- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Induction and Analysis of Anti-CD40-induced Colitis in Mice
小鼠中抗-CD40抗体诱导的结肠炎的诱导和分析
发布: 2019年02月05日第9卷第3期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3153 浏览次数: 11021
评审: Ruth A. FranklinWathsala WijayalathAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
来自骨髓增生性肿瘤患者的造血祖细胞的血小板生成素不依赖性巨核细胞分化
Chloe A. L. Thompson-Peach [...] Daniel Thomas
2023年01月20日 2347 阅读
Abstract
Colon inflammation or colitis affects more than 1 million people worldwide. Several pre-clinical models, including chemical-induced (i.e., DSS, TNBS) or pathogen-induced (i.e., Citrobacter rodentium) have been used to study mechanisms involved in the development and regulation of colitis. Anti-CD40 induced colitis model has gained acceptance to study the roles of innate immune cells during acute intestinal inflammation. Here we describe a rapid, robust and reproducible protocol to induce and analyze anti-CD40 mediated colitis in mice.
Keywords: Anti-CD40 (抗CD40抗体)Background
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis, affects about 1.5 million people in the United States (Ng et al., 2017). To better understand the mechanisms involved in the development and progression of IBD, a number of pre-clinical models (i.e., DSS, TNBS, anti-CD40, etc.) have been developed to address various aspects of immune response during tissue injury over the last two decades. CD40 is highly expressed by the colon lamina propria antigen presenting cells. We have demonstrated that activation of CD40 signaling using an agonist anti-CD40 antibody can trigger colitis in T and B cells deficient mice (here referred as Rag-/- mice) driven by excessive production of IL-23, IL-1β and IL-12 by myeloid cells (Uhlig et al., 2006). Anti-CD40 model is a unique model of colitis driven by IL-23-producing gut resident CX3CR1+ macrophages and