- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolation and Detection of the Chlorophyll Catabolite Hydroxylating Activity from Capsicum annuum Chromoplasts
辣椒青霉色素中叶绿素的分离及含量羟化活性的测定
发布: 2017年09月20日第7卷第18期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2561 浏览次数: 8553
评审: Marisa RosaMohan TCWenrong He
Abstract
Hydroxylation of chlorophyll catabolites at the so-called C32 position (Hauenstein et al., 2016) is commonly found in all plant species analyzed to date. Here we describe an in vitro hydroxylation assay using Capsicum annuum chromoplast membranes as a source of the hydroxylating activity, which converts the substrate epi-pFCC (epi-primary Fluorescent Chlorophyll Catabolite) (Mühlecker et al., 2000) to epi-pFCC-OH.
Keywords: TIC55 (Translocon at the inner chloroplast membrane 55 kDa) (TIC55(叶绿体内膜易位子55 kDa))Background
During leaf senescence and fruit ripening, light-absorbing chlorophylls are degraded to non-fluorescent catabolites to prevent oxidative damage. The chlorophyll breakdown pathway (PAO/phyllobilin pathway) consists of consecutive steps catalyzed by several enzymes and the final degradation products, called phyllobilins, are ultimately stored in the vacuole (Kräutler, 2016). epi-primary Fluorescent Chlorophyll Catabolite (epi-pFCC) is the first non-phototoxic intermediate. After its formation in the chloroplast, side-chain modifications of epi-pFCC can occur, most of which take place outside the chloroplast. One of these modifications, however, is the hydroxylation of the C32 position (Figure 1) catalyzed by the inner chloroplast envelope enzyme TIC55, a member of the family of ferredoxin (Fd)-dependent non-heme oxygenases. TIC55 contains a Rieske and a mononuclear iron-binding domain and was shown to require a Fd reducing system as well as molecular oxygen for its hydroxylating activity. Here we describe an in vitro enzyme assay for TIC55, which was used to characterize the epi-pFCC hydroxylating enzyme activity from red pepper chromoplasts.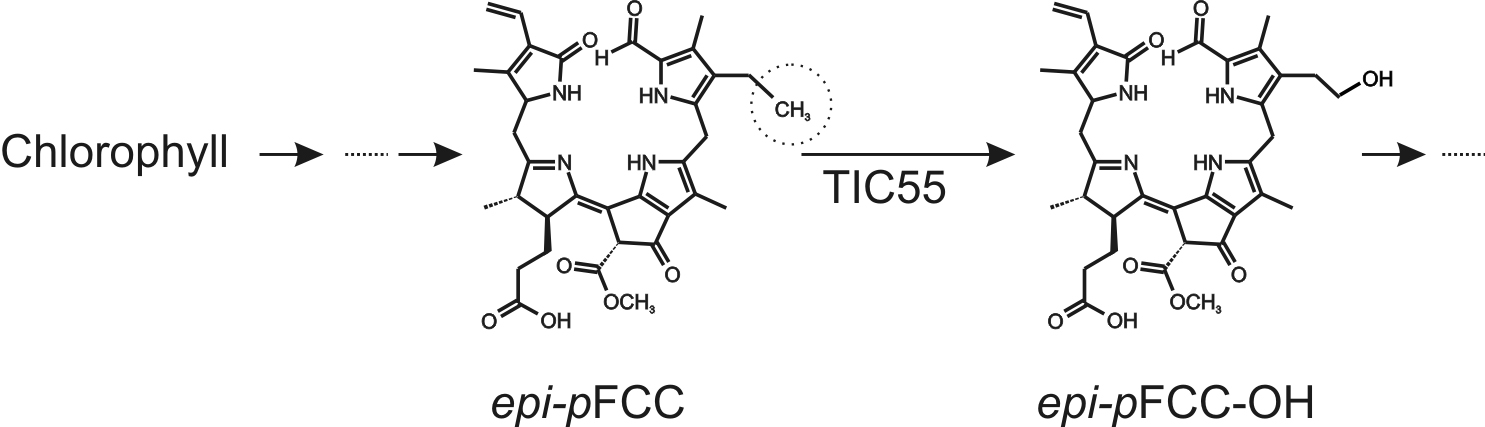
Figure 1. Outline of the pathway of chlorophyll breakdown, highlighting the TIC55-catalyzed reaction from epi-pFCC to epi-pFCC-OH. The circle shows the C32 position, the site of hydroxylation.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (SARSTEDT)
- 2 ml SafeSeal micro tubes, PP (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.695.500 )
- Miracloth (pore size 22-25 µm) (Merck)
- 10 ml syringe with 0.6 mm needle
- Watercolor paint brush, number 10 (for example: FILA, Giotto brush art series 400)
- Fully ripe red-colored Capsicum annuum fruits, from local supermarket
- Sucrose (AppliChem, catalog number: A2211,500 0)
- Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) (Carl Roth, catalog number: AE15.3 )
- 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1074.1000 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (EDTA) (AppliChem, catalog number: A2937.1000 )
- Polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 81240 )
- 1,4-Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 6908.3 )
- (+)-Sodium L-ascorbate (Vitamin C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A4034 )
- Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (FNR) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F0628 )
- Ferredoxin (Fd) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F3013 )
- β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 2’-phosphate reduced tetrasodium salt hydrate (NADPH) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1395 )
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (GDH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8404 )
- Glucose-6-phosphate (Glc6P) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7879 )
- Epi-primary fluorescent chlorophyll catabolite (epi-pFCC) (according to Mühlecker et al., 2000)
- Methanol, HPLC grade (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 34860 )
- Chromoplast isolation buffer (for composition, see Recipes)
- Tris MES pH 8 buffer (for composition, see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes (Gilson)
- Fruit juicer (Vitality 4 Life, model: Oscar Vitalmax 900 ) or Sorvall mixer
- Microcentrifuge: Biofuge fresco (Heraeus, model: Biofuge fresco )
- Centrifuge: Avanti J-20 XPi (Beckman Coulter, model: Avanti® J-XN 26 ); Rotors: JLA-10.500 (Beckman Coulter, model: JLA-10.500 with 500 ml polypropylene bottles) and JA-25.50 (Beckman Coulter, model: JA-25.50 with 50 ml polypropylene tubes)
- Ultracentrifuge: Optima LE-80K (Beckman Coulter, model: OptimaTM LE-80K ); Rotor: SW-41Ti (Beckman Coulter, model: SW 41 Ti with 13.2 ml polyallomer tubes)
- -80 °C freezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: HERAfreezeTM HFU 586 Top )
- LC-MS/MS: Ultimate3000-Compact (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: UltiMate 3000 ; Bruker Daltonics, model: Compact )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Hauenstein, M. and Hörtensteiner, S. (2017). Isolation and Detection of the Chlorophyll Catabolite Hydroxylating Activity from Capsicum annuum Chromoplasts. Bio-protocol 7(18): e2561. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2561.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link