- EN - English
- CN - 中文
In vivo CD40 Silencing by siRNA Infusion in Rodents and Evaluation by Kidney Immunostaining
小鼠体内siRNA转染CD40沉默和肾免疫染色评价
发布: 2021年05月20日第11卷第10期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4032 浏览次数: 10006
评审: Fereshteh AzediAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The co-stimulatory molecule CD40 and its ligand CD40L play a key role in the regulation of immunological processes and are involved in the pathophysiology of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Inhibition of the CD40-CD40L axis is a promising therapy, and a number of strategies and techniques have been designed to hinder its functionality. Our group has broad experience in silencing CD40 using RNAi technology, and here we summarize protocols for the systemic administration of a specific anti-CD40 siRNA in different rodents models, in addition to the subsequent quantification of CD40 expression in murine kidneys by immunostaining. The use of RNAi technology with specific siRNAs to silence genes is becoming an essential method to investigate gene functions and is rapidly emerging as a therapeutic tool.
Graphic abstract:
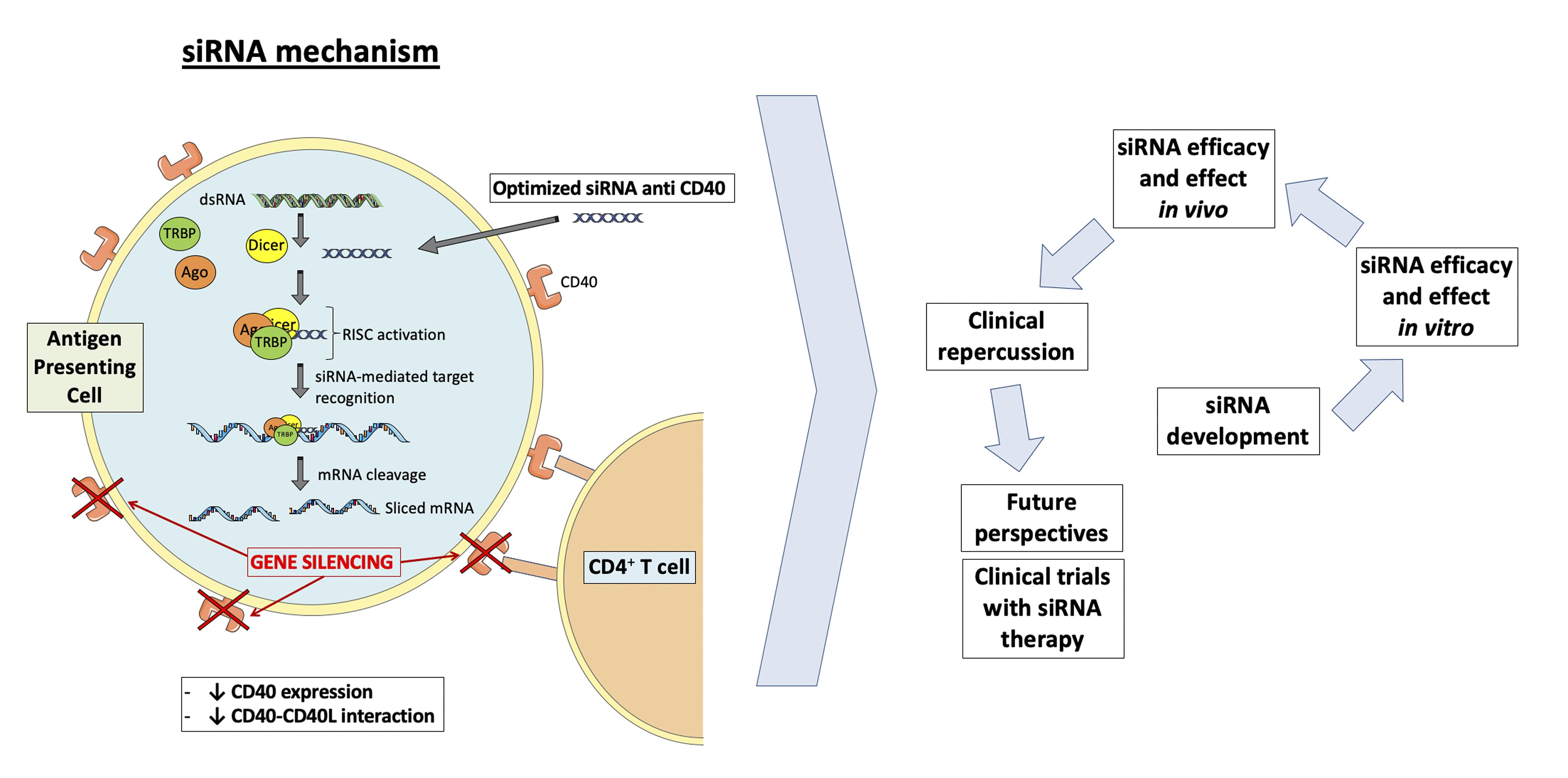
CD40 siRNA mechanism
Background
The co-stimulatory molecule CD40 and its ligand CD40L are one of the best characterized immune checkpoints involved in the pathophysiology of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including cancer, Graft-versus-Host-Disease, inflammatory bowel diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, allograft rejection, and atherosclerosis (Lutgens et al; 2010; Ripoll et al., 2013; deRamón et al., 2015; Hueso et al., 2016; Hueso et al., 2019; Karnell et al., 2019). CD40 is a 43-50 kDa transmembrane protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily and is