IL-22-producing group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) (Bauche et al., 2018). This model of colitis is restricted to the proximal colon and is a potent model to study the role of innate immunity in colon inflammation. Here, we describe a robust and reproducible method to induce and analyze anti-CD40-induced colitis in mice. Anti-CD40-treated Rag2-/- mice lose up to 20% of their initial weight within three days post injection, and then return to their initial weight by Day 7 post induction (Figure 1A). Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines can be detected in the proximal colon as soon as Day 1 post induction (Cayatte et al., 2012) (Figure 1B) but maximal disease–characterized by massive infiltration of innate immune cells, loss of goblet cells and development of mitotic figures–is observed in the proximal colon at day 7 post disease induction (Figure 1C). Immune cell infiltration in the proximal colon and cytokine production, such as IL-22, by innate lymphoid cells can be measured by flow cytometry (Figure 1D).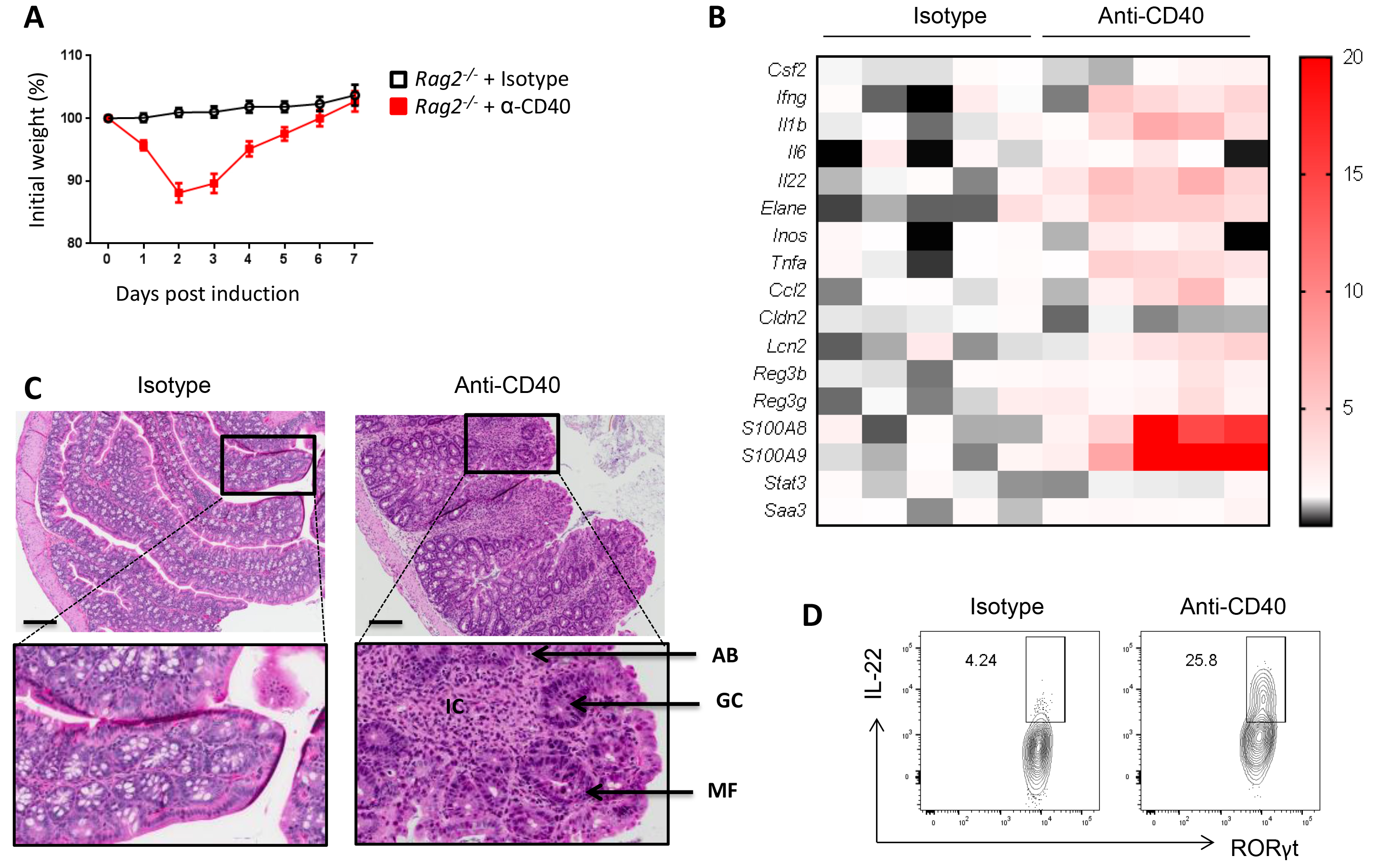
Figure 1. Induction and analysis of the anti-CD40 colitis mouse model. A. Percentage of initial weight over a 7 days period. Initial weight is measured right before injection of isotype or anti-CD40 antibodies. B. Gene expression profile of the proximal colon at Day 7 post treatment. Data shows relative fold change over the isotype control. C. Representative photomicrographs of H&E stained colon section 7 days after injection of isotype (left) or anti-CD40 antibodies (right). IC: Immune cell infiltration; GC: Loss of Goblet cells; AB: Apoptotic body; MF: Mitotic figures. Scale bars = 250 μm. D. Representative dot plot of IL-22 production by proximal colon lamina propria ILC3 (gated on lineage-, CD90high, CD45int, RORγt+ cells) at Day 2 post treatment.
