- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Versatile Protocol to Quantify BCR-mediated Phosphorylation in Human and Murine B Cell Subpopulations
量化人类和小鼠B细胞亚群中BCR介导的磷酸化的通用实验方法
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2021年02月05日第11卷第3期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3902 浏览次数: 4145
评审: Alessandro DidonnaTakashi NishinaSvetlana Kurilova

相关实验方案

研究免疫调控血管功能的新实验方法:小鼠主动脉与T淋巴细胞或巨噬细胞的共培养
Taylor C. Kress [...] Eric J. Belin de Chantemèle
2025年09月05日 3522 阅读
用于比较人冷冻保存 PBMC 与全血中 JAK/STAT 信号通路的双磷酸化 CyTOF 流程
Ilyssa E. Ramos [...] James M. Cherry
2025年11月20日 2283 阅读
Abstract
Signal transduction is the process by which molecular signals are transmitted from the cell surface to its interior, resulting in functional changes inside the cell. B cell receptor (BCR) signaling is of crucial importance for B cells, as it regulates their differentiation, selection, survival, cellular activation and proliferation. Upon BCR engagement by antigen several protein kinases, lipases and linker molecules become phosphorylated. Phosphoflow cytometry (phosphoflow) is a flow cytometry-based method allowing for analysis of protein phosphorylation in single cells. Due to recent advances in methodology and antibody availability – together with the relatively easy quantification of phosphorylation – phosphoflow is increasingly and more commonly used, compared to classical western blot analysis. It can however be challenging to set-up a method that works for all targets of interest. Here, we present a step-by-step phosphoflow protocol allowing the evaluation of the phosphorylation status of signaling molecules in conjunction with extensive staining to identify various human and murine B cell subpopulations, as was previously published in the original paper by Rip et al. (2020). Next to a description of phosphoflow targets from the original paper, we provide directions on additional targets that play a pivotal role in BCR signaling. The step-by-step phosphoflow protocol is user-friendly and provides sensitive detection of phosphorylation of various BCR signaling molecules in human and murine B cell subpopulations.
Keywords: Phosphoflow cytometry (磷酸流式细胞术)Background
B cells are a crucial part of the adaptive immune system and play an important role in protection against pathogens. B cells can sense pathogens by innate receptors such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs). The most important receptor for the development and activation of B cells, however, is the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR). The genes encoding the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains that comprise the BCR are assembled during B cell development in the bone marrow through a stepwise process called V(D)J recombination (Tonegawa, 1983). The functionality and autoreactivity of the BCR are checked during three crucial checkpoints in B cell development: (i) productive heavy chain rearrangement is monitored at the pre-B stage by surface deposition of the heavy chain protein together with pre-existing surrogate light chain as the pre-BCR complex; (ii) productive light chain recombination enables surface expression of the BCR, which is checked for auto-reactivity at the immature B cell stage and (iii) upon bone marrow egress when transitional B cell progress to mature, naive B cells in peripheral lymphoid tissues. When expression of (pre-)BCR signaling molecules is altered, B cell development in the bone marrow is severely affected (Martensson et al., 2010; Pieper et al., 2013). Balanced BCR signaling is also crucial for appropriate selection, survival and activation of mature B cells and its distortion is a key factor in the development of autoimmune disease or leukemia (Nishizumi et al., 1995; Kil et al., 2012; Rip et al., 2018).
Upon BCR engagement by antigen, Src family kinases phosphorylate the intracellular tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of CD79a (Ig-α) and CD79b (Ig-β), which are the transmembrane proteins that form a complex with the BCR, as well the cytoplasmic tail of co-receptor CD19. Phosphorylation of the CD79a/b ITAM in turn activates spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK), which subsequently activates the SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 65 kDa (SLP-65) linker protein. Simultaneously, phosphorylated CD19 will activate phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), which in turn phosphorylates and converts phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2) to phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate (PIP3). Signaling molecules containing a pleckstrin-homology domain, such as Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) and phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2), are recruited to the cell membrane by the newly formed PIP3 (Saito et al., 2001). After BTK recruitment to the cell membrane, SLP-65 mediates SYK-dependent activation of BTK, which in turn will phosphorylate PLCγ2 (Wang et al., 2000). The activation of this signaling complex eventually results in activation of protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) signaling (Craxton et al., 1999), NF-κB translocation to the cell nucleus (Bajpai et al., 2000), calcium mobilization (Fluckiger et al., 1998) and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (Jiang et al., 1998). The complex containing BTK, SLP-65, PLCγ2 together with other PI3K-derived signals is essential for B cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. BCR signal transduction is regulated by the equilibrium of kinase activity and negative regulation of signaling through recruitment of tyrosine phosphatases including SHP-1 (Franks and Cambier, 2018).
