- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Analysis of Functional Virus-generated PAMP RNAs Using IFNα/β ELISA Assay
利用干扰素α/β酶联免疫吸附试验检测分析病毒产生的功能性PAMP RNAs
发布: 2019年06月20日第9卷第12期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3282 浏览次数: 5532
评审: Vamseedhar RayaproluOmar AkilAmar Parvate

相关实验方案

诱导型HIV-1库削减检测(HIVRRA):用于评估外周血单个核细胞中HIV-1潜伏库清除策略毒性与效力的快速敏感方法
Jade Jansen [...] Neeltje A. Kootstra
2025年07月20日 2460 阅读
Abstract
Virus-generated PAMP RNAs are key factors that activate host immune response. The PAMP RNAs are therefore usually closely related with viral disease pathogenesis. Quantitative real time PCR is a conventional method to assess RNA. However, it cannot be used for detecting short dsRNAs generated by viral replicase. This protocol was established to analyze the PAMP RNAs produced by viruses which are able to induce host immune response. Classical viral PAMP RNAs and non-classical viral PAMP RNAs are analyzed separately. Briefly, to access total viral PAMP RNAs, total RNA was extracted from the virus infected cells and then transfected into Cop5 cells. Whereas, to assess non-classical viral PAMP RNAs, the constructs expressing viral replicase are transfected into Cop5 cells. The amount of IFNα/β produced by Cop5 cells, determined by ELISA, is correlated with the total and non-classical viral PAMP RNAs. Since this method is based on type I IFN response, it is therefore suitable for measuring the functional virus-generated PAMP RNAs and also for assessing the efficiency of these PAMP RNAs.
Keywords: Virus (病毒)Background
Under virus infection, the activation of host immune system usually starts with the recognition of viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) by host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) (Medzhitov and Janeway, 2002). Viral PAMPs, associated with virus invasion, include virus surface glycoproteins, viral DNA and RNAs (Mogensen and Paludan, 2005). In case of RNA virus infection, virus replication generated RNAs are essential PAMPs portion which is able to be recognized by the host intracellular PRRs (Alexopoulou et al., 2001). Two possible candidates for the role of such viral-generated PAMP RNAs have been recently reported. First, classical viral PAMP RNAs are dsRNA replication forms that are recognized by RIG-I and MDA5 and non-capped positive-strand RNAs (polyA+) generated by alphaviruses (Sokoloski et al., 2015) that may be recognized by RIG-I (Akhrymuk et al., 2015). Second, non-classical viral PAMP RNAs are short non-polyadenylated dsRNAs with 5’ triphosphate. They are IFN-inducing RNAs generated by viral replicase using cellular RNA templates (Nikonov et al., 2013). In Semliki Forest virus (SFV) infected cells these RNAs represent the majority of PAMP RNAs (Nikonov et al., 2013).
Given the essential role of viral PAMP RNAs to activate host immune system, a robust protocol to analyze different types of virus-generated PAMP RNAs is useful for virus-host interaction study. Quantitative real time PCR could be used to quantify classical viral dsRNAs by targeting negative strands. However, it is hard to differentiate between capped and non-capped positive strands. Furthermore, the approach is neither able to tell if the targeted PAMP RNA is functional nor able to access the PAMP efficiency and cannot detect the non-classical viral PAMP RNAs. To analyze the functional PAMP RNAs that are able to trigger host immune response, we established this protocol to analyze both classical and non-classical viral PAMP RNAs. To assess the total viral PAMP RNAs, total RNA from the infected cells were extracted for the assessment. Since all types of classical alphaviral PAMP RNAs have unpaired polyA tails and they are presumably the biggest proportion in the viral PAMP RNAs, they may overshadow other types of PAMP RNAs. Therefore, in a parallel experiment, we separated and examined the polyA- fraction from the total RNAs (Nikonov et al., 2013). To assess the non-classical viral PAMP RNAs, viral replicase constructs were used for analysis because the system did not have replication competent viral RNA templates and therefore no classical viral PAMP RNAs were produced. Cop5 cells were used as IFNα/β activation host for all PAMP RNAs analyses. The quantity of the IFNα/β produced by the transfected PAMP RNAs can be determined by ELISA assay.
