- EN - English
- CN - 中文
ELISPOT Assay to Measure Peptide-specific IFN-γ Production
采用ELISPOT测定法测定肽特异性IFN-γ的生成
发布: 2017年06月05日第7卷第11期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2302 浏览次数: 20464
评审: Ivan ZanoniPer AndersonAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
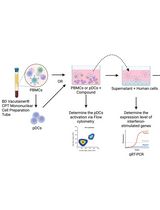
基于人外周血单个核细胞(PBMCs)和浆细胞样树突细胞(pDCs)的宿主靶向抗病毒药物(HTA)筛选方案
Zhao Xuan Low [...] Pouya Hassandarvish
2025年03月05日 3049 阅读
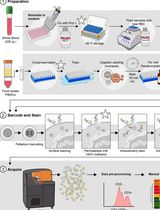
用于比较人冷冻保存 PBMC 与全血中 JAK/STAT 信号通路的双磷酸化 CyTOF 流程
Ilyssa E. Ramos [...] James M. Cherry
2025年11月20日 2282 阅读
Abstract
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is crucial for immunity against intracellular pathogens and for tumor control. It is produced predominantly by natural killer (NK) and natural killer T cells (NKT) as well as by antigen-specific Th1 CD4+ and CD8+ effector T cells. When investigating immune responses against pathogens and cancer cells, measuring antigen-specific cytokine-responses by cells of adaptive immunity offers an advantage over total non-specific cytokine responses. Significantly, the measurement of antigen-specific IFN-γ responses against pathogens or cancer cells, when compared to a treatment group, provides a quantitative measure of how well the treatment works. Measuring antigen-specific IFN-γ responses involves culture of the cells being considered (CD4+ or CD8+ T cells) with antigen presenting cells (APC) and a specific peptide from the target pathogen or cancer cell compared to control cultures without a peptide. After a suitable timeframe, the cytokine released is measured by an ELISPOT assay. The difference in the number of cells secreting IFN-γ, with and without peptide, is a measure of antigen-specific IFN-γ responses. This assay can be applied to other cytokines such as IL-10.
Keywords: IFN-gamma (IFN-γ)Background
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons (Gray and Goeddel, 1982). IFN-γ has anti-pathogen, immuno-regulatory, and anti-tumor properties (Schroder et al., 2004) which promotes NK cell activity, increase in antigen presentation, activates inducible nitric oxide synthase, induces the production of IgG2a from activated plasma cells and promotes Th1 differentiation by up-regulating the transcription factor T-bet.
Given the significant role of this cytokine in immune responses, there are several protocols to quantify IFN-γ. Perhaps the simplest measure is an ELISA assay which is used to measure levels of the cytokine in serum samples and tissue culture supernatants by capturing the cytokine with antibodies (Schreiber, 2001). There is also a flow cytometry based-assay where intracellular IFN-γ is detected by flow cytometry following cell-permeabilization (Andersson et al., 1988). The percentage of cells containing the cytokine is usually low, and does not indicate if the protein is functional, if it would be secreted and does not measure if it is in response to a specific target antigen or multiple antigens.
