- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Adoptive Transfer of Basophils Enriched from Mouse Spleen
小鼠脾脏富集的嗜碱性粒细胞的过继转移
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2019年11月05日第9卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3416 浏览次数: 4430
评审: Meenal SinhaLaura CampisiKrisztina Vukman
Abstract
CD49b is a member of the integrin family, expressed on basophils, natural killer (NK) cells and a subset CD4+ T cells in the spleen. This protocol describes the adoptive transfer of basophil-enriched CD49b+ cells obtained from mouse spleens by magnetic enrichment. This protocol can be used to assess the contribution of basophils or basophil-derived mediators to a certain immune response.
Keywords: Adoptive transfer (过继转移)Background
Basophils are evolutionarily conserved in vertebrates, despite their small numbers and short lifespan, suggesting that basophils have beneficial roles in maintaining health. However, these roles are not fully defined. The use of Cre-loxP approaches has allowed the generation of conditional mice with basophil deficiency, or deficiencies in basophil-derived mediators, which have significantly contributed to our understanding of basophil function in health and disease. For example, we recently demonstrated that mice with basophils lacking tumor necrosis factor (TNF) exhibited high morbidity and reduced ability to clear bacteria in the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) mouse model of sepsis, highlighting a role for basophils in innate immunity against bacteria (Piliponsky et al., 2019). Moreover, we showed that basophils are recruited into the infection site, the peritoneal cavity, as early as 1 h after CLP. To rule out potential non-specific effects of the Cre-loxP approach, the ultimate proof for our findings was provided by rescuing mice with a deficiency in basophil-derived TNF. To do this, we adoptively transferred the basophil-enriched CD49b+ fraction obtained from the spleens of wild type mice into the peritoneal cavities of septic mice (Figure 1). Please note that this protocol does not compare the method used to other available methodologies, as it was specifically designed to assess the basophil-derived-TNF dependency for the enhancement of innate immune responses after CLP. More extensive studies than the ones described in this protocol are required to determine how long basophils live and how they distribute in the adoptive host. 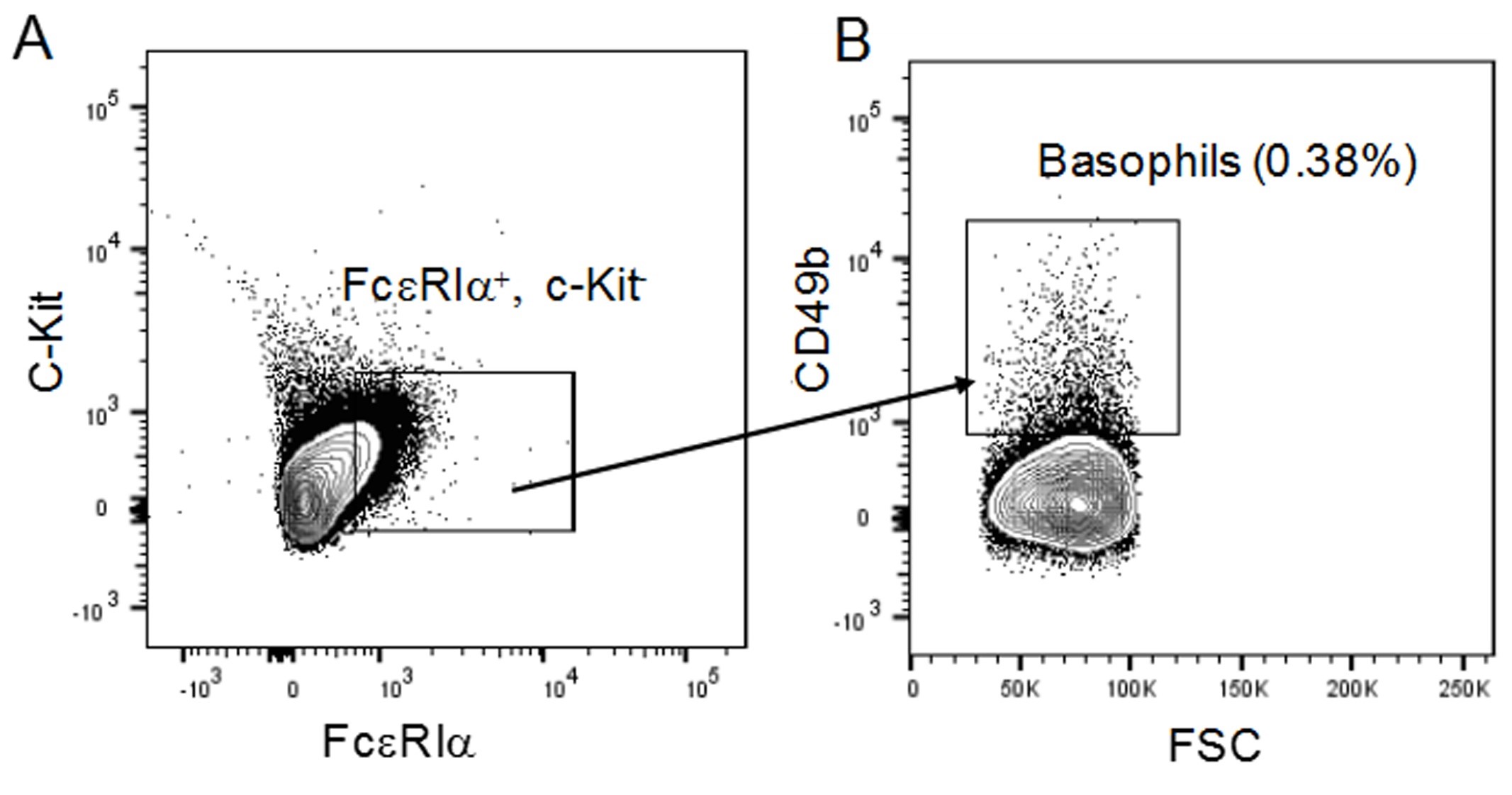
Figure 1. Strategy to identify basophils among total peritoneal cells in mice that received an adoptive transfer of basophils after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Representative flow cytometry plots and frequencies used to identify basophils amongst peritoneal cells obtained from mice that received an adoptive transfer with the CD49b+ basophil-enriched fraction of splenocytes (4 x 105 cells) at 3 h after induction of CLP of moderate severity (50% ligation, one puncture with a 22G needle). A and B. FcεRiα+, c-Kit- (A) and CD49b+ (B) cells were gated and defined as basophils amongst peritoneal cells obtained from mice at 24 h after CLP.
