- EN - English
- CN - 中文
RNase Sensitivity Screening for Nuclear Bodies with RNA Scaffolds in Mammalian Cells
哺乳动物细胞中含RNA支架的核体的核糖核酸酶敏感性筛选
发布: 2017年04月20日第7卷第8期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2232 浏览次数: 10809
评审: Gal HaimovichAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

自动层次分析(ALAn):用于无偏见表征培养中哺乳动物上皮结构的图像分析工具
Christian Cammarota [...] Tara M. Finegan
2024年04月20日 4233 阅读
Abstract
The mammalian cell nucleus is highly organized and contains membraneless nuclear bodies (NBs) characterized by distinct resident factors. The NBs are thought to serve as sites for biogenesis and storage of certain RNA and protein factors as well as assembly of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Some NBs are formed with architectural RNAs (arcRNAs) as their structural scaffolds and additional NBs likely remain unidentified in mammalian cells. Here, we describe an experimental protocol to search for new NBs built on certain arcRNAs. RNase-sensitive NBs were identified by monitoring nuclear foci visualized by tagging thousands of human cDNA products.
Keywords: Nuclear bodies (核体)Background
The mammalian cell nucleus is highly organized and composed of multiple distinct substructures called nuclear bodies (NBs). So far ~15 NBs have been identified as subnuclear membraneless granular structures containing various proteins and RNA factors, many of which function as sites of biogenesis, maturation, storage, and sequestration of specific RNAs, proteins, and/or ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes (Mao et al., 2011; Sleeman and Trinkle-Mulcahy, 2014) (Table 1).
Table 1. Nuclear bodies in mammalian cells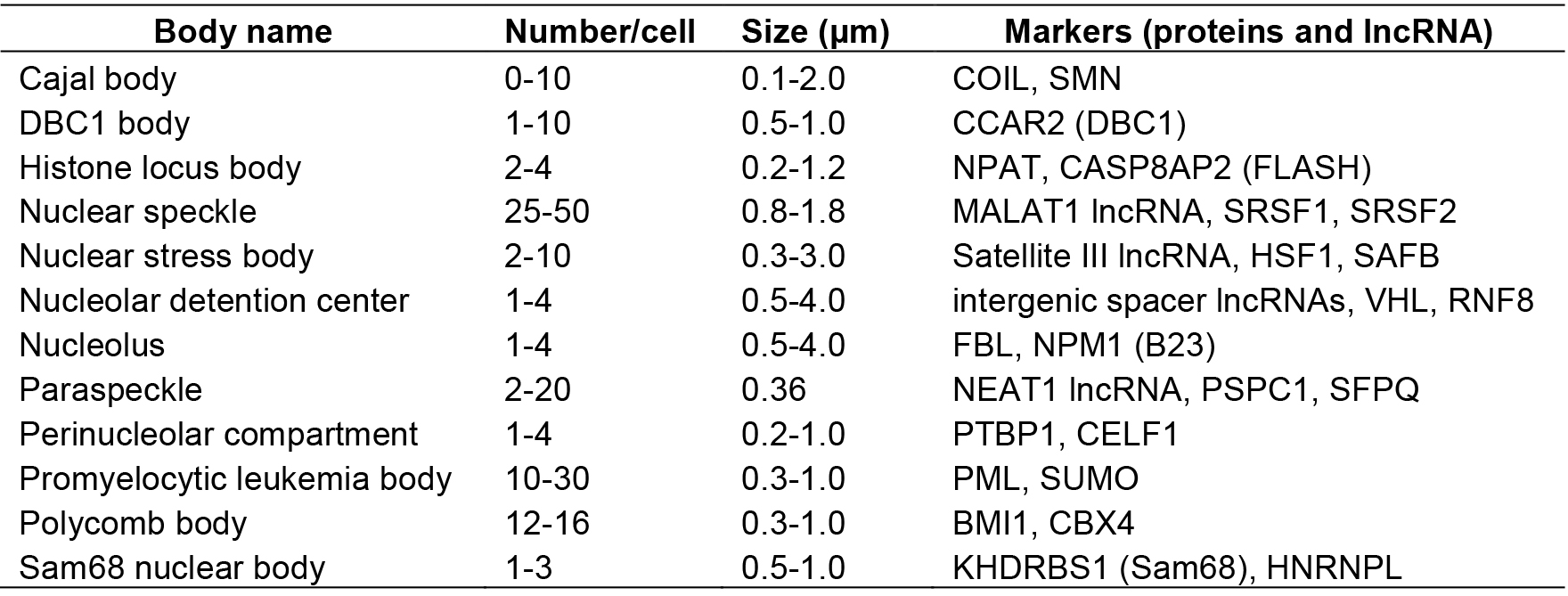
Some NBs are constructed on specific long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) called architectural RNAs (arcRNAs), which are defined as structural core of NBs (Chujo et al., 2016). The arcRNA-dependent NBs are composed of numerous RNA-binding proteins that interact with the arcRNAs. The most remarkable example is the paraspeckle, which is composed of several characteristic RNA-binding proteins (Fox et al., 2002; Prasanth et al., 2005). RNase treatment disintegrates the paraspeckle structure (Fox et al., 2005). Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1), a lncRNA, localizes exclusively to paraspeckles and acts as an arcRNA of these massive RNP complexes (Chen and Carmichael, 2009; Clemson et al., 2009; Sasaki et al., 2009; Sunwoo et al., 2009).
