- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Rodent Model for Chronic Brain Hypoperfusion Related Diseases: Permanent Bilateral Occlusion of the Common Carotid Arteries (2VO) in Rats
慢性脑灌注不足相关疾病的啮齿动物模型:大鼠双侧颈总动脉永久性闭塞(2VO)
发布: 2018年01月05日第8卷第1期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2668 浏览次数: 9322
评审: Jeremy FerrierAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Permanent occlusion of bilateral common carotid arteries (2VO) in rat is considered as a suitable animal model to mimic chronic brain hypoperfusion status, which is proved to be a risk factor to precede the Alzheimer’s disease or/and vascular dementia. In this protocol, we describe how to successfully ligate the bilateral common carotid arteries covered by anterior cervical muscle group, and provide the details for understanding the surgical procedures of 2VO.
Keywords: Permanent occlusion of bilateral common carotid arteries (双侧颈总动脉永久性闭塞)Background
Currently, chronic brain hypoperfusion (CBH) is considered as a preclinical condition of mild cognitive impairment, which is thought to precede dementia (Ruitenberg et al., 2005; Gorelick et al., 2011). However, how CBH produces dementia is largely unknown.
The method of permanent occlusion of bilateral common carotid arteries (2VO) in rat was first established in the 1970s (Eklof and Siesjo, 1972). Since 2VO in rats provokes CBH without motor dysfunction, it is considered as a suitable animal model to elicit CBH status (Tanaka et al., 1996). After the 2VO procedures, three phases are theoretically determined by the degree of cerebral blood flow (CBF) and metabolic changes of rats (Farkas et al., 2007). After initiation of 2VO procedures, the first phase of acute ischemia lasts for about 2-3 days (Ohta et al., 1997; Otori et al., 2003; Tomimoto et al., 2003). During this period, the CBF drops dramatically and remains at a significantly low level in the following 4 weeks with reduced glucose utilization (Otori et al., 2003), sudden depletion of ATP and phosphocreatine (Plaschke, 2005). The second phase lasts for 8 to 12 weeks and corresponds well with the CBH in aging and dementia, and a slight reduction of the CBF with restored ATP as well as remaining low level of phosphocreatine. However, in the final phase, the CBF recovers to the baseline and the metabolic changes gradually cease after 6 months of 2VO (Ohta et al., 1997; Otori et al., 2003).
We also noted that numerous studies using 2VO rat model also reveal lots of pathological characteristics, including impaired learning and memory evaluated by both Morris water maze or eight-arm radial maze, where the 2VO rats display longer escape latencies to find hiding platform in Morris water maze (Liu et al., 2005) and commit more errors to enter a never-baited arm than the rats from sham group in the eight-arm radial maze (Sopala and Danysz, 2001); the neuronal cell death in hippocampus (Farkas et al., 2004); reduced dendritic arborizations (Chen et al., 2017); astrocytic reactions (Panickar and Norenberg, 2005) and microglial activation (Abraham and Lazar, 2000), etc. All these phenomena provide the sounded evidence that 2VO rat model is a valuable animal model to study the molecular mechanism of CBH associated diseases. In this protocol, we describe the detailed procedures of how to successfully establish a rodent model of CBH by permanently ligating the bilateral common carotid arteries of rat. And this protocol was based on and modified from the previously published paper: Kumaran et al., 2008.
