- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Analysis of Isotopically-labeled Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol Molecular Species from [14C]Acetate-Labeled Tobacco Leaves
[14C]醋酸标记烟叶中同位素标记的单半乳糖基二酰甘油分子组成分析
发布: 2020年12月20日第10卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3864 浏览次数: 3071
评审: Agnieszka ZienkiewiczKumiko OkazakiVenkatasalam Shanmugabalaji
Abstract
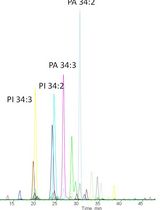
Plant lipid metabolism is a dynamic network where synthesis of essential membrane lipids overlaps with synthesis of valuable storage lipids (e.g., vegetable oils). Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) is a key component of the chloroplast membrane system required for photosynthesis and is produced by multiple pathways within the lipid metabolic network. The bioengineering of plants to enhance oil production can alter lipid metabolism in unexpected ways which may not be apparent by static quantification of lipids, but changes to lipid metabolic flux can be traced with isotopic labeling commonly with [14C]acetate. Because lipid classes such as MGDG are composed of many different molecular species, full analysis of metabolically labeled lipids requires separation and quantification of the individually labeled molecular species which is traditionally performed by thin layer chromatography. Here we present a reverse phase HPLC method for the separation of MGDG molecular species from tobacco leaves in under 35 min. The quantification of each 14C-labeled molecular species was accomplished by an in-line flow radio detector. This method of analysis for [14C]Acetate labeled MGDG molecular species by radio-HPLC provides a rapid, high throughput, and reliable analytical approach to identify changes in MGDG metabolism due to bioengineering or other perturbations of metabolism.
Keywords: Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (单半乳糖酰二酰甘油)Background
Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) is a class of glycerolipid comprising of two fatty acid chains and a galactose moiety attached to the sn-1, -2, -3 positions of the glycerol backbone, respectively. MGDG is found as a major component in photosynthetic membranes of all plants. The complexity of MGDG lies in the chemical composition of acyl chains. Depending on the fatty acid carbon chain length and degree of unsaturation, each MGDG molecule could be further categorized into different molecular species, with different metabolic pathways leading to distinct molecular species compositions. In the research findings reported in the original research paper (Zhou et al., 2020), [14C]acetate metabolic labeling of wild-type and bioengineered oil producing leaves of tobacco was utilized to understand how oil accumulation in leaves affected fatty acid flux into essential membrane lipids. Quantification of specific 14C-labeled MGDG molecular species was utilized to estimate acyl flux through different branches of the lipid metabolic network. In this report we discuss a HPLC protocol for MGDG molecular species separation adapted from Yamauchi et al. (1982) and optimized for radio-HPLC quantification of 14C-MGDG molecular species with in-line flow liquid scintillation counting as reported in Zhou et al. (2020).
Materials and Reagents
HPLC Grade Methanol (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: A452-4 )
Water, CHROMASOLVTM, for HPLC (Honeywell Riedel-de HaenTM, Fisher Chemical, catalog number: 60-048-247 )
FlowLogic U Scintillation Cocktail (LabLogic, catalog number: SG-BXX-05 )
Equipment
HPLC Equipment: Agilent 1260 Infinity II High Performance Liquid Chromatography System
Flow Radio Detector: LabLogic β-Ram 6
Thermo Scientific Accucore C18 Column; 3 x 150 mm, 2.5 μm spherical solid core particles. (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 17126-153030 )
Accucore C18 Guard Column; 3 x 10 mm, 2.6 μm spherical solid core particles (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 17126-013005 )
Software
LabLogic Laura version 6.0.1.40
GraphPad Prism version 8.1.2 (332)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2020 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Kotapati, H. K. and Bates, P. (2020). Analysis of Isotopically-labeled Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol Molecular Species from [14C]Acetate-Labeled Tobacco Leaves. Bio-protocol 10(24): e3864. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3864.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 代谢物
生物化学 > 其它化合物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link