- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Generation of Targeted Knockout Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana Using CRISPR/Cas9
拟南芥中利用CRISPR/Cas9技术生成定向基因敲除突变体
发布: 2017年07月05日第7卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2384 浏览次数: 25789
评审: Jihyun KimAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The CRISPR/Cas9 system has emerged as a powerful tool for gene editing in plants and beyond. We have developed a plant vector system for targeted Cas9-dependent mutagenesis of genes in up to two different target sites in Arabidopsis thaliana. This protocol describes a simple 1-week cloning procedure for a single T-DNA vector containing the genes for Cas9 and sgRNAs, as well as the detection of induced mutations in planta. The procedure can likely be adapted for other transformable plant species.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9 (CRISPR/Cas9)Background
The CRISPR/Cas9 system (Cas9) provides a simple and widely applicable approach to modify genomic regions of interest and has therefore become the tool of choice for genome editing in plants and other organisms (Schiml and Puchta, 2016). The system relies on the bacterial Cas9 nuclease from Streptococcus pyogenes (Cas9), which can be directed by a short artificial single guide RNA molecule (sgRNA) towards a genomic DNA sequence (Jinek et al., 2012), where it creates a double strand break (DSB). These DSBs are then repaired by the innate DNA repair mechanism of the plant cell. Here, two main pathways can be distinguished (Salomon and Puchta, 1998). (i) DNA molecules with high homology to the DSB site can be used as repair template. This homology directed repair (HDR) approach can be exploited to introduce specific sequences at the site of the DSB (Schiml et al., 2014; Baltes and Voytas, 2015). However, due to low integration rates of these sequences, HDR mediated gene editing in plants remains challenging. (ii) An easier and more efficient approach is the use of the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair pathway of the plant, which is the dominant repair pathway in most plants, such as Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis). Since NHEJ is error-prone, small insertions or deletions (indels) of a few base pairs (bp) occur often at the DSB site, leading to frameshift mutations and gene knockouts (Pacher and Puchta, 2016). Here, we provide a detailed protocol for targeted gene knockout in the model plant Arabidopsis including a simple 1-week cloning protocol for a plant vector system containing the Cas9 and sgRNA, and then Arabidopsis transformation and detection of mutations.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.690.001 )
- 200 µl PCR tubes (Labomedic, catalog number: 2081644AA )
