- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Method to Convert mRNA into a Guide RNA (gRNA) Library without Requiring Previous Bioinformatics Knowledge of the Organism
不需预知生物体生物信息学条件下将其mRNA转化为向导RNA(gRNA)库的方法
发布: 2017年05月20日第7卷第10期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2319 浏览次数: 10723
评审: Jihyun KimManuela RoggianiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
While the diversity of species represents a diversity of special biological abilities, many of the genes that encode those special abilities in a variety of species are untouched, leaving an untapped gold mine of genetic information; however, despite current advances in genome bioinformatics, annotation of that genetic information is incomplete in most species, except for well-established model organisms, such as human, mouse, or yeast. A guide RNA (gRNA) library using the clustered regularly interspersed palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) system can be used for the phenotypic screening of uncharacterized genes by forward genetics. The construction of a gRNA library usually requires an abundance of chemically synthesized oligos designed from annotated genes; if one wants to convert mRNA into gRNA without prior knowledge of the target DNA sequences, the major challenges are finding the sequences flanking the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) and cutting out the 20-bp fragment. Recently, I developed a molecular biology-based technique to convert mRNA into a gRNA library (Arakawa, 2016) (Figure 1). Here I describe the detailed protocol of how to construct a gRNA library from mRNA.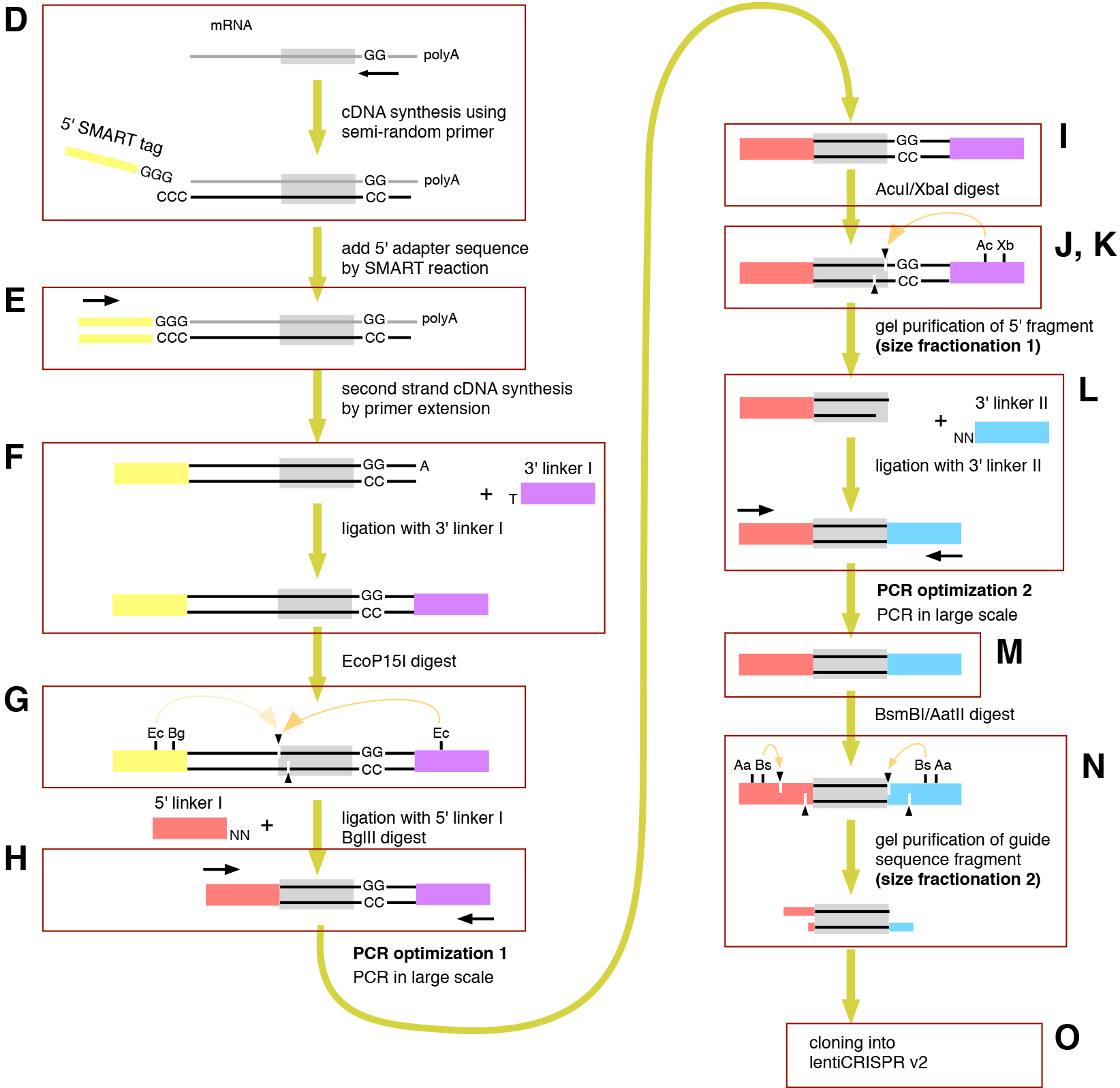
Figure 1. A method to convert mRNA into a gRNA library construction (Sanjana et al., 2014). The scheme of the method is summarized. Each step of D-O is described in detail in the Procedure. Bg, BglII; Xb, XbaI; Bs, BsmBI; Aa, AatII. PCR, polymerase chain reaction; lentiCRISPR v2, lentiCRISPR version 2.