Western blotting used to be the method of choice for detection and quantification of phosphorylation of the BCR signaling molecules described above. The main drawbacks of Western blotting are the large number of purified cells that are required to perform the analysis and that quantification is not sensitive enough to detect subtle differences between samples. Phosphoflow is a flow-cytometry based technique that allows for quantification of multiple subpopulations within a single sample without prior purification and requires relatively few cells. In addition, phosphoflow cytometry is less time-consuming compared to Western blotting. Although for the quantification of protein phosphorylation phosphoflow appeared to be superior to Western blotting, the fixation and permeabilization procedure of phosphoflow often affected cellar epitopes or features of the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that were required to identify the immune cell population of interest. Due to recent advances in phosphoflow procedures, it is now possible to combine the analysis of phosphorylation of signaling proteins with a comprehensive staining for B cell subpopulations. In addition, more and more mAbs become available for phosphoflow analysis.
Here, we present our step-by-step phosphoflow protocol that is complementary to our original research paper (Rip et al., 2020). The phosphoflow protocol allows for sensitive detection of phosphorylation of numerous BCR signaling molecules in human and murine B cell subpopulations. Next to a description of phosphoflow targets as published in the original paper (Rip et al., 2020), we also present additional BCR signaling targets that can be sensitively quantified using this phosphoflow protocol.
Materials and Reagents
Acquisition of human PBMCs from whole blood
Leucosep Tube, 50 ml (Greiner Bio-One, catalog number: 227290 )
2 ml Cryovial (Starstedt, catalog number: 72.694.006 )
Total peripheral blood (~25 ml) from a healthy donor or patient. In general, 1 ml of blood contains 1 × 106 PBMCs.
Ficoll-PaqueTM Plus (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-1440-03 )
Fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, catalog number: 10270-106 )
CRITICAL: Heat-inactivate for 1 h at 56 °C prior to use.
20% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2650-100ML)
CAUTION: DMSO is a toxic product and should be handled with care and discarded.
RPMI 1640 Medium containing L-glutamine (Lonza, catalog number: BE12-702F ) supplemented with 5% (vol/vol) fetal bovine serum (Gibco, catalog number: 10270-106 ) (see Recipes)
Freezing medium containing 80% FBS (Gibco, catalog number: 10270-106 ) (see Recipes)
Collection of Murine organs
10 ml syringes (Braun, catalog number: 4616103V ) and 25-gauge × ⅝ inch needle (Braun, catalog number: 4657853 )
C57BL/6J mice (Charles River) that are 8-12 weeks of age, either males and females
Note: All animal experiments should comply with national laws and institutional regulations.
PBS (Gibco, catalog number: 14190169 )
100 µm nylon strainers (Corning, catalog number: 352360 )
2 ml syringes (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 307727 )
Nunc Cell Culture/Petri dishes (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 1533066 )
RPMI 1640 Medium, GlutamaxTM Supplement (Gibco, catalog number: 61870036 ) containing 2% (vol/vol) FBS (Capricorn, catalog number: FBS-12A ) (see Recipes)
CRITICAL: Heat-inactivate for 1 h at 56°C prior to use.
In vitro Stimulation of Single-Cell Suspension/Direct fixation for ex vivo (basal) measurements
96-wells plate (U-shaped, 310 µl/w, Greiner Bio-One, catalog number: 650201 )
eBioscience FoxP3/Transcription Factor staining kit (Invitrogen, catalog number: 00-5523-00 ) containing:
Fixation and permeabilization concentrate
CAUTION: This product contains paraformaldehyde (PFA), a toxic and mutagenic product. It should be handled with care and discarded as hazardous waste.