- Petri dishes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 82.1472 )
- 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.691 )
- 20 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.1116 )
- 200 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.760.012 )
- 1,000 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.762.010 )
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens (A. tumefaciens) strain GV3101::pMP90
- Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (Col-0)
- Vectors (see Figure 1)
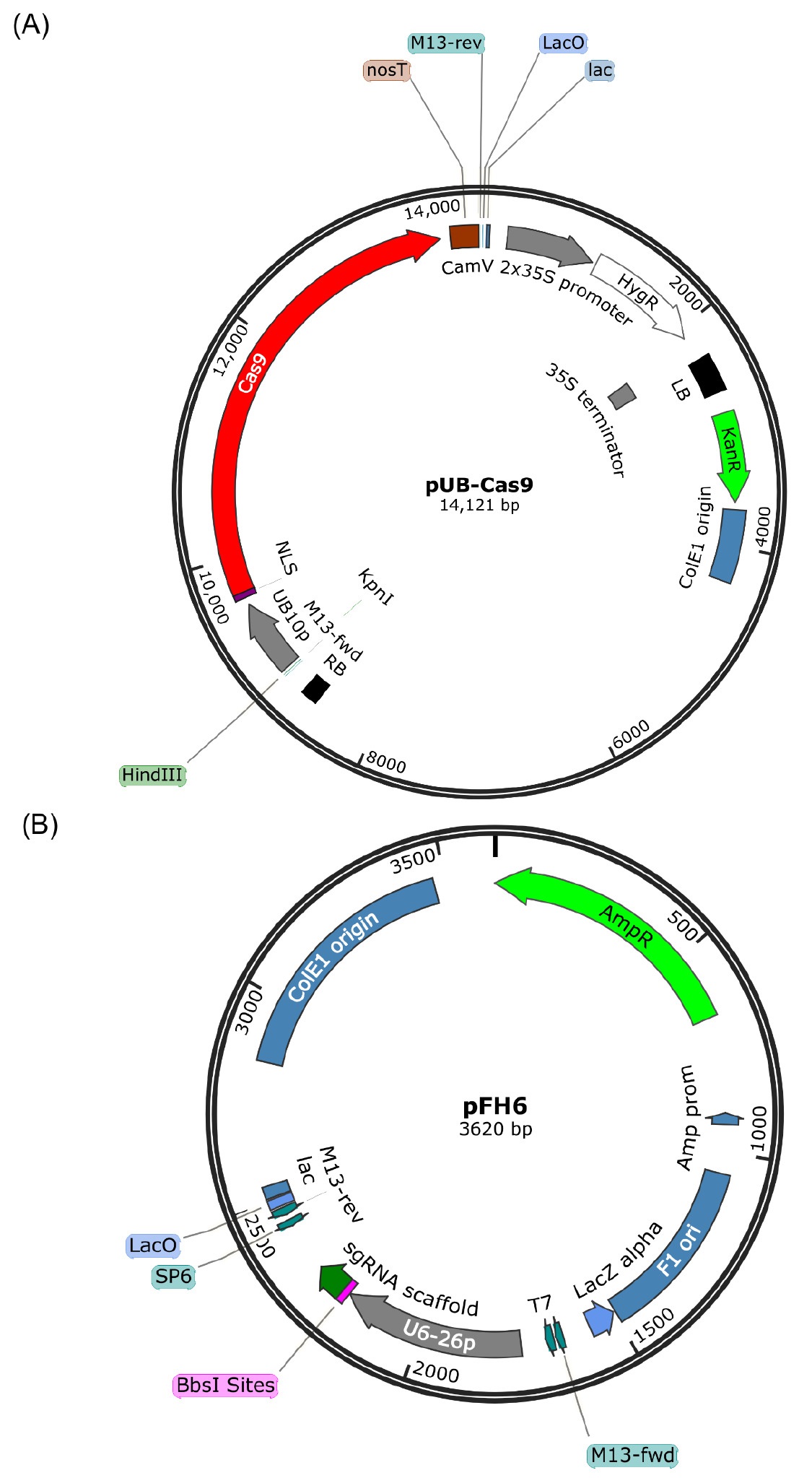
Figure 1. Vector maps of pUB-Cas9 (A) and pFH6 (B). pFH6 is used to integrate the 20 bp target sequence upstream of the sgRNA scaffold and under the control of the Arabidopsis U6-26 RNA polymerase III promoter. The whole sgRNA cassette is then transferred via Gibson cloning into the binary T-DNA vector pUB-Cas9 (contains the Cas9 gene under the control of the Ubiquitin10 promoter) for plant transformation. Maps were generated using SnapGene Viewer (http://www.snapgene.com/products/snapgene_viewer/).- Plant T-DNA Cas9 vector pUB-Cas9 (GenBank accession number KY080691), containing a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii codon-optimized ubiquitously (UBIQUITIN10 promoter) expressed Cas9 gene, a kanamycin resistance cassette for bacterial selection and a hygromycin resistance cassette as plant selection marker (Hahn et al., [2017]; available at Addgene, catalog number: 86556 )
- sgRNA subcloning vector pFH6 (GenBank accession number KY080689) containing the Arabidopsis U6-26 promoter, the integration site for the 20 bp protospacer sequence, the sgRNA scaffold and an ampicillin resistance cassette (Hahn et al. [2017]; available at Addgene, catalog number: 86555 )
Note: pFH6 contains an additional 9 bp fragment (GTCCCTTCG) between the 3’ end of the U6-26 promoter and the protospacer integration site. In several experiments, we could show that this does not affect gene editing activity. However, we have also cloned a new version of the subcloning vector without the additional fragment (pFH6_new), which shows high cleavage activity in preliminary experiments and can be obtained from us. This version only contains an additional guanine (G) between the 3’ end of the U6-26 promoter and the protospacer integration site, which allows the integration of any 20 bp protospacer without restriction of G as first bp (compare e.g., Fauser et al. [2014]). The cloning strategy for pFH6_new is analogous to the one described in this protocol, the only difference is that the forward primer for cloning your 20 bp protospacer sequence contains a different overlap and lacks the need for an initial G at the beginning (ATTG-N20, compare procedure section).