Background
The clustered regularly interspersed palindromic repeats (CRISPR) system is responsible for the acquired immunity of bacteria (Barrangou et al., 2007), which is shared among 40% of eubacteria and 90% of archaea (Grissa et al., 2007). While CRISPR/Cas9 is, physiologically, an endonuclease used to eliminate the infectious pathogen (Barrangou et al., 2007), CRISPR/Cas9 can be used to cleave any locus of the genome if a guide RNA (gRNA) is provided (Cong et al., 2013; Mali et al., 2013). By designing gRNA for the gene of interest, individual genes can be knocked out one-by-one by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) (Cong et al., 2013; Mali et al., 2013); additionally, CRISPR/Cas9 can be utilized to make a gRNA library available for genetic screening (Zhou et al., 2001; Koike-Yusa et al., 2014; Shalem et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2014). The gRNA for Streptococcus pyogenes (Sp) Cas9 can be designed as a 20-bp sequence adjacent to the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) NGG (Cong et al., 2013; Mali et al., 2013). Such a sequence can usually be identified from the coding sequence or locus of interest by bioinformatics techniques. Here, I describe a method to construct a gRNA library via molecular biology techniques without relying on bioinformatics. Briefly, one synthesizes cDNA from the extracted RNA using a semi-random primer containing a PAM-complementary sequence and then cuts out the 20-mer adjacent to the PAM using type IIS and type III restriction enzymes to create a gRNA library. The described approach does not require prior knowledge about the target DNA sequences, making it applicable to any species.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube
- 0.2 ml PCR tube
- Disposable pipette tip
- OligodT column (QIAGEN, supplemented with the Oligotex mRNA Mini Kit [QIAGEN, catalog number: 70022 ])
- STBL4 electro-competent cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11635018 )
- Lentiviral vector
lentiCRISPR v2 (Sanjana et al., 2014) (Addgene, catalog number: 52961 ) - Oligonucleotides
Semi-random primer p NNNCCN
5’ switching mechanism at RNA transcript (SMART) tagTGGTCAAGCTTCAGCAGATCTACACGGACGTCGCrGrGrG
5’ SMART PCR primer TGGTCAAGCTTCAGCAGATCTACACG
3’ linker I forward p CTGCTGACTTCAGTGGTTCTAGAGGTGTCCAA
3’ linker I reverse GTTGGACACCTCTAGAACCACTGAAGTCAGCAGT
5’ linker I forward GCATATAAGCTTGACGTCTCTCACCG
5’ linker I reverse p NNCGGTGAGAGACGTCAAGCTTATATGC
3’ linker II forward p GTTTGGAGACGTCTTCTAGATCAGCG
3’ linker II reverse CGCTGATCTAGAAGACGTCTCCAAACNN
3’ linker I PCR primer GTTGGACACCTCTAGAACCACTGAAGTCAGCAGTNNNCC
3’ linker II PCR primer CGCTGATCTAGAAGACGTCTCCAAAC
LentiCRISPR forward CTTGGCTTTATATATCTTGTGGAAAGGACG
LentiCRISPR reverse CGGACTAGCCTTATTTTAACTTGCTATTTCTAG - TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15596026 )
- Phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol 25:24:1 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2069-100ML )
- Ethanol
- RNase-free water
- Oligotex mRNA Mini Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 70022 )
- T4 DNA ligase reaction buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: B0202S )
- SMART Scribe reverse transcriptase (Takara Bio, Clontech, catalog number: 639536 )
- DTT (Takara Bio, supplemented with SMART Scribe reverse transcriptase [Takara Bio, Clontech, catalog number: 639536 ])
- dNTP mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 18427013 )
- RNaseOUT (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 10777019 )
- RNase H (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 18021014 )
- MilliQ water
- Advantage 2 polymerase mix (Takara Bio, Clontech, catalog number: 639201 )
- QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28104 )
- Quick Ligation Kit (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M2200S )
- EcoP15I (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0646S )
- BglII (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0144S )
- AcuI (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0641S )
- XbaI (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0145S )
- BsmBI (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0580S )
- AatII (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0117S )
- 10-bp ladder
- 1x CutSmart buffer (included in XbaI [New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0145S ])
- S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) (New England Biolabs, supplemented with AcuI [New England Biolabs])
- 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.5) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9740 )
- Acrylamide/Bis solution (19:1) (40 % w/v, 5 % C) (SERVA Electrophoresis, catalog number: 10679.01 )
- Glycogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: R0561 )
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: Q32851 )
- TE buffer (pH 8.0) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, models: 5424 R , 5810 R )
- Heating block
- Glass beaker
- GeneAmp PCR System 9700 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: GeneAmp PCR System 9700 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Vertical Electrophoresis Cell (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Vertical Electrophoresis Cell )
- GenePulser II (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: Gene Pulser II )
- High Performance Laboratory Incubator–Mod. 2800 (F.lli GALLI, model: MOD. 2800 )
- CLC Genomics Workbench (QIAGEN, model: CLC Genomics Workbench )
- Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies)
- Autoclave
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Arakawa, H. (2017). A Method to Convert mRNA into a Guide RNA (gRNA) Library without Requiring Previous Bioinformatics Knowledge of the Organism. Bio-protocol 7(10): e2319. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2319.
分类
分子生物学 > DNA > 基因表达
系统生物学 > 基因组学 > 测序
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link


.jpg)