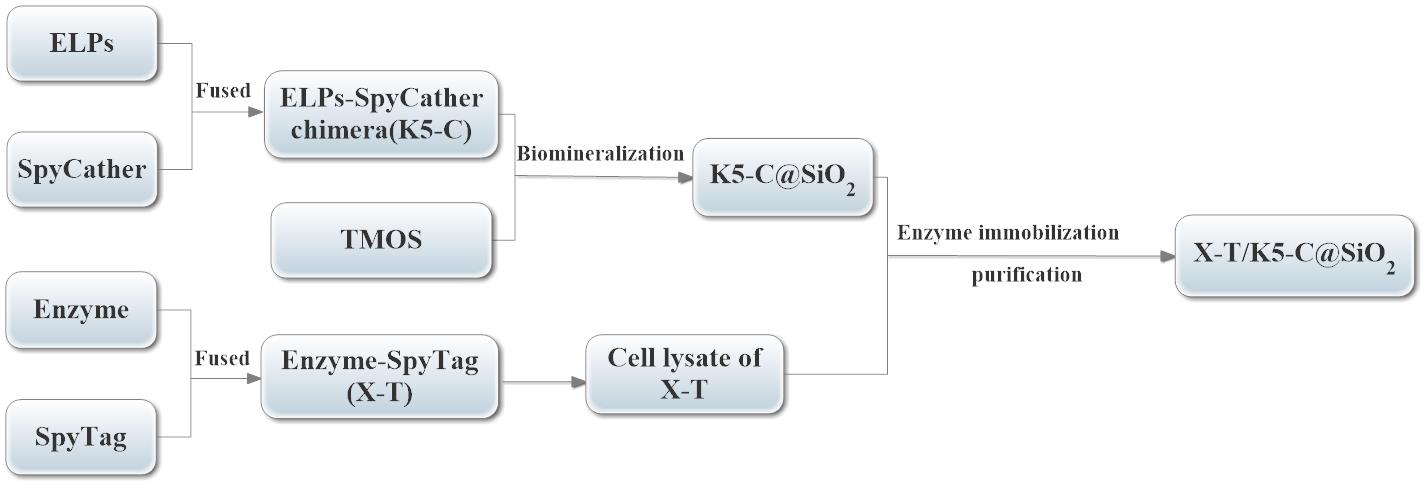
Figure 1. The flow chart of the simple technique for direct immobilization of target enzymes from cell lysates.
Materials and Reagents
1.5 mL microtubes (Axygen, catalog number: MCT150LC)
500 mL erlenmeyer flask (Shuniu, catalog number: GG17)
0.45 μm sterilized filter (Millipore, catalog number: SLHV033)
Dialysis bags (Solarbio, 8000-14000, catalog number: YA1072)
Caulerpa lentillifera (Nha trang, Vietnam,Vmax)
Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cell (Klang, catalog number: KL9050510)
Plasmid: pET-22b(+), ambenzyl resistant, provided by Suzhou Jinweizhi Biotechnology Company, and preserved by our laboratory.
Yeast extract (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0021)
Tryptone (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0042)
Ampicillin (Amresco, catalog number: LP0339)
Isopropyl-β-D-Thiogalactoside:IPTG (Solarbio, catalog number: I8070)
NaCl (Xilong scientific, catalog number: 7647145)
PageRuler prestained protein ladder (Therom, catalog number: 142546)
Tetramethoxysilane:TMOS (Macklin, catalog number: T819504)
SiO2 standard solution (Macklin, catalog number: I821744)
NaOH (Xilong Scientific, catalog number: 100154)
Sulfuric acid solution (Xilong Scientific, catalog number: 7664939)
NaClO4 (Xilong Scientific, catalog number: 7791073)
Anhydrous ethanol (Xilong Scientific, catalog number: 64175)
Acetic acid (Xilong Scientific, catalog number: 64197)
Dichloroethanol (Merck, catalog number: 107073)
BCA protein assay kit (Yanxi, catalog number: PDBCA500)
SDS-PAGE gel preparation kit (Beyotime,catalog number: P0012A)
Nickel affinity column (Smart-Lifesciences, catalog number: SA003025)
Elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs, K5V4F means the ratio of K:V:F=5:4:1)
Phosphate buffer solution (PBS, 100 mmol/L, pH 7.0) (see Recipes)
Citrate phosphate buffer (CPB, 20 mmol/L, pH 6.6) (see Recipes)
TB medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
Eppendorf mixer (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5382000074)
-80°C freezer (Therom, catalog number: 905)
Beaker (Shuniu, catalog number: 056245)
Gel imaging analysis system (Tanon, catalog number: GIS-2008)
Ultrasonic cell disruption system (Scientz, catalog number: TY92-II)
Temperature controlled ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Analyticjena, catalog number: SPECORD40)
High speed refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5418RL)
Constant temperature shaker (HerryTech, catalog number: GG-100C)
Weigh scale (Sartorius, catalog number: BSA2202S)
Pipette (Eppendorf Research plus)
Scanning electron microscopy (Hitachi, catalog number: S-4800)
Transmission electron microscopy (Hitachi, catalog number: H7650)
Grinder (Leimai, catalog number: FS-100)
Mesh (Shuyin, catalog number:JD-12)
Dryer (Jinchen, catalog number: JC-9023AE)
Flasks (Shuniu, catalog number: GG-17)
Spectrophotometer (Mapada, catalog number: GDJ355)
Software
NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
ImageJ (NIH; https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/download.html)
ProtParam (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Cai, L., Lin, Y., Chu, Y., Chen, X., Liu, L., Zhang, M. and Zhang, G. (2022). A Simple Technique for Direct Immobilization of Target Enzymes from Cell Lysates Based on the SpyTag/SpyCatcher Spontaneous Reaction. Bio-protocol 12(1): e4282. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4282.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物工程 > 生物医学工程
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