Diluent
10× Wash Buffer (dilute 10 times in deionized water)
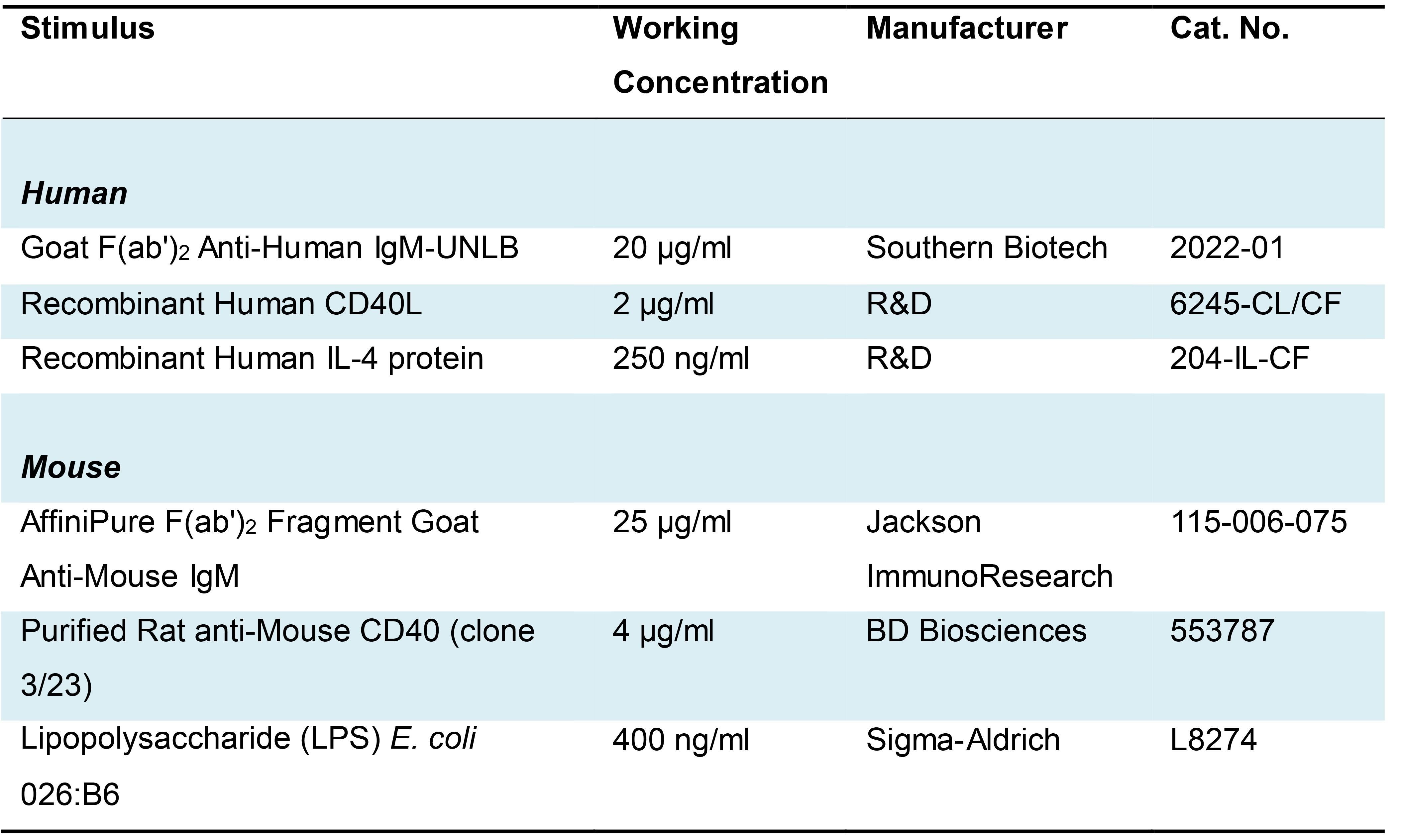
Stimuli for BCR signaling and co-receptor engagement, see Table 1.
CAUTION: Sodium azide is highly toxic and dangerous to the environment. It should be handled with care and discarded as hazardous waste.