This protocol is a reliable method to analyze alphavirus-generated PAMP RNAs during the virus replication and, with exception of separation of polyA- fraction, applied to viruses that lack unpaired polyA tails. It is not only to measure the level of the PAMP RNAs but also is able to assess the PAMP RNAs efficiency. Therefore, this protocol is suitable for the study involving the interaction between RNA virus invasion and the host immune response.
Materials and Reagents
- Materials
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf® DNA LoBind microcentrifuge tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030108051)
- 100 mm Corning® tissue-culture treated culture dishes (Corning, catalog number: 430167)
- 12-well CorningTM CostarTM flat bottom cell culture plates (Corning, catalog number: 3513)
- 15 ml FalconTM conical centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 352096)
- 6-well plate
- Cell lines
- ATCC® BHK-21[C13] cells (ATCC, catalog number: CCL-10TM)
- Cop5 cells (Tyndall et al., 1981)
- Viruses of interest
Note: Prepare the viruses of interest from infectious clones. It is recommended that the virus titer should be prepared between 105 and 107 plaque forming units (PFU)/ml. The viruses listed below are for a demonstration. These viruses are derived from infectious clones, released (passage 0), passaged in BHK-21 cells and stored at -80 °C.
- RRV-T48
- RRV-T48A534V
- Viral replicase constructs
Note: Prepare the constructs expressing the viral replicase (non-structural proteins) of the viruses of interest. The constructs listed below are for a demonstration. As shown in the construct map below (Figure 1), the regions encoding the replicase of RRV-T48, RRV-T48A534V and SFV4 (used as positive control [Nikonov et al., 2013]) were cloned into pMC-gtGTU2 vector, which contains cytomegalovirus early promoter, leader sequence from the thymidine kinase of Herpes Simplex virus (HSV) with an inserted synthetic intron and late polyadenylation signal from simian virus 40 (SV40).
- RRV-T48
- RRV-T48A534V
- SFV
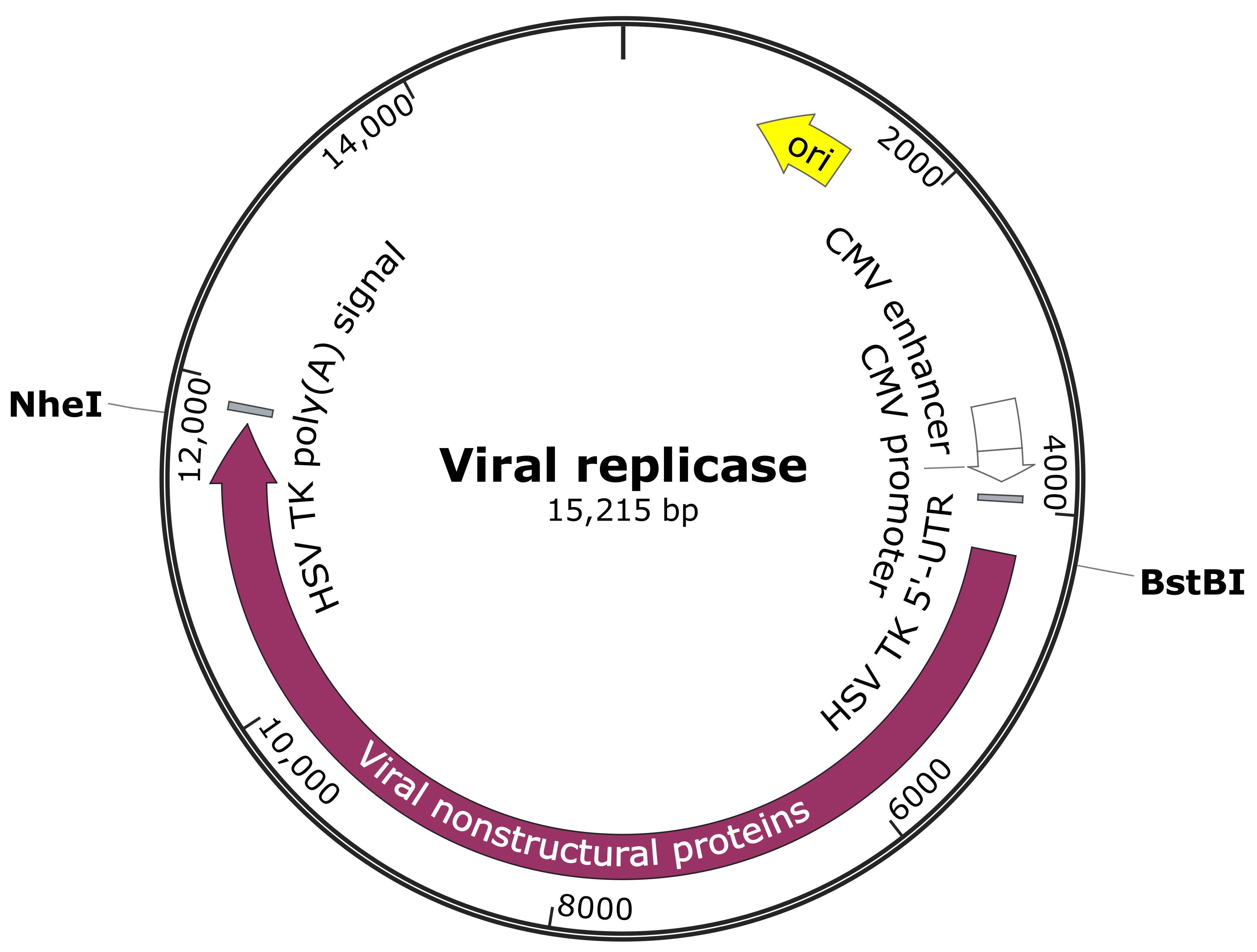
Figure 1. Viral replicase construct map
- Reagents
- Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5030)
- Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium (IMDM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 51471C)
- L-Glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G6392)
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F6178)
- 100x Penicillin-streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4333)
- Tryptose phosphate broth solution (TPB) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8159)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5493)
- 1 M HEPES buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 83264)
- 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4049)
- RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 74104)
- TRIzol® Reagent (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15596026)
- DNase I (Roche, catalog number: 04716728001)
- PolyATtract® mRNA Isolation Systems (Promega, catalog number: Z5210)
- LipofectamineTM 2000 reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11668019)
- VeriKine Mouse Interferon Beta ELISA Kit (PBL Assay Science, catalog number: 42400-1)
- pMC-gtGTU2 vector (Nikonov et al., 2013) or any mammalian expression vector (such as pcDNA or pCMV series from Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Equipment
- -80 °C freezer
- 4 °C refrigerator
- Vortexer (Bio-Rad)
- Pipettes (Bio-Rad, catalog numbers: 166-0506, 166-0507 and 166-0508)
- CO2 incubator (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 4110)
- Biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) cabinet
- Autoclave (Tuttnauer, ELV-D Line)
- UVC5000 Ultraviolet Crosslinker (Hoefer, code number: UVC5000-230V)
- SunriseTM absorbance microplate reader (Tecan)
- Microfuge 16 Centrifuge (Beckman Coulter Life science, catalog number: A46473)
Software
- Microsoft Excel or Prism 5
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Mutso, M., Liu, X., Merits, A. and Mahalingam, S. (2019). Analysis of Functional Virus-generated PAMP RNAs Using IFNα/β ELISA Assay. Bio-protocol 9(12): e3282. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3282.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物-宿主相互作用 > 病毒
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link