expressed on the surface of many immune cells. The interaction of CD40 with its ligand CD40L (CD154) induces the trimerization of CD40 and stimulates downstream signaling, including the NF-κB pathway that upregulates proinflammatory genes (Elgueta et al., 2009). Thus, inhibition of the CD40-CD40L dyad is a promising therapy, and a number of strategies and techniques have been designed to hinder its functionality, such as the administration of small molecule inhibitors of the interaction of CD40 with TRAF6 (Bosmans et al., 2020), liposome-loaded anti-CD40 antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) (Arranz et al., 2013), anti-CD40 siRNAs (Pluvinet et al., 2004; deRamón et al., 2015; Hueso et al., 2016), or monoclonal antibodies (Remer et al., 2017). Currently, there are three clinical trials testing the safety and efficacy of the anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody, CFZ533, to prevent acute rejection in renal (NCT03663335) or liver (NCT03781414) transplant patients and to evaluate its effects on the kidney in patients with lupus nephritis (NCT03610516). Other clinical trials under development use an anti-CD40L antibody (NCT03605927) to prevent acute Graft-Versus-Host-Disease (NCT03605927), or an oncolytic adenoviral vector that expresses an anti-CD40 antibody (NCT03852511) to treat advanced or metastatic tumors. Our group has developed a chemically stabilized, cholesterol-conjugated small inhibitory RNA molecule against murine CD40 and reported the evaluation of its potency, distribution, and durability of effects following systemic administration (Ripoll et al., 2013; deRamón et al., 2015, Hueso et al., 2016, Hueso et al., 2019). Here, we summarize a protocol describing the systemic administration of this specific anti-CD40 siRNA in different mouse models.