Table 1. BCR and co-receptor ligands for stimulation of human and murine B cells
Flow Cytometry Procedures
Insert tubes (Greiner Bio-One, catalog number: 102280 ) and 5 ml round bottom polystyrene tubes (Corning, catalog number: 352052 )
UltraComp eBeadsTM Compensation Beads (Invitrogen, catalog number: 01-2222-42 )
10× Wash Buffer (dilute 10 times in deionized water) from the eBioscience FoxP3/Transcription Factor staining kit (Invitrogen)
FcR Blocking agent (Human TruStain FcX, Biolegend, catalog number: 422302 )
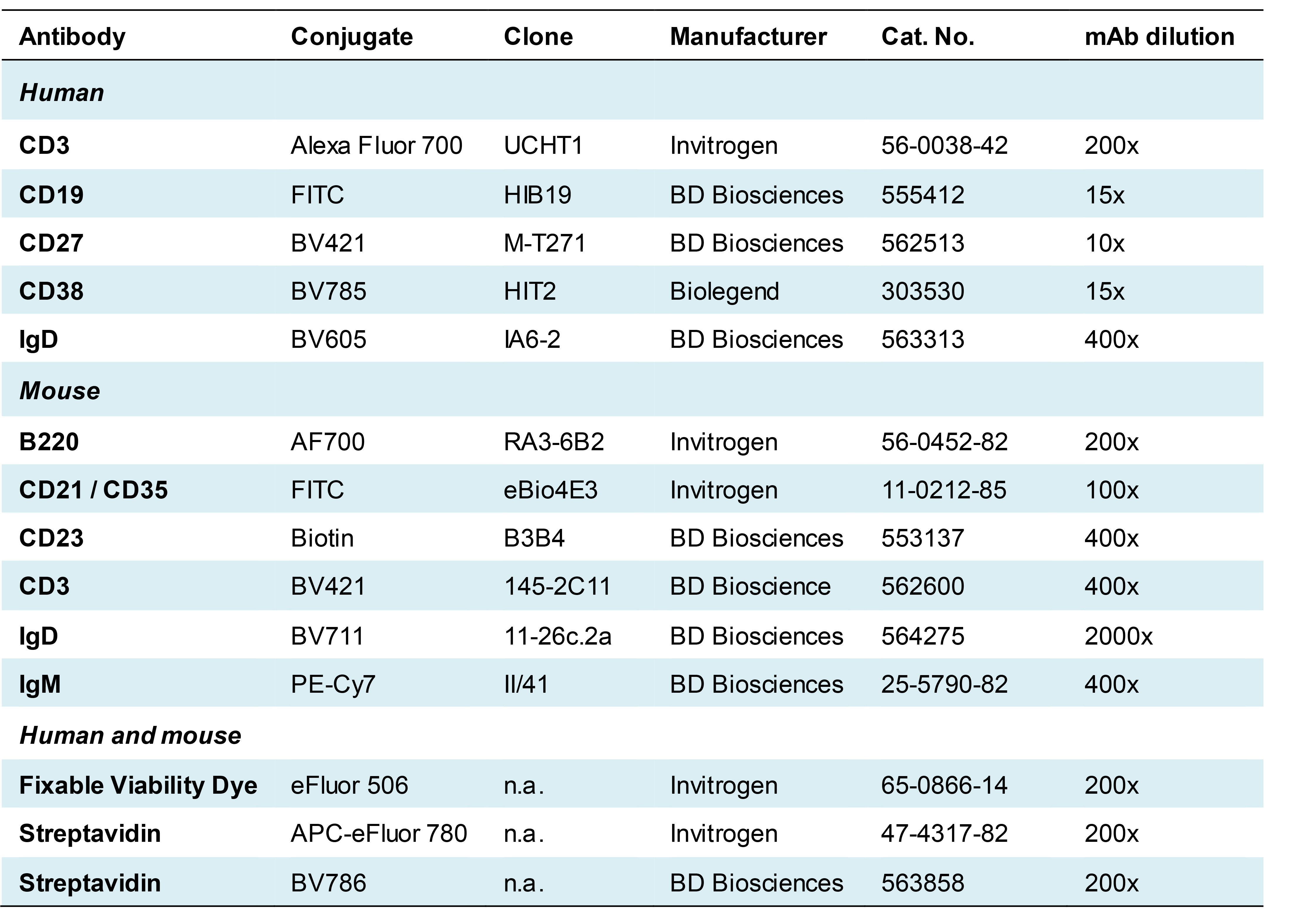
Antibodies for flow cytometry are listed in Table 2 (phospho-protein-specific antibodies) and Table 3 (antibodies used for an accurate identification of B cell subpopulations). For mouse studies, another 2.4G2 antibody was used from own production.
CAUTION: Sodium azide is highly toxic (see above).