Here, we describe such a protocol that can be used in other mouse models to confirm a dependency on basophils, or basophil-derived mediators, for the development of a biological response.
Materials and Reagents
- Sterile culture hood (Sterilgard)
- Surgical scissors and forceps
- Pipettes 20, 200, and 1000 μl (Eppendorf)
- Six well tissue culture plate (Olympus, catalog number: 25-105)
- Frosted glass slides (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-550-143)
- 5 ml round-bottom tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 352008)
- 15 ml tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 352096)
- 50 ml conical tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 352070)
- 22 G needle (BD, catalog number: 305155)
- 1 ml syringe (BD, catalog number: 309659)
- Cell strainer, 40 mm nylon (Falcon, catalog number: 352340)
- Steritop, 0.22 mm PES, 250 ml (Millipore, catalog number: S2GPT02RE)
- CD49b (clone DX5) Microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-052-501)
- Purified rat anti-mouse CD16/CD32 (FcBlock) (clone 2.4G2) (BD Pharmingen, catalog number: 553141)
- APC-conjugated anti-CD49b antibody (clone DX5) (Biolegend, catalog number: 108909)
- PE-conjugated anti- FcεRIα (clone MAR-1) (Biolegend, catalog number: 134307)
- APC/Cy7-conjugated anti-c-Kit (clone 2B8) (Biolegend, catalog number: 105825)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Corning, catalog number: 21-040-CV)
- NH4Cl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A-4514)
- KHCO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 237205)
- EDTA (Corning, catalog number: 46-034-Cl)
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7409)
- DAPI (4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dilactate) (Biolegend, catalog number: 422801)
- UltraComp eBeads (Invitrogen, catalog number: 01-2222-42)
- Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (Gibco, catalog number: 11960-044)
- Ethanol (Koptec, catalog number: V1001)
- 70% ethanol (see Recipes)
- ACK lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- MACS buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge Avanti J-15R (Beckman Coulter)
- BD LSR II (BD Biosciences)
- autoMACS Pro Separator-Starter Kit (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-092-545)
- Biosafety cabinet
Software
- BD FACSDiva software
- FlowJo software (version 8.8.7, Tree Star)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Piliponsky, A. M. and Galli, S. J. (2019). Adoptive Transfer of Basophils Enriched from Mouse Spleen. Bio-protocol 9(21): e3416. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3416.
分类
免疫学 > 动物模型 > 小鼠
免疫学 > 宿主防御 > 鼠
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离 > 免疫磁珠
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link