Presently, two lncRNAs are classified as arcRNAs in addition to NEAT1, namely, intergenic spacer lncRNAs for nucleolar detention center (Audas et al., 2012) and human satellite III lncRNA for nuclear stress body (Biamonti and Vourc’h, 2010) (Table 1). It is expected that additional arcRNAs remain to be characterized in mammalian cells. Here, we describe a novel method called ‘RNase sensitivity screening’ to identify novel arcRNA-dependent NBs by screening for nuclear foci whose structures are disintegrated by RNase treatment. This method employed a Venus-tagged human full-length (FLJ) cDNA library (32,651 clones), which was originally constructed during the NEDO full-length human cDNA sequencing project in Japan (FLJ-PJ), and obtained 571 cDNA clones whose products (463 proteins) localize in certain nuclear foci (Hirose and Goshima, 2015; Naganuma et al., 2012). We explored whether the respective nuclear focus was abolished or diffused upon RNase treatment after cell permeabilization to select candidate RNase-sensitive nuclear foci that potentially contain arcRNAs (Figure 1). We identified 32 Venus-tagged proteins that required RNA for their localization in distinct nuclear foci (Mannen et al., 2016). Immunostaining of the corresponding endogenous proteins confirmed that the Sam68 nuclear body (SNB) was an RNase-sensitive NB. In the following protocol, we describe the detailed procedure of the RNase sensitivity screening. This protocol is for screening for RNase-sensitive NBs under normal conditions in HeLa cells, but it should be applicable to other cell lines under various conditions.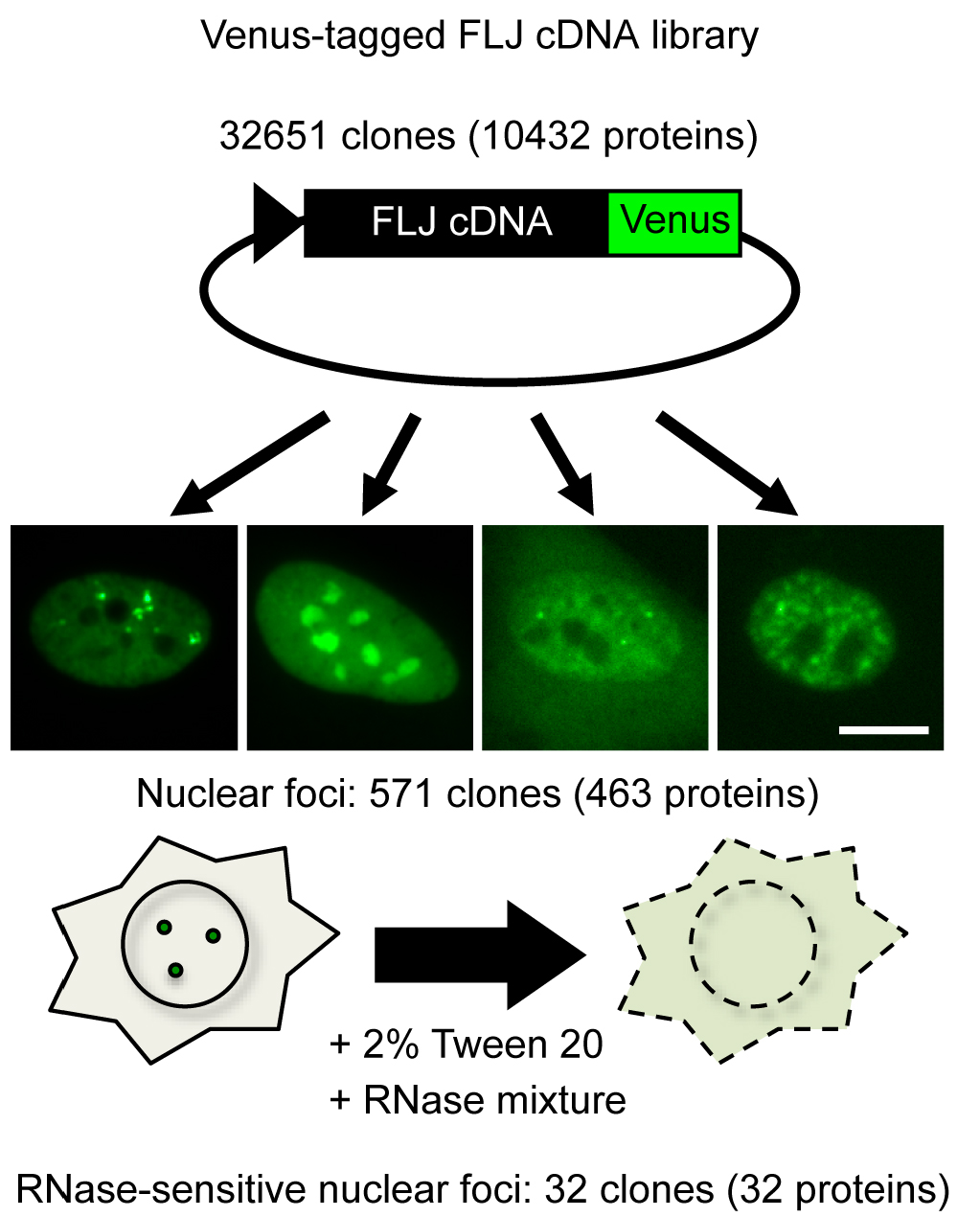
Figure 1. Outline of RNase sensitivity screening of NBs. Venus-tagged human FLJ cDNA clones were transfected into HeLa cells. cDNA clones whose products localized to certain nuclear foci were selected (571 clones). Subsequently, the RNase sensitivity of the nuclear foci labeled by Venus was investigated (32 clones). To this end, the cells were permeabilized with 2% Tween 20, followed by treatment with an RNase mixture. Bar = 10 μm.
Materials and Reagents
Note: Prepare all solutions using ultrapure water (prepared by purifying deionized water to attain a sensitivity of 18.2 MΩ cm at 25 °C) and analytical grade reagents.
- Preparation of collagen IV-coated plate
- Pipette tips (Labcon, catalog number: 1030-260-000 )
- 96-well glass bottom microplate (IWAKI, catalog number: 12-017-006 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 190-14565 )