Materials and Reagents
Consumables
Disposable gloves
RNAase-free 1.5 ml polypropylene tubes
96-well plates
0.5 ml polypropylene tubes
50 ml Falcon conical tubes (Corning, catalog number: 45352054)
70 μm nylon cell strainers (BD Biosciences , catalog number: 45352350)
Cell culture plates
Syringes
Towels
Sample collection tubes
23-25 G needles
2 ml RNAase-free Eppendorf tubes (Merck KGaA, catalog number: T2795)
Poly-L-lysine-coated slides (Merck KGaA, catalog number: P0425)
Whatman No. 1 filter paper
Reagents and Kits
Nuclease-free water (DEPC-treated water)
Absolute isopropanol (Merck KGaA, catalog number: I9516)
Tris base (Tris-hydroxymethyl-aminomethane; Bio-Rad Lab, catalog number: 161-0719)
3 M sodium acetate (Merck KGaA, catalog number: S7899)
Bromophenol Blue-Xylene Cyanole Dye Solution (Merck KGaA, catalog number: B3269-5mL)
N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine, TEMED (Bio-Rad, Hercules, catalog number: 161-0800)
Amonium persulfate, APS (Bio-Rad, Hercules, catalog number: 161-0700)
Methanol (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 82762)
Absolute ethanol (Obtained from general chemical providers)
Hydrogen peroxide (Obtained from general chemical providers)
D+ sucrose (AppliChem GmbH, catalog number: 200-334-9)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic (EDTA, Merck KGaA, catalog number: E6758)
RNase-ZAP (Merck KGaA, catalog number: R2020)
BHT (Butylated hydroxytoluene; Merck KGaA, catalog number: W218405)
FACS lysing solution (Becton Dickinson, catalog number: 349202)
Xylene (mixture of isomers, VWR International, catalog number: 28975.360)
DPX mounting medium (VWR International, catalog number: 360294H)
Jelly from porcine skin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G1890)
Oil-Red O (Merck KGaA, catalog number: O0625)
RPMI 1640 medium (Biological Industries)
Note: Reagents 1-20 were stored at room temperature.
Opti-MEM (Themo Fisher, catalog number: 51985034)
Fetal bovine serum (Lonza Pharma&Biotech, catalog number: 14-802F)
Albumin ELISA kit (Active Motif)
DEPC (Diethyl Pyrocarbonate; Merck KGaA, catalog number: D5758).
40% acrylamide/Bis 29:1 (Bio-Rad, Hercules, catalog number: 161-0146)
Propidium iodine (StemCell Technologies, catalog number: 75002)
TRIzol (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15596026)
DAB substrate (3,3’Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride hydrate, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5637-5G)
Flow cytometry staining buffer (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-4222)
100 mM Penicilin/Streptomycin (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 15070-063)
Note: Reagents 21-30 were stored at 4°C.
200 mM L-glutamine (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 25030-024)
High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 4368814)
PureLinkTMRNA Mini kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 12183020)
5’ RACE system for rapid amplification of cDNA ends kit (ThermoFisher Scientific)
Oligofectamine 2000 (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 12252011)
GM-CSF (R&D systems, catalog number: 215-GM)
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from E. coli Serotype O111:B4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L4391)
GeneEraser Luciferase Suppression-Test System (Stratagene/Agilent, catalog number: 240192)
Luciferase Assay System (Promega, catalog number: E1531)
Polyfect transfection reagent (Qiagen, catalog number: 301105)
Serum normal goat (Merck KGaA, catalog number: G9023) or horse 20% (Merck KGaA, catalog number: H0146)
Note: Reagents 31-41 are stored at -20°C.
Taqman gene expression assays (ABI/ThermoFisher Scientific) (Table 1)
Table 1. Commercial TaqMan probes used in this study
Name
of the gene tested
Probe code1
Gene unique identifier2
Position3
CD40
Mm00441891_m1
NM_011611
121
CD40L
Mm00441911_m1
NM_011616
348
IL1b
Mm01336189_m1
NM_008361
55
NLRP3
Mm00840904_m1
NM_145827
499
Apelin (Apln)
Mm00443562_m1
NM_013912
414
C3
Mm01232779_m1
BC029976
517
CD55
Mm00438377_m1
NM_010016
1154
FOXP3
Mm00475165_m1
NM_001199347
1307
IL6
Mm99999064_m1
NM_031168
233
IL10
Mm00439614_m1
NM_010548
232
MCP1 (Ccl2)
Mm00441242_m1
NM_011333
165
RANTES (Ccl5)
Mm01302428_m1
NM_013653
245
TLR3
Mm00628112_m1
NM_126166
280
TLR4
Mm00445273_m1
NM_021297
112
TLR9
Mm00446193_m1
NM_031178
106
AIM2
Mm01295719_m1
NM_001013779
869
18S rRNA
Hs99999901_s1
X03205
604(1) Commercial code of the Taqman probes used (ThermoFisher Scientific).
(2) Refseq/Genbank unique identifiers of the genes tested.
