- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Fatty Acid Content and Composition of Triacylglycerols of Chlorella kessleri
凯氏小球藻中脂肪酸含量及三酰甘油组成
发布: 2018年01月05日第8卷第1期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2676 浏览次数: 9220
评审: Maria SinetovaRoman A. SidorovAgnieszka Zienkiewicz
Abstract
Triacylglycerols (TAGs) are esters formed from one glycerol and three fatty acids. TAGs are induced to accumulate in algal cells under environmental stress conditions including nutrient-limitation, hyperosmosis, and low temperature, for the storage of metabolic energy and carbon, and also for the consumption of excess energy (e.g., Hirai et al., 2016; Hayashi et al., 2017). Beside their physiological significance, the commercial utilization of algal TAG has been expected for the production of biodiesel, the methyl esters of fatty acids, from the aspect of carbon-neutral conception. The amounts of TAGs can be determined through quantitative measurement of their constituent fatty acids. This protocol consists of the following three parts: the first is the extraction of total lipids from algal cells with the use of organic solvents, chloroform and methanol, according to the method of Bligh and Dyer (1959), the second is the separation of TAG from the other lipid classes by thin-layer chromatography (TLC), and the third is the production of methyl-esterified derivatives of their constitutive fatty acids and subsequent quantitation of them by capillary gas-liquid chromatography (GLC). This protocol adapted from Sato and Tsuzuki (2011) is used for TAG analysis in a green alga, Chlorella kessleri.
Keywords: Chlorella kessleri (Chlorella kessleri)Background
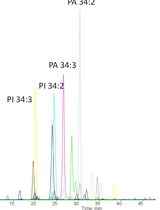
Several methods have been used for determination of the fatty acid content of TAG. Simple and convenient protocols, e.g., include conversion of TAG to glycerol on treatment with a lipase, and subsequent measurement of the glycerol content through enzymatic generation of a product that reacts with a color- or fluorescence-generating probe (McGowan et al., 1983; Mendez et al., 1986). However, this enzymatic reaction based quantitation of TAG, inevitably, gives no information about the composition of constituent fatty acids. Meanwhile, HPLC provides information on TAG molecular species through their separation based on the numbers of carbon atoms and double bonds of constituent fatty acids, and enables their respective quantitation when combined with tandem mass spectrometer like in LC-MS/MS (Mu et al., 2000; Dorschel, 2002; MacDougall et al., 2011). The LC-MS/MS instrument, however, is very expensive. In this context, TLC/GLC based protocol for the measurement of the fatty acid content of TAG is introduced here, in view of the requirement of less expensive equipment than LC-MS/MS and definite information that can be obtained on quality and quantity of the constituent fatty acids.
Materials and Reagents
- 50 ml polypropylene centrifuge tubes with conical bottom (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352070 )
- 50 ml glass screw cap centrifuge tubes with PTFE lined phenolic caps (AGC Techno Glass, catalog number: 8422CTF50 )
- 9 inch glass Pasteur pipettes (AGC Techno Glass, catalog number: IK-PAS-9P )
- TLC silica gel 60 glass plates 20 x 20 cm (Merck, catalog number: 105721 )
- Chromatography filter paper 1CHR 200 x 200 mm (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 3001-861 )
- Glass microcapillary pipette (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z543292 )
- 100 µl microsyringe (1710 RN, Hamilton, catalog number: 81030 ) with 22s/51/2 needle (Hamilton, catalog number: 7758-03 )
- 14 ml glass screw cap test tubes with PTFE lined phenolic caps (AGC Techno Glass, catalog number: TST-SCR16-125 )
- Inserts for large opening vials volume 0.15 ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 24719 )
- 2 ml large opening vials with open-top screw cap (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 29116-U )
- ULBON HR-Thermon-3000B GLC capillary column I.D. 0.25 x 25 m (Shinwa Chemical Industries)
- Chlorella kessleri 11 h, which corresponds to Parachlorella kessleri of NIES collection (http://mcc.nies.go.jp/) (National Institute for Environmental Studies, catalog number: NIES-2160 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 163-03545 )
- Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 029-07392 )
- Methanol (CH3OH) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 138-06473 )
- Chloroform (CHCl3) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 033-08631 )
- Primuline (C21H15N3O3S3) (Tokyo Chemical Industry, catalog number: P0603 )
- Acetone (CH3COCH3) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 016-00346 )
- Tripalmitin (C51H98O6) as TAG standard (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 200-03002 )
- N2 gas
- Hydrogen chloride-methanol reagent (5-10%) (Tokyo Chemical Industry, catalog number: X0041 )
- n-Hexane (C6H14) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 084-03421 )
- Supelco 37 component FAME mix (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 47885-U )
- Gamborg’s B5 medium salt mixture (Nihon Pharmaceutical, catalog number: 399-00621 ; Gamborg et al., 1968)
- Sorbitol (C6H14O6) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 198-03755 )
- Arachidic acid (C20H40O2) (Tokyo Chemical Industry, catalog number: E0006 )
- 1/4 GB medium with or without 0.6 M sorbitol (see Recipes)
- Arachidic acid solution as an IS (see Recipes)
Equipment
- High-pressure steam sterilizer (TOMY SEIKO, model: LBS-245 )
- Tabletop centrifuge (Kubota, model: 5220 ) equipped with ST-720M swing rotor (16 x 50 ml)
- Vortex mixer (Scientific Industries, model: Vortex-Genie 2 )
- Rotary evaporator (Tokyo Rikakikai, model: N-1110V-W ) equipped with screw cap tube adaptor
- UV transilluminator (UVP, model: LM-20 )
- Fume hood (Yamato Scientific, model: KFS )
- Forced air flow oven (Tokyo Rikakikai, model: WFO-451SD )
- Spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, model: DU 640 )
- Double trough TLC chamber for 20 x 20 cm plates (Camag, catalog number: 022.5256 )
- Capillary gas-liquid chromatograph (Shimadzu, model: GC-2025 ) equipped with split/splitless injector, frame ion detector (FID) and autoinjector
- Chromatopac integrator (Shimadzu, model: C-R7A plus )
- Glass chromatographic reagent atomizer (Corning, PYREX®, catalog number: 2153-125 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Aoki, M. and Sato, N. (2018). Fatty Acid Content and Composition of Triacylglycerols of Chlorella kessleri. Bio-protocol 8(1): e2676. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2676.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 脂质
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 脂质
生物化学 > 脂质 > 脂质测定
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
提问指南
+ 问题描述
写下详细的问题描述,包括所有有助于他人回答您问题的信息(例如实验过程、条件和相关图像等)。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link