MACS-buffer containing 0.5% (vol/vol) bovine serum albumin (BSA, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A8327 ) and 2 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid solution (EDTA, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 0 3690 ) in PBS (see Recipes)
Table 2. Phospho-specific antibodies for the analysis of human and mouse B cells and directions on stimulation timing and antibody dilution
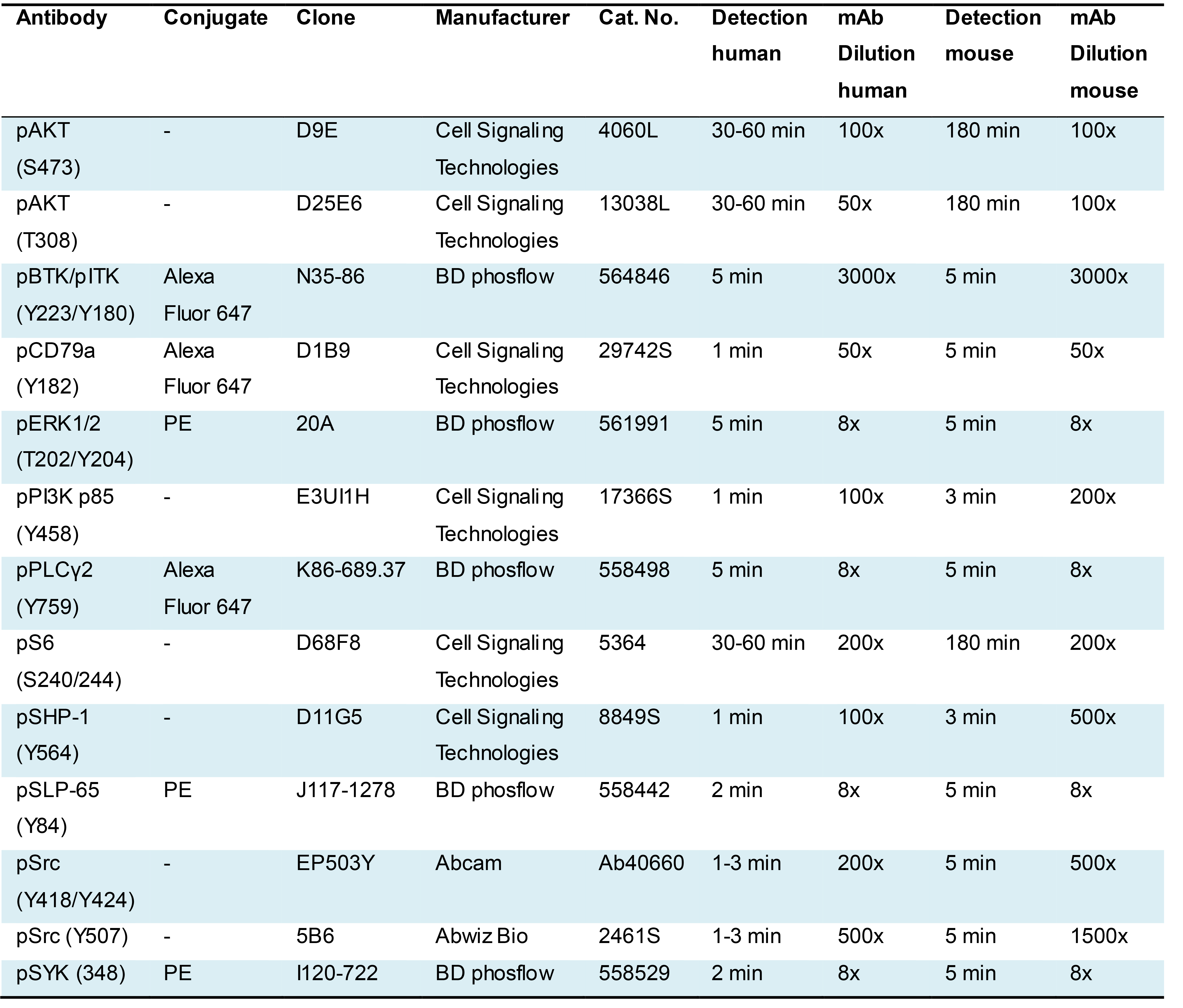
Table 3. Antibodies used for accurate gating of B cell subsets
Equipment
Standard laboratory materials or equipment, such as pipettes, tubes, and tips
Tools suitable for sacrificing mice and harvesting organs, including: scissors, tweezers and 70% ethanol
Mortar and pestle
Stopwatch or timer
Water bath incubator and/or CO2 incubator
Multifuge x 3R Refrigerated Centrifuge (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 75004515 ) with TX-1000 swinging bucket rotor (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 75003017 ).
LSR II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, catalog number: BD LSR-II ) equipped with a red, blue and violet laser
Flow cabinet
4 °C fridge
-80 °C freezer
Software
Data acquisition by FACSDivaTM Software (BD Biosciences)
FlowJo software (BD Biosciences) to analyze data
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Rip, J., Hendriks, R. W. and Corneth, O. B. (2021). A Versatile Protocol to Quantify BCR-mediated Phosphorylation in Human and Murine B Cell Subpopulations. Bio-protocol 11(3): e3902. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3902.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫细胞功能 > 淋巴细胞
免疫学 > 免疫细胞染色
细胞生物学 > 细胞信号传导 > 胞内信号传导
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link