- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Simple Method to Generate Super-sensitive AID (ssAID)-based Conditional Knockouts using CRISPR-based Gene Knockout in Various Vertebrate Cell Lines
小胶质细胞的分离及蛋白表达的流式细胞仪分析:避免小胶质细胞背景荧光的陷阱
发布: 2021年07月20日第11卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4092 浏览次数: 4136
评审: Alessandro DidonnaQin TangSabine Le Saux
Abstract
Inducing loss of function of a target protein using methods such as gene knockout is a powerful and useful strategy for analyzing protein function in cells. In recent years, the CRISPR/Cas-9-based gene knockout technology has been widely used across a variety of eukaryotes; however, this type of simple gene knockout strategy is not applicable to essential genes, which require a conditional knockout system. The auxin-inducible degron (AID) system enables rapid depletion of the target protein in an auxin-dependent manner and has been used to generate conditional mutants in various eukaryotic cell lines. One problem with the AID system is the use of high auxin concentrations for protein degradation, which can cause cytotoxicity. Recently, we established a super-sensitive AID (ssAID) system that allowed a reduction in the amount of auxin required by more than 1,000-fold. We also utilized a single-step method to generate AID-based conditional knockout cells with a ssAID system in various cell lines. In this protocol, we introduce our improved method, which provides a powerful tool for the investigation of the roles of essential genes.
Keywords: Auxin (生长素)Background
The auxin-inducible degron (AID) system enables the direct and conditional depletion of a target gene product in various eukaryotic cells (Nishimura et al., 2009; Holland et al., 2012). This system utilizes an auxin-dependent degradation system in plants. Transport inhibitor response 1 (TIR1) is a plant-specific F-box protein that forms an E3 ubiquitin ligase, namely the SCFTIR1 complex, which ubiquitinates and degrades proteins in the AUX/IAA family in an auxin-dependent manner in plant cells (Dharmasiri et al., 2005; Kepinski and Leyser, 2005). In non-plant cells, SCFTIR1 is formed via the expression of TIR1, with the target protein fused with an AID-tag, which is degraded in an auxin-dependent manner (Figure 1, AID). The AID system has been widely used to generate conditional knockout yeast and vertebrate cell lines (Holland et al., 2012; Maric et al., 2014; Nora et al., 2017; Gibcus et al., 2018).
In the conventional AID system, a natural auxin, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), is used to induce degradation (Nishimura et al., 2009; Holland et al., 2012). However, one issue with this system is the amount of IAA required for protein degradation (Yesbolatova et al., 2019), as high IAA concentrations (500 μM) can cause cytotoxicity in some mammalian cell lines. To overcome this problem, we focused on a high-affinity binding pair, the synthetic auxin 5-Ad-IAA and its high-affinity partner Oryza sativa (Os) TIR1F74A, which was identified based on previous studies in A. thaliana (Uchida et al., 2018; Yamada et al., 2018). We succeeded in establishing a super-sensitive AID (ssAID) system that incorporates a high-affinity binding pair, 5-Ad-IAA and OsTIR1F74A (Figure 1, ssAID) (Nishimura et al., 2020). This ssAID system was shown to have a 1,000-fold higher sensitivity than the conventional AID system using OsTIR1WT and IAA. Another group developed a similar system called auxin-inducible degron 2, which uses OsTIR1F74G instead of OsTIR1F74A (Yesbolatova et al., 2020). Additionally, they suggested that OsTIR1F74A and OsTIR1F74G had similar effects on AID degradation; however, we found that OsTIR1F74A is 100-fold more sensitive to 5-Ad-IAA than is OsTIR1F74G.
Moreover, we also developed a single-step method to quickly generate AID-based conditional knockouts in various vertebrate cell lines (Nishimura and Fukagawa, 2017). In this method, we use CRISPR/Cas9-based gene targeting combined with integration of an AID plasmid that contains the expression cassettes for OsTIR1 and the target protein with an AID-tag. The combination of an ssAID system and a single-step method may provide a powerful tool for elucidating the roles of various gene products in vertebrate cells. Here, we introduce a protocol to generate AID-based conditional knockouts in various vertebrate cell lines using an ssAID system.
