- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Spectrophotometric Assessment of Heme Oxygenase-1 Activity in Leishmania-infected Macrophages
利什曼原虫感染巨噬细胞中血红素加氧酶-1活性的分光光度法测定
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2020年04月05日第10卷第7期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3578 浏览次数: 5519
评审: Alexandros AlexandratosVasudevan AchuthanLuis Alberto Sánchez Vargas
Abstract
Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is a stress responsive enzyme that metabolizes heme and releases free iron, carbon monoxide (CO), and biliverdin (BV), which rapidly undergoes conversion to bilirubin (BL). Estimation of bilirubin is the basis of HO-1 assay. HO-1 activity is widely employed to determine antioxidant response of cells under different physiological stress environment. Intra-macrophage infection often acts as such a stress inducer and measurement of HO-1 activity in infected cells indicates the ability of pathogens towards modulating oxidative response of host. The present protocol describes analysis of HO-1 activity in infected macrophages by spectrophotometric method, which is much less complex and therefore advantageous over other methods like high-performance liquid chromatography, radiochemical methods and detection of CO by gas chromatography. The main steps include: (1) Preparation of macrophage microsomal fraction containing HO-1 (2) Isolation of rat liver cytosolic fraction containing biliverdin reductase and (3) Assessment of heme oxygenase-1 activity by spectrophotometric detection of bilirubin. This method provides a simple and sensitive approach to measure cellular antioxidant response under infected condition.
Background
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is one of the major host defense arsenals against invading pathogens used by macrophages (Missall et al., 2004). On the other hand, intra-macrophage pathogens neutralize early oxidative burst for their successful persistence within macrophages (Paiva and Bozza, 2014). In response to such oxidative stress, organisms can deploy antioxidant enzymes of host cells such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) to scavenge ROS (Kathirvel et al., 2010). Intracellular parasite Leishmania donovani could effectively exploit host antioxidant enzyme HO-1 for ROS neutralization (Saha et al., 2019). HO-1 is a potent anti-oxidant enzyme catalysing the oxidative cleavage of heme to generate carbon monoxide (CO), ferrous iron (Fe2+), and biliverdin (BV). The biliverdin is further acted upon by another enzyme biliverdin reductase (BVR) to produce bilirubin (BL) (Tenhunen et al., 1969).There are several techniques to quantify the activity of HO-1 based on detection of one of its ultimate reaction product bilirubin via high-performance liquid chromatography (Lincoln et al., 1988; Ryter et al., 1999), visible spectrophotometry (Schacter, 1978; Tenhunen et al., 1969) and radiochemical methods (Sierra and Nutter, 1992). Detection of CO by gas chromatography (Vreman and Stevenson, 1988) has also been used to assay HO-1 activity, but because of its complexity and subsequent product analysis steps the protocol is not variedly applicable. Now, biliverdin is the primary metabolite of the heme degradation by HO-1. However, it has poor spectral properties with an extinction coefficient (ε) of ~8 to 10 mM-1 cm-1 (Kutty and Maines, 1981). Thus, most common HO-1 activity assays rely on the reduction of biliverdin to bilirubin. Original spectrophotometric quantification of bilirubin for detection of HO-1 activity was outlined by Tenhunen et al. (1969). In the method, bilirubin formation was monitored spectrophotometrically by the increase in absorbance at 468 nm (ε468 = 43.5 mM-1 cm-1), which is approximately 5-fold higher than that of biliverdin. Modifications of this main spectrophotometric assay for assessment of HO-1 activity was carried out and HO-1 activity was determined by monitoring bilirubin formation using the difference in absorbance at 464 to 530 nm (ε464-530 = 40 mM-1 cm-1) (Maines, 1996; Maines and Kappas, 1974).The current protocol (Figure 1) utilises the same principle but are performed with certain minor modifications to make it much more convenient.