(3) Base position contained within the probe.
0.1 M citrate buffer, pH 6 (see Recipes), stored at room temperature
0.01 M citrate buffer (see Recipes), stored at room temperature
Oil-Red working solution (see Recipes), stored at room temperature
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.5 (see Recipes), stored at room temperature
PBS-Triton (PBST) (see Recipes), stored at room temperature
PS buffer (see Recipes), stored at room temperature
Complete culture medium (see Recipes), stored at 4°C
Secondary antibodies (for a 1:200 dilution) (see Recipes), keep at -20°C
Annealing buffer 10× (see Recipes)
DEPC-treated water (see Recipes)
1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 (see Recipes)
12% acrylamide gel (see Recipes)
Non-denaturing gel loading buffer (see Recipes)
4% PFA solution in PBS (see Recipes)
0.3% Oil-Red O stock solution (see Recipes)
Serum normal goat or horse 20% (see Recipes)
Primary antibodies
In this work we used the following specific primary antibodies:
Rabbit polyclonal anti-CD40 antibody (C-20, Santa Cruz Biotech, catalog number: sc-975)
Rabbit polyclonal anti-CD154 antibody (H215, Santa Cruz Biotech, catalog number: sc-9097)
Mouse monoclonal anti-DC-SIGN antibody (1B10, Santa Cruz Biotech, catalog number: sc-23926)
Rabbit polyclonal anti-NF-κB p65 antibody (anti-phospho-S536, Abcam, catalog number: Ab86299)
Anti-F4/80 antibody (Hycult Biotech, catalog number: HM1066)
Rabbit anti-mouse collagen-IV antibody (Chemicon international, catalog number: AB756p)
Goat polyclonal anti-human C3c antibody conjugated to FITC (Nordic-MuBio, catalog number: GAHu/C3c/FITC)
Furthermore, the following antibodies from BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA, USA) were used for flow cytometry:Anti-CD11c antibody (clone HL3)
Anti-CD11b antibody (clone M1/70)
Anti-CD40 antibody (clone HM40-3)
Anti-CD80 antibody (clone 16-10A1)
Anti-CD86 antibody (clone GL1)
Note: All primary antibodies were stored at -20°C, unless another temperature was specifically stated by the manufacturer.
Secondary antibodies and histological reagents
The following secondary antibodies were used in this work:
Alexa 488-labeled chicken anti-goat (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: AB_2535870)
Goat anti-rabbit (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: AB_2633280)
Alexa 555-labeled goat anti-mouse (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: AB_2535844)
Alexa 546-labeled goat anti-rabbit (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: AB_2633280)
Unconjugated goat anti-rat (Novus Biologicals)
Biotinylated horse anti-goat (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: BA-9500)
FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse (Merck KGaA, catalog number: F0257)
VECTASTAIN Elite ABC HRP kit (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: PK-6100)
Avidin/Biotin blocking kit (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: PK-4001-NB)
Note: All secondary antibodies were stored at 4°C, unless another temperature was specifically stated by the manufacturer.
The following histological reagents were used:Harris hematoxylin solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: HHS32-1L)
Eosin Y solution, alcoholic (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: HT110132-1L)
Periodic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0430-25G)
Schiff reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 3952016-500ML)
PAS staining kit (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 101646)
Oil Red-O reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: O0625-100G)
Tissue Tec OCT inclusion compound (Sakura FinetekEurope)
UltraCruz Tm mounting medium (Santa Cruz Biotech, catalog number: sc-24941)
DRAQ5 (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 65-0880-92)
Notes:
Used for nuclear counterstaining.
All histological reagents were stored at room temperature.