Materials and Reagents
- 75% alcohol cotton ball (Bettering, catalog number: BY ACB )
- 22 mm (3/8 circle) surgical needle with suture (Foosin Medical Supplies, Weigao, model: 300 series ) (Figure 1B)
- 1 ml syringe for anesthetizing (Xi’an Sentansha Medical Investment Management, catalog number: STS-SY003-#0037 ) (Figure 1H)
- 3-0 silk suture (Jinhuan, model: 3-0 ) (Figure 1A)
- Medical absorbent cotton (Zhushi Parmaceutical Group, model: ZS-HM019 )
- Animals
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (weight 280-300 g, usually 4-5 months old, obtained from the Animal Center of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, China) were housed at 23 ± 1 °C with 55 ± 5% of humidity and maintained on 12 h dark/light artificial cycle (lights on at 7:00 AM) with food and water available ad libitum. All procedures regarding the animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Harbin Medical University (No. HMUIRB-2008-06) and the Institute of Laboratory Animal Science of China (A5655-01) - 0.9% sodium chloride (Qingdao Fraken International Trading, model: High Quality 0.9% Compound Sodium Chloride Injection )
- Chloral hydrate (Aladdin, catalog number: C104202 )
- Gentamycin sulfate, 50 mg/ml solution, sterile (Sangon Biotech, catalog number: B540724 )
- 10% chloral hydrate solution (see Recipes)
- 20 mg/ml gentamycin sulfate solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Glass dish (Canfort Laboratory and Education Supplies, catalog number: LG075 ) (Figure 1C)
- Needle holder (Sklar Surgery Instrument, model: 5-1/4”, catalog number: 21-8001 ) (Figure 1D)
- Forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11009-13 ) (Figure 1E)
- Artery clips (Nut Link International, model: Approximator Clamps ) (Figure 1F)
- Scissors (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 14068-12 ) (Figure 1G)
- Glass hook (Figure 1I)
- Electric animal shaver (Yiwu Kemei Electric Appliances, model: KM-970 ) (Figure 1J)
- Fiber optic illuminator (Mineralogical Research, catalog number: MA312101 ) (Figure 1K)
- Electric heating pad for pet (Dongxiyi, catalog number: wi95919 ) (Figure 1L)
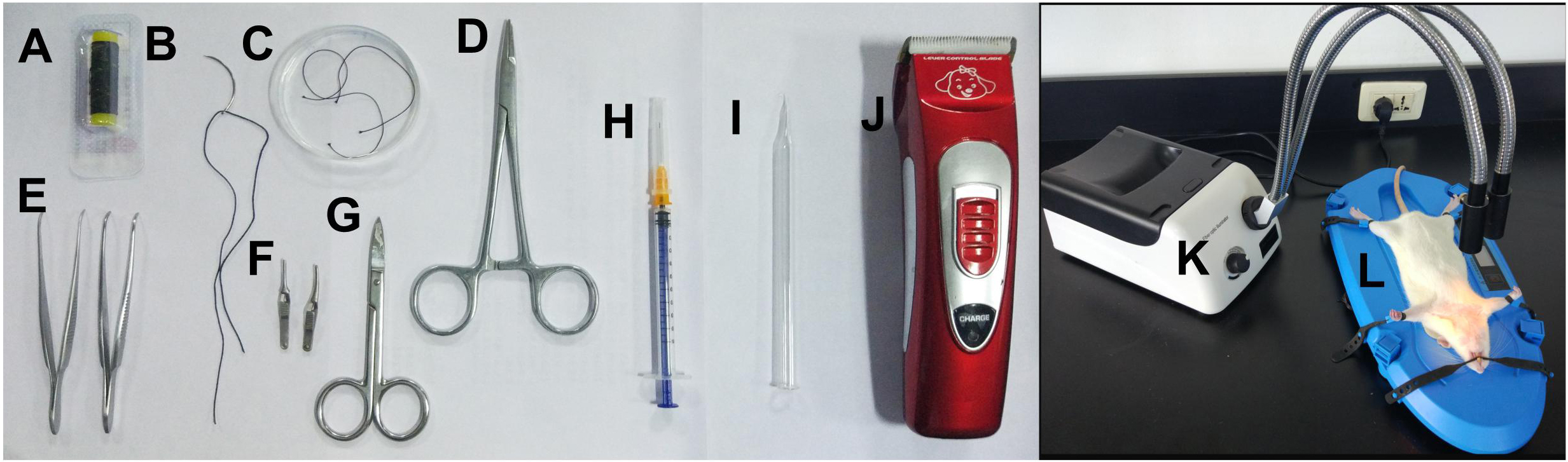
Figure 1. The materials and equipment. A. 3-0 silk suture; B. Surgical needle with suture; C. Glass dish with the sterile 0.9% sodium chloride; D. Needle holder; E. Forceps; F. Artery clips; G. Scissors; H. 1 ml syringe for anesthetizing; I. Glass hook; J. Electric animal shaver; K. Fiber optic illuminator; L. Electric heating pad.
Notes: Before the surgery, all the metal instruments should be sterilized at high temperature, 200 °C.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Yan, M. and Ai, J. (2018). A Rodent Model for Chronic Brain Hypoperfusion Related Diseases: Permanent Bilateral Occlusion of the Common Carotid Arteries (2VO) in Rats. Bio-protocol 8(1): e2668. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2668.
分类
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 实验动物模型 > 大鼠
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 生理学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