- Plant T-DNA Cas9 vector pUB-Cas9 (GenBank accession number KY080691), containing a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii codon-optimized ubiquitously (UBIQUITIN10 promoter) expressed Cas9 gene, a kanamycin resistance cassette for bacterial selection and a hygromycin resistance cassette as plant selection marker (Hahn et al., [2017]; available at Addgene, catalog number: 86556 )
- Competent Escherichia coli (E. coli) cells (e.g., Mach1TM competent cells, Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: C862003 )
- BbsI-HF + CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3539S )
- Distilled H2O
- Plasmid mini prep kit and agarose gel extraction kit (e.g., GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit, Roboklon, catalog number: E3545 )
- T4 DNA ligase with 10x ligation buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0202S )
- Ampicillin (Amp) (Carl Roth, catalog number: K029.2 )
- Primers (see Table 1)
Table 1. List of oligonucleotides
- 5x Green GoTaq Reaction buffer (Promega, catalog number: M791A )
- dNTPs (10 mM each) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: R0192 )
- GoTaq G2 polymerase (Promega, catalog number: M7841 ) or other standard PCR polymerase
- HindIII-HF + CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3104S )
- KpnI-HF + CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3142S )
- Phusion High-Fidelity polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0530S ) or other proofreading polymerases
- Gibson Assembly Cloning Kit (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E5510S )
- Kanamycin sulfate (Kan) (Carl Roth, catalog number: T832.4 )
- Rifampicin (Rif) (Molekula, catalog number: 32609202 )
- Gentamycin sulfate (Gent) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 0233.3 )
- Hygromycin B (Hyg) (Carl Roth, catalog number: CP12.2 )
- T7 Endonuclease I (optional; New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0302S )
- LB medium (agar plates and liquid), supplemented with 200 μg/ml ampicillin (see Recipes)
- LB medium (agar plates and liquid), supplemented with 30 μg/ml kanamycin sulfate (see Recipes)
- YEP medium (agar plates and liquid), supplemented with 150 μg/ml rifampicin, 50 μg/ml gentamycin sulfate, 50 μg/ml kanamycin (see Recipes)
- ½ MS medium agar plates, supplemented with 33.3 μg/ml hygromycin B (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Agarose gel electrophoresis equipment (e.g., VWR, Peqlab, model: PerfectBlueTM Gel System Mini M, catalog number: 700-0434 )
- Bacteria plate incubators (28 °C, 37 °C, e.g., Memmert, model: IN55 ) and shaker (28 °C, 37 °C; e.g., Eppendorf, New BrunswickTM, model: Innova® 44 , catalog number: M1282-0002)
- Heating blocks (e.g., Eppendorf, model: Thermomixer Compact , catalog number: T1317-1EA)
- PCR cycler (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosytemsTM, model: VeritiTM 96-well Thermal Cycler, catalog number: 4375786 )
- 10 µl pipette (e.g., Pipetman Neo P10N, Gilson, catalog number: F144562 )
- 20 µl pipette (e.g., P20N, Gilson, catalog number: F144563 )
- 200 µl pipette (e.g., P200N, Gilson, catalog number: F144565 )
- 1,000 µl pipette (e.g., P1000N, Gilson, catalog number: F144566 )
- Plant growth chamber (e.g., CLF Plant Climatics, Percival Scientifici, model: AR-66L )
Software
- SerialCloner
- Cas-OFFinder
- 4Peaks software
- MUSCLE (Optional)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Hahn, F., Eisenhut, M., Mantegazza, O. and Weber, A. P. M. (2017). Generation of Targeted Knockout Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana Using CRISPR/Cas9. Bio-protocol 7(13): e2384. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2384.
分类
植物科学 > 植物分子生物学 > DNA > 诱/突变
分子生物学 > DNA > 诱/突变
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