Animals
Six-month-old NZB/NZW (F1) female mice (The Jackson Lab, Charles River, Wilmington, MA, USA)
Six to eight-week-old male ICR mice (The Jackson Lab, Charles River, Wilmington, MA, USA)
Eight-week-old ApoE-/- female mice (The Jackson Lab, Charles River, Wilmington, MA, USA)
Note: Animals were housed in a room maintained at a constant temperature and given free access to water and a standard laboratory diet. To accelerate atherosclerosis, ApoE-/- mice were fed a Western diet that contained 0.2% cholesterol and provided 42% of the energy as fat (TD.88137; Harlan-Tekland, Madison, WI, USA). Animals were euthanized by inhalation of isoflurane. Protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Research of UB-Bellvitge, and experiments were performed in accordance with the European legislation on Laboratory Animal Experiments.
siRNA oligonucleotides
In this work, we used a CD40-specific ds-siRNA homologous to both the mouse and rat CD40 mRNA sequence (herein antiCD40-siRNAChol) and a scrambled sequence (s/s) ds-siRNA as the control (herein s/s-control siRNAChol). Both were modified by conjugating a cholesterol (chol) molecule to the 3’ end of the sense strand by means of a pyrrolidine linker.
The siRNA sequences were as follows:
Anti-CD40 sense strand: 5’-GUGUGUUACGUGCAGUGACUU-3’
Anti-CD40 antisense strand: 5’-GUCACUGCACGUAACACACTG-3’
(s/s), control siRNA sense strand: 5’-ACUACAAGACUCGUGACCAUU-3’
(s/s), control siRNA antisense strand: 5’-UGGUCACGAGUCUUGUAGUUU-3’
To determine the transfection efficiencies and organ distributions of the siRNAs, a cholesterol-conjugated and an unmodified anti-CD40 siRNA were labeled with Cy5.5.
Note: All oligonucleotides were obtained from Microsynth AG (Balgach, Switzerland) and stored at -20°C.
Cell lines
The highly transfectable human embryonic kidney 293FT cell line (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: R70007)
Primary dendritic cells (obtained from the bone marrow of ICR mice)
Equipment
Cell scrapers (Sarstedt AG & CO, Nümbrecht, GE, catalog number: 83.3950)
Scalpels
Forceps: Straight, serrated-tip forceps; straight or curved, serrated-tip fine forceps; and straight fine-tip forceps
Scissors: Straight, blunt scissors; straight, sharp, fine scissors; and micro-dissecting spring scissors
Automatic pipettes (1-10 μl, 20-200 μl)
Hemocytometer
Water bath
Jasco V-650 spectrophotometer (Easton, MD, USA, used to determine the melting point of siRNA duplexes)
Olympum autoanalyzer AU400 (Hamburg, Germany, used to determine urinary protein and creatinine concentrations)
TaqMan real-time PCR ABI Prism® 7700 (ThermoFisher Scientific, used for the qPCR experiments)
BD FACS Canto II cytometer (BD Biosciences, used in the flow cytometry experiments)
Zeiss SteREOLumar V12 microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, used for microscopy experiments)
Leica TCS-SL spectral confocal microscope (Leica Camera AG, used for microscopy experiments)
TD-20/20 luminometer (Turner Designs, used for luciferase assays)
T-25 ULTRA-TURRAXTM homogenizer (IKA®-Werke GmbH & Co)
NanoDrop 2000c spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific)
Tabletop centrifuge (Eppendorf Cooled Centrifuge, mode: 5424R)
Cell culture CO2 incubator (NuAire Autoflow NU 8700)
Software
Leica confocal software (Leica Camera AG, Wetzlar, Germany)
Image analysis software ProgResCapturePro 2.7.7 (JenoptiK AG, Jena, GE)
ImageJ v1.48 (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA)
ExpressionSuite software v1.0 or later (ABI, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA)
SDS software v2.4 (ABI, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA)
FACS DIVA software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Hueso, M., Mallen, A., Ripoll, E., de Ramon, L., Bolaños, N., Valera, C., Guiteras, J., Checa, J., Navarro, E., Grinyo, J. M., Cruzado, J. M., Aran, J. M. and Torras, J. (2021). In vivo CD40 Silencing by siRNA Infusion in Rodents and Evaluation by Kidney Immunostaining. Bio-protocol 11(10): e4032. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4032.
分类
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
免疫学 > 动物模型 > 小鼠
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