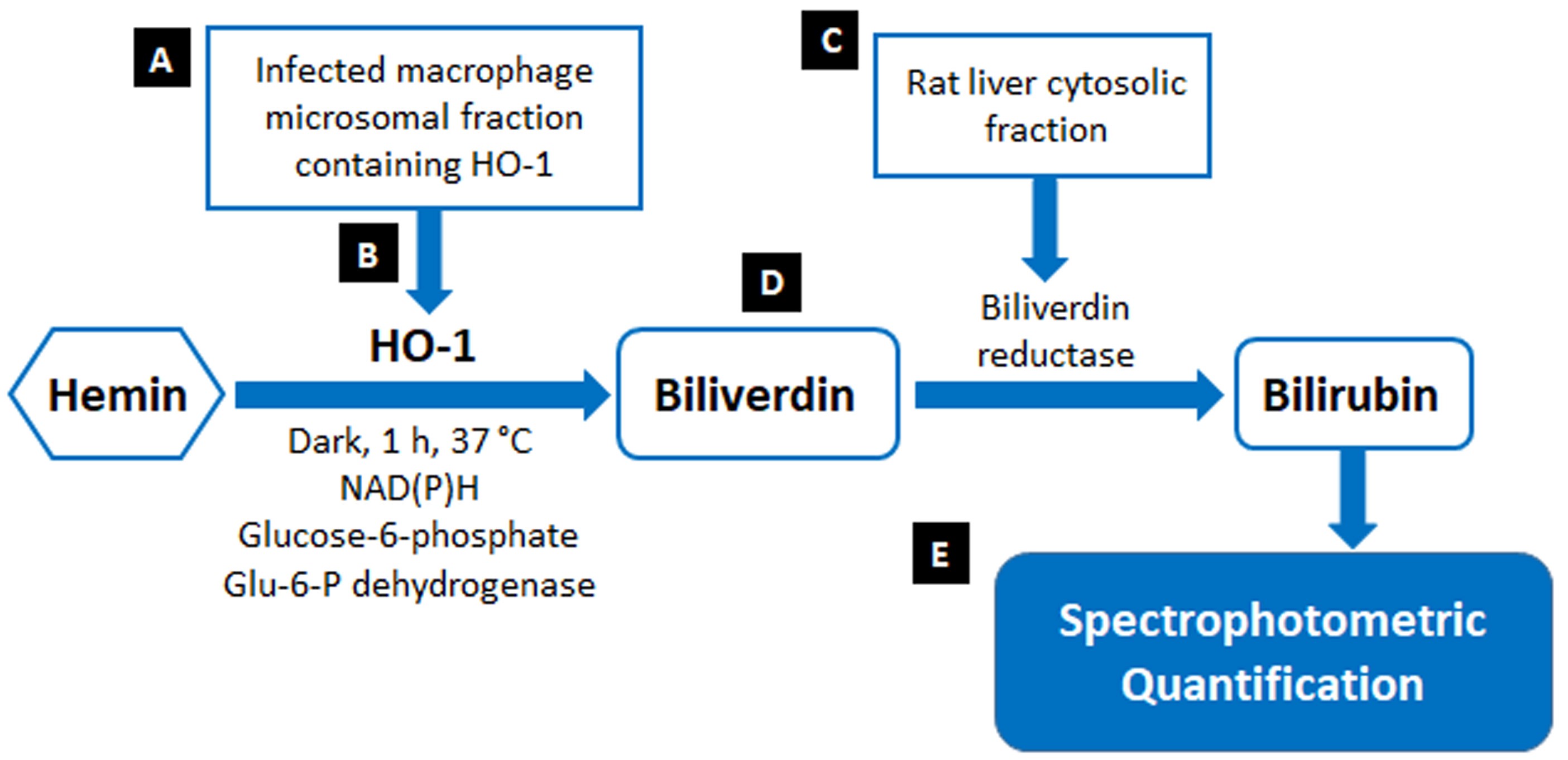
Figure 1. Schematic representation of HO-1 activity assay
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (Tarsons, catalog numbers: 521020 , 521010 , 521000 )
- Tissue culture flasks, 50 ml (Falcon, catalog number: 353108 )
- Cell scraper (Falcon, catalog number: 353086 )
- Polypropelene conical tube, 50 ml (Falcon, catalog number: 352070 )
- Microcentrifuge tubes, 1.5ml (Falcon, catalog number: 500010 )
- 0.2 µm syringe-driven filter unit (Millipore, catalog number: SLGP0033RS)
- Quartz cuvette [10 mm, 1 ml volume] (Optiglass, catalog number: MCQ-254)
- Tissue papers
- 26-gauge needle
- 10 ml syringe
- Petri dish
- RAW 264.7 cell (ATCC, catalog number: TIB-71 )
- Murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) (isolated from BALB/c mice) (for details, see Recipes)
- Leishmania donovani (MHOM/IN/1983/AG83)
- DMEM medium (Gibco, catalog number: 11885-084 )
- M199 medium (Gibco, catalog number: 12340-030)
- FCS (Gibco, catalog number: 10082-147 )
- Antibiotic solution, 100x (Himedia, catalog number: A001A)
- Protein assay dye reagent concentrate (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 5000006 )
- 1 mM NAD(P)H (Santa Cruz, catalog number: sc-202725)
- 2 mM glucose-6-phosphate (Santa Cruz, catalog number: sc-210728)
- 1 U glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G-6378)
- 25 µM hemin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 51280 )
- Biliverdin hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 30891)
- NaCl (M.W.= 58.44 g/mol)
- Na2HPO4 (M.W.= 141.96 g/mol)
- KCl (M.W.= 74.55 g/mol)
- KH2PO4 (M.W.= 136.08 g/mol)
- K2HPO4 (M.W.= 174.18 g/mol)
- MgCl2 (M.W.= 95.211 g/mol)
- Sucrose (M.W. = 342.29 g/mol)
- Sodium citrate (M.W. = 258.06 g/mol)
- Glycerol
- 70% ethanol
- Phosphate buffer saline/buffer (pH 7.4) (for details, see Recipes)
- 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) containing 2 mM MgCl2 and complete protease inhibitor (see Recipes)
- 0.6 M sucrose solution (see Recipes)
- 0.1 M sodium citrate buffer (pH 5) containing 10% glycerol (see Recipes)
- 2 mg of rat liver cytosolic protein (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 250 ml bottle
- -80 °C freezer
- Sterile scissors and forceps
- Variable volume pipettes (Tarsons, catalog numbers: 0 30050 , 030040, 030020, 030000)
- Incubator (Thermo Scientific)
- Autoclave
- Centrifuge (Thermo Scientific)
- Ultracentrifuge (Thermo Scientific, model: WXUltra90 )
- Laminar air flow (NEO Equipments, model: LX80)
- Vortex (Tarsons, catalog number: 3020 )
- pH meter (Sartorius, model: PB-11)
- Magnetic stirrer (Tarsons, catalog number: 6030 )
- Spectrophotometer (Jasco, catalog number: V-630 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2020 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Basu, M., Saha, S. and Ukil, A. (2020). Spectrophotometric Assessment of Heme Oxygenase-1 Activity in Leishmania-infected Macrophages. Bio-protocol 10(7): e3578. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3578.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
细胞生物学 > 细胞新陈代谢 > 其它化合物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link