- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Low-input Capture-C: A Chromosome Conformation Capture Assay to Analyze Chromatin Architecture in Small Numbers of Cells
低样品量Capture-C:采用染色体构象采集分析法分析少量细胞中的染色质结构
发布: 2017年12月05日第7卷第23期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2645 浏览次数: 12807
评审: Jyotiska ChaudhuriAlexandros AlexandratosAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Chromosome conformation capture (3C) techniques are crucial to understanding tissue-specific regulation of gene expression, but current methods generally require large numbers of cells. This protocol describes two new low-input Capture-C approaches that can generate high-quality 3C interaction profiles from 10,000-20,000 cells, depending on the resolution used for analysis.
Keywords: Nuclear organization (核结构)Background
3C techniques play a key role in investigating how nuclear organization and structural interactions between regulatory elements relate to gene activity (Dekker et al., 2002). As these interactions are highly tissue-specific, it is crucial that 3C experiments are performed in well defined, purified cell populations.
A major limitation of 3C techniques is the large numbers of cells required: current methods use between 100,000 and 10 million cells (Davies et al., 2017). Many primary tissues and rare cell populations are not available in these numbers. We have therefore developed two new low-input Capture-C approaches that can generate high-quality interaction profiles from ~20,000 cells at maximum resolution (individual DpnII fragments), and from ~10,000 cells using windowing based analysis (Oudelaar et al., 2017).
Materials and Reagents
- 3C library preparation
- LowBind DNA 1.5 ml microtube
- Phase Lock Gel (PLG) Light tubes (VWR, Quantabio, catalog number: 733-2477 )
- Genomic DNA ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5366 )
- Tapestation Loading Tips (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5153 )
- 1 M glycine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7126 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10010031 )
- Growth media
- 37% formaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 252549 )
- Ethanol absolute > 99.8% (VWR, catalog number: 20821.330 , or equivalent)
- Dry ice or liquid nitrogen
- PCR grade water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9932 )
- SDS (20% v/v in water) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9820 )
- Triton X-100 (20% v/v in water) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787 )
- DpnII (50,000 U/ml) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0543M )
- T4 DNA ligase (30 U/μl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: EL0013 )
- Proteinase K (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: EO0491 )
- RNase (DNase-free) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11119915001 )
- Phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (PCI) 25:24:1 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 77617 )
- 3 M NaOAc (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9740 )
- GlycoBlue (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9515 )
- Genomic DNA Reagents (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5365 )
- TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix II without UNG (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosystemsTM, catalog number: 4440040 )
- KAPA Sybr Fast Universal (Kapa Biosystems, catalog number: KK4602 )
- Fresh lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Tris pH 8 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9855G )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9760G )
- Igepal CA-630 (100 μl of 10%) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I8896 )
- cOmplete Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (1 tablet in 2 ml of PCR grade water for 25x; store at -20 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11873580001 )
- PCR grade water
- Tris pH 8 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9855G )
- qPCR primers (Appendix I)
- LowBind DNA 1.5 ml microtube
- Addition of Illumina sequencing adaptors by ligation or tagmentation to generate Capture-C libraries
LI-Capture-C- Covaris microTUBE AFA Fiber pre-split snap-cap 6 x 16 mm (Covaris, catalog number: 520045 )
- LowBind DNA 1.5 ml microtube
- PCR tube
- D1000 ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5582 )
- TapeStation Loading Tips (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5153 )
- NEBNext Ultra DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E7370S/L )
- Agencourt Ampure XP SPRI Beads (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: A63881 )
- NEBNext Multiplex Oligos for Illumina Primer set 1 (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E7335S/L )
- NEBNext Multiplex Oligos for Illumina Primer set 2 (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E7500S/L )
- Herculase II Fusion Polymerase Kit (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 600677 )
- PCR grade water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9932 )
- Ethanol absolute > 99.8% (VWR, catalog number: 20821.330 , or equivalent)
- D1000 Reagents (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5583 )
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: Q32850 )
Tag-Capture-C- LowBind DNA 1.5 ml microtube
- PCR tube
- High Sensitivity D1000 ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5584 )
- D1000 ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5582 )
- TapeStation Loading Tips (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5153 )
- Nextera DNA Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina, catalog number: FC-121-1030 / 1031 )
- Zymo DNA Clean & Concentrator-5 Kit (Zymo Research, catalog number: D4013 )
- KAPA HiFi PCR Kit with dNTP (KK2102) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 07958846001 )
- Custom designed index primers
- Agencourt Ampure XP SPRI Beads (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: A63881 )
- PCR grade water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9932 )
- Ethanol absolute > 99.8% (VWR, catalog number: 20821.330 , or equivalent)
- High Sensitivity D1000 Reagents (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5585 )
- D1000 Reagents (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5583 )
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: Q32850 )
- Covaris microTUBE AFA Fiber pre-split snap-cap 6 x 16 mm (Covaris, catalog number: 520045 )
- Enrichment for viewpoints of interest by oligonucleotide capture
- Safeseal Microcentrifuge Tubes (Sorenson BioScience, catalog number: 39640T )
- D1000 ScreenTape (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5582 )
- Tapestation Loading Tips (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5153 )
- Nimblegen SeqCap EZ Hybridization and wash kit (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 05634261001 )
- Nimblegen SeqCap EZ Accessory kit v2 (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 07145594001 )
- 1 μg/μl COT DNA of relevant species (Mouse) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 18440016 )
- M-270 Streptavidin Dynabeads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 65305 )
- Agencourt Ampure XP SPRI Beads (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: A63881 )
- PCR grade water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9932 )
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: Q32850 )
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: Q32851 )
- D1000 Reagents (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-5583 )
- KAPA Library Quantification Complete Kit (Universal) (Kapa Biosystems, catalog number: KK4824 )
- LI-Capture-C
Nimblegen SeqCap EZ HE-oligo kit A (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 06777287001 )
Nimblegen SeqCap EZ HE-oligo kit B (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 06777317001 ) - Tag-Capture-C
xGen Custom Blocking Oligos (P5/i5 & P7/i7 Nextera blocker)
- Safeseal Microcentrifuge Tubes (Sorenson BioScience, catalog number: 39640T )
Equipment
- Centrifuge
- Incubator (any)
- Eppendorf Thermomixer C (or equivalent shaking incubator) (Eppendorf, model: ThermoMixer® C , catalog number: 5382000015)
- P10, P20, P200 and P1000 pipettes (any)
- Thermocycler (any)
- NanoDrop
- Agilent 2200 TapeStation (Agilent Technologies, model: Agilent 2200 TapeStation System )
Note: Assessments on the Agilent TapeStation can also be performed on the Agilent BioAnalyzer. - Sonicator (Covaris, model: S220 Focused-ultrasonicator)
- DynaMag-2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12321D )
- Vacuum Concentrator (SciQuip, CHRIST series)
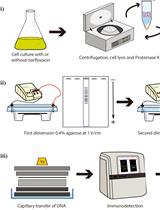
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Oudelaar, A. M., Downes, D. J., Davies, J. O. and Hughes, J. R. (2017). Low-input Capture-C: A Chromosome Conformation Capture Assay to Analyze Chromatin Architecture in Small Numbers of Cells. Bio-protocol 7(23): e2645. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2645.
分类
系统生物学 > 表观基因组学 > 染色质结构
分子生物学 > DNA > DNA 结构
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link