Materials and Reagents
- Materials
- Pipette tips (Thermo Scientific)
- Eppendorf tubes, 1.5 ml (Eppendorf, catalog number: 05-402-5)
- 1 ml sterile sub-Q syringe 26 G (BD, catalog number: 3095971)
- Sterile cell strainer 70 μm Nylon mesh (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 22363548)
- 50 ml centrifuge tube (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 05-539-13)
- 15 ml conical centrifuge tube (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 339650)
- 15 ml sterile plastic tube (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-956-1D)
- 5 ml Serological pipettes (Falcon, catalog number: 357543)
- 25 ml Serological pipettes (Fisher Brand, catalog number: 13-678-11)
- Petri dishes (Falcon, catalog number: 351029)
- Serum or plasma separation tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 41.1378.005)
- Parafilm (Pechiney, catalog number: PM-996)
- V bottom 96-well plate (Costar, catalog number: 3894)
- 70 μm cell strainer
- Animals
Eight to twelve weeks old Rag2-/- mice (Taconic, catalog number: RAGN12) were used to study anti-CD40 mediated colitis. - Reagents
- Liquid nitrogen
- Anti-mouse CD45 APC-eFluor780 antibody (eBioscience, catalog number: 47-0451-82)
- Anti-mouse CD90.2 BV786 antibody (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 564365)
- Anti-mouse RORγt PerCP-eFluor710 antibody (eBioscience, catalog number: 46-6981-82)
- Anti-mouse NK1.1 Alexa Fluor 700 antibody (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 560515)
- Anti-mouse CD11c PE-Cy7 antibody (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 561022)
- Anti-mouse CD11b FITC antibody (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 557396)
- Anti-mouse IL-22 APC antibody (eBioscience, catalog number: 17-7222-82)
- Endotoxin-free Anti-CD40 antibody (Clone FKG45, BioXCell, catalog number: BE0016-2)
- Anti-Rat IgG2a isotype control (Clone 2A3, BioXCell, catalog number: BP0089)
- HyClone Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS), 1x (GE Healthcare, catalog number: SH30028.02)
- Hank’s buffered salt solution (HBSS)
- 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 245-685)
- Penicillin/streptomycin solution 100x (Corning, catalog number: 30-002C1)
- Sodium pyruvate 100 mM (Gibco, catalog number: 11360070)
- 2-Mercaptoethanol 55 mM (Gibco, catalog number: 21985023)
- Ultra Pure 0.5 μM EDTA pH 8.0 (Gibco, catalog number: 15575-038)
- HEPES buffer solution 1 M (Gibco, catalog number: 15630-080)
- Hyclone Standard Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SH30088.03)
- Collagenase type VIII (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C2139)
- DNase I (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5025)
- Dispase (Corning, catalog number: 354235)
- Percoll (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-0891-01)
- IMDM, GlutaMAX supplement (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 31980097)
- Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8139)
- Ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I0634)
- Brefeldin A (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 555029)
- Stain Buffer (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number: 554656)
- Transcription Factor Buffer Set (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number: 562725)
- Fixable viability stain 510 (BD, Horizon, catalog number: 564406)
- Mouse BD Fc Block (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number 553141)
- Ethanol 70% (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: HC1500)
- Ethanol 95% (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: HC1300)
- Ethanol 100% (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: HC600)
- Xylene (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: HC700)
- Paraffin (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 23-0210-400)
- Hematoxylin (MasterTech Scientific, catalog number: HXHHEGAL)
- Eosin (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 71311)
- Collagenase D (Sigma, catalog number: C5138-1G)
- Epithelial cell dissociation solution (see Recipes)
- Enzyme digestion mix (see Recipes)
- Complete IMDM media (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Scalpel (Southmedic, catalog number: SMI1/73-0121)
- Pipettes (Thermo Scientific)
- Forceps and Scissors (Fine Science Tools)
- Sterile cell culture hood
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Shaking water bath (Precision)
- Brightfield Microscope
- LSRII Flow cytometer (BD Biosciences)
- Incubator
- Vortex (Scientific Industries)
Software
- FlowJo_V10 (FlowJo, LLC, https://www.flowjo.com)
- GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad, https://www.graphpad.com)
- Microsoft Excel (Microsoft)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Joyce-Shaikh, B., Cua, D. J. and Bauché, D. (2019). Induction and Analysis of Anti-CD40-induced Colitis in Mice. Bio-protocol 9(3): e3153. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3153.
分类
免疫学 > 动物模型 > 小鼠
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离 > 流式细胞术
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link