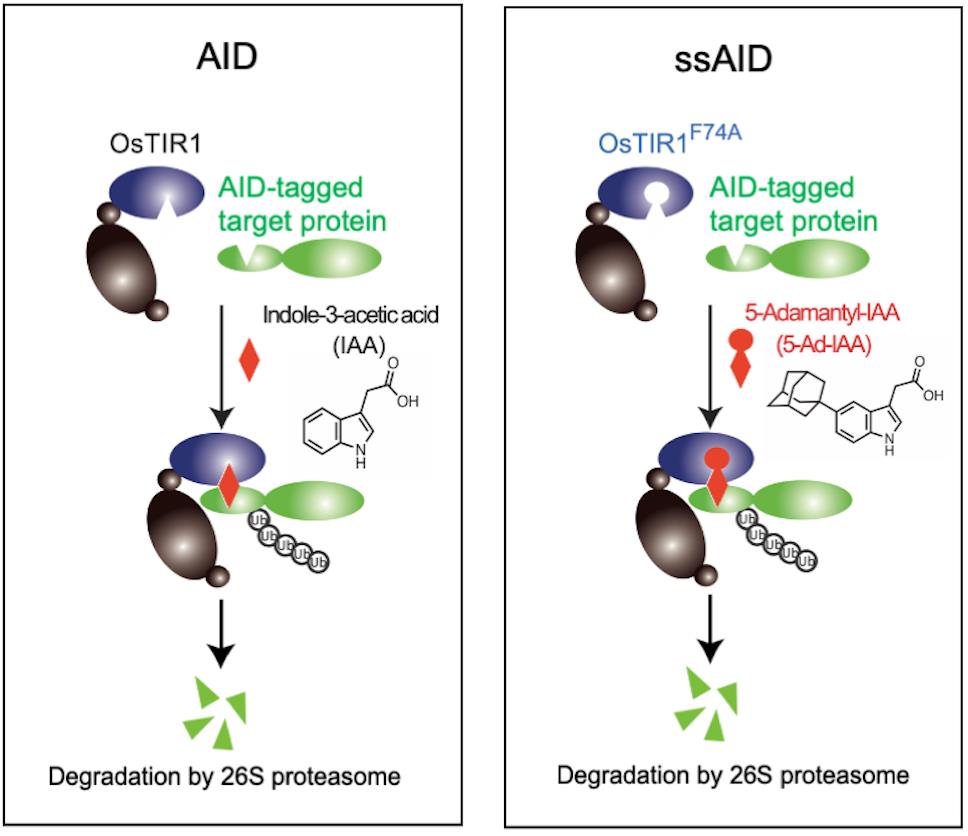
Figure 1. The concept of Auxin Inducible Degron (AID) for rapidly degrading AID-tagged target proteins in an auxin (IAA)-dependent manner. The protein of interest with an AID-tag is conditionally degraded by applying the auxin IAA. ssAID uses the IAA derivative 5-Ad-IAA and its high-affinity binding partner OsTIR1F74A.