To measure IFN-γ responses to specific antigens, culture assays were developed. Here, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were stimulated in culture with APC and peptides from the target protein and the supernatants were tested by ELISA for IFN-γ levels (Bradley et al., 1991). Recently, instead of ELISA, several commercial flow cytometry-based bead array assays (e.g., BD Biosciences) are available which offer greater sensitivity to detect low cytokine levels at the nanogram level. However, while the assay can quantify total cytokine secreted, it does not differentiate between a few cells producing a lot of cytokine from a large number of cells secreting little cytokine. The number of cells secreting the cytokine quantifies the number of cells committed to a specific target of immunity. Thus, the enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay is a highly sensitive immunoassay that measures the frequency of cytokine-secreting cells at the single-cell level. An antigen-specific ELISPOT assay allows the quantification of the number of a specific cell type (CD4+ or CD8+ T cells) which secretes IFN-γ in response to a specific antigen (Carvalho et al., 2001; Schmittel et al., 2001)
The IFN-γ–specific antibody on an ELISPOT plate captures the IFN-γ immediately after secretion from the cells with a limit of detection typically around 1 in 100,000 cells. The high sensitivity of the assay makes it particularly useful for studies of the small population of cells found in specific immune responses (Horne-Debets et al., 2013 and 2016; Karunarathne et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- Nitrile gloves
- Sterile 15 ml and 50 ml polypropylene tubes
- Disposable sterile pipettes: 2 ml, 5 ml, 10 ml, 25 ml
- Filters for syringes: 0.45 μM and/or 0.22 μM
- Multiscreen HTS-IP plates (PVDF membrane) (Merck, catalog number: MSIPS4510 )
- Mouse (BioLegend, catalog number: 575402 ) or human (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: PHC0026 ) recombinant IL-2
- Microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec)
Note: Catalog numbers depend on the cell type to be tested. - Dynabeads magnetic beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA, https://www.thermofisher.com/kr/en/home/brands/product-brand/dynal.html)
Note: Catalog numbers depend on the cell type tested. - Ethanol
- Peptides or antigen from the protein of choice to stimulate antigen-specific IFN-γ
- Rat anti-mouse IFNγ mAb, clone AN18, purified (capture) (50 μg, Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBioscienceTM, catalog number: 14-7313-81 or 500 μg, Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBioscienceTM, catalog number: 14-7313-85 ) mouse anti-human IFNγ mAb, p clone NIB42, purified (capture) (50 μg, BioLegend, catalog number: 502403 or 500 μg, BioLegend, catalog number: 502404 )
Note: Either titrate or use as recommended by manufacturer. Prepare immediately before coating wells. - Rat anti-mouse IFNγ mAb, clone R4-6A2, biotinylated (detection) (50 μg, Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBioscienceTM, catalog number: 13-7312-81 or 500 μg, Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBioscienceTM, catalog number: 13-7312-85 ) or mouse anti-human IFNγ mAb, clone 4S.B3, biotinylated (detection) (50 μg, BioLegend, catalog number: 502503 or 500 μg, BioLegend, catalog number: 502504 )
Note: Either titrate or use as recommended by manufacturer. - 0.5% BSA
- Streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (BioLegend, catalog number: 405210 )
- 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole (AEC) substrate/chromogen (BD, catalog number: 551951 )
- Milli-Q water
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4)
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
- Sodium phosphate (Na2CO3)
- IMDM-1640
- Fetal calf serum (FCS)
Note: Any brand that is suitable for cell culture and is heat inactivated at 56 °C for 30 min. - Penicillin-streptomycin (Tissue culture grade; Life technologies)
- β-mercaptoethanol
- Tween 20 (store at room temperature)
- IMDM culture medium
- L-glutamine (Tissue culture grade; Life technologies)
- Phytohemagglutinin-L (PHA, positive control) stock (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11249738001 ). Refer to Recipes section for details
- Sterile phosphate buffered saline (1x PBS) (see Recipes)
- Coating buffer working solution (see Recipes)
- Blocking solution (see Recipes)
- Anti-IFN-γ capture working solution (see Recipes)
- Biotin-anti-IFN-γ working solution (see Recipes)
- Streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase working solution (see Recipes)
- Tween 20 working solution (see Recipes)
- 10% fetal calf serum in IMDM culture medium (see Recipes)
- PHA stock solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
Note: ELISPOTS on the plate can be manually counted under a dissection microscope, or stereomicroscope (For example, Greenough, high-performance zoom stereomicroscope, SMZ 168-series). Alternatively, there are several specialist automated systems for high throughput screening (AELVIS, Autoimmun Diagnostika, Bio-Sys, Cellular Technology and the Zeiss reader) and there pros and cons discussed elsewhere and beyond the scope of this protocol (Janetzki et al., 2015).
- Waste container
- Gilson pipette and tips: P-2, P-10, P-20, P200, P1000
- Gilson multichannel pipette with matched tips
- Beckman Allegra 12 refrigerated centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Allegra X-12 )
- Class II biohazard hood
- Incubator
- 1 L bottles
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Wykes, M. N. and Rénia, L. (2017). ELISPOT Assay to Measure Peptide-specific IFN-γ Production. Bio-protocol 7(11): e2302. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2302.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫细胞功能 > 细胞因子
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 蛋白质分泌
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link