Materials and Reagents
Laboratory disposables:
Pipettes (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog numbers: FN-4641010N, FN-4641060N, FN-4641080, FN-4641100)
15-ml tubes (e.g., Greiner, catalog number: 188261)
50-ml tubes (e.g., Greiner, catalog number: 227261)
1.5-ml tubes (e.g., Watson, catalog number: 9833)
PCR tubes (e.g., Greiner, catalog number: 673210)
96-well plates (Corning, catalog number: 3596)
24-well plates (Corning, catalog number: 3526)
6-well plates (Corning, catalog number: 3516)
10-cm culture dishes (Corning, catalog number: 430167)
E. coli (Dh5α) competent cells (Takara, catalog number: 9057)
pX330 plasmid (Addgene, catalog number: 42230)
pAID plasmids
pAIDFA-EF1a-NmScarlet-mAID (Addgene, catalog number: 140615)
pAIDFA-CMV-NmScarlet-mAID (Addgene, catalog number: 140616)
pX330 plasmids for linearization of the pAID plasmids
pAID-CMV linearizing in pX330 (Addgene, catalog number: 140609)
pAID-EF1a linearizing in pX330 (Addgene, catalog number: 140610)
EcoRV (NEB, catalog number: R0195S)
PrimeStar GXL PCR polymerase (Takara, catalog number: R050A)
Gibson Assembly Cloning kit (NEB, catalog number: E5510S)
InFusion HD Cloning Plus (Takara, catalog number: Z8909N)
1× Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE) buffer (0.04 M Tris-acetate and 0.001 M EDTA) for electrophoresis
Agarose (SeaKem LE Agarose: 50001) for electrophoresis
Ethidium bromide solution for staining DNA gels (Nacalai, catalog number: 14631-51)
Gotaq Master Mix (Promega, catalog number: M7122)
Wide range DNA ladder (Takara, catalog number: 3415A)
Wizard SV Gel and PCR Clean-Up System (Promega, catalog number: A9281) for plasmid construction
NucleoBond Xtra Maxi kit (Macherey-Nagel, catalog number: 740414.100)
Neon transfection system 100 µl kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: MPK10096)
Polyethylenimine MW 25000, transfection grade (PolySciences, catalog number: 23866-1)
DMEM (Nacalai, catalog number: 09891-25)
PBS (Nacalai, catalog number: 14249-95)
FBS (Gibco, catalog number: 10270-106)
Chicken serum (Gibco, catalog number: 16110-082)
Trypsin solution (Nacarai, catalog number: 32777-15)
Penicillin-streptomycin (Nacalai, catalog number: 09357-34)
Knockout serum replacement (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10828010)
MEM non-essential amino acids (Nacalai, catalog number: 06344-56)
L-glutamate (Nacalai, catalog number: 16948-04)
2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma, catalog number: M6250)
1× PBS (Nacalai, catalog number: 14249-95)
Gelatin (Sigma, catalog number: G1890-100G)
Blasticidin S hydrochloride (Wako, catalog number: 029-18701)
L-glutamic acid (Wako, catalog number: 072-00501)
5-adamantyl-IAA (TCI, catalog number: A3390)
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Wako, catalog number: 043-07216)
1 M NaOH solution (Wako, catalog number: 193-02175)
Filter (Merck, catalog number: S2HVU11RE)
LB medium (Nacalai, catalog number: 20068-75)
Kanamycin (Nacalai, catalog number: 19860-31)
Ampicillin (Nacalai, catalog number: 02739-74)
Culture medium for chicken DT40 cells (see Recipes)
Culture medium for mammalian cells (see Recipes)
Culture medium for mouse ES cells (see Recipes)
0.1% gelatin solution (see Recipes)
1 mg/ml polyethylenimine solution (see Recipes)
5-Ad-IAA solution (see Recipes)
20 mM glutamic acid solution (pH 4.0) (see Recipes)
Equipment
Thermal cycler (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific: MiniAmp)
Mupid 2plus (Mupid: AD110)
CO2 incubator (at 5% CO2 and 37°C for mammalian cells, 38.5°C for chicken DT40 cells) (e.g., PHCBi: MCO-170AIC)
Countess II (Thermo Fisher Scientific: C10228)
Neon transfection system (Thermo Fisher Scientific: MPK5000)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Nishimura, K. and Fukagawa, T. (2021). A Simple Method to Generate Super-sensitive AID (ssAID)-based Conditional Knockouts using CRISPR-based Gene Knockout in Various Vertebrate Cell Lines. Bio-protocol 11(14): e4092. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4092.
分类
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 靶向降解
干细胞 > 胚胎干细胞
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link