- Phosphate Buffered Salts (PBS) (Takara Bio, catalog number: T900 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 080-01066 )
- Type IV collagen solution (Life Laboratory Company, catalog number: LL-10043 )
- Collagen solution (see Note 1; see Recipes)
- Pipette tips (Labcon, catalog number: 1030-260-000 )
- Cell culture
- HeLa (Human cervical cancer) cells (see Note 2)
- 10 cm dish
- MEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11095080 ) (see Note 3)
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 26140079 )
- Trypsin-EDTA (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 32778-34 )
- HeLa (Human cervical cancer) cells (see Note 2)
- Administration of plasmids with transfection reagent
- 96-well U-bottom plate (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 351177 )
- Venus-tagged human FLJ cDNA clone plasmids expressing proteins localized to certain nuclear foci (see Note 4)
- TransIT-LT1 reagent (Mirus Bio, catalog number: MIR2300 )
- Opti-MEM I reduced serum medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 31985070 )
- 96-well U-bottom plate (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 351177 )
- RNase treatment
- 96-well plate sealing film (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 12261012 )
- 0.45 μm filter
- RiboShredder RNase Blend (Epicentre, catalog number: RS12500 )
- Polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20) (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 28353-85 )
- 2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol (Tris) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 011-20095 )
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 20909-55 )
- Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 08907-42 )
- cOmplete, EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11873580001 )
- Paraformaldehyde (PFA) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 1.04005.1000 )
- DAPI (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D9542 )
- Pyronin Y (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9172 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 (see Recipes)
- Permeabilization buffer (see Recipes)
- 4% PFA (see Note 5; see Recipes)
- DAPI solution (see Recipes)
- Pyronin Y solution (see Recipes)
- 96-well plate sealing film (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 12261012 )
Equipment
- Multichannel pipette L8 x 200 (Gilson, catalog number: FA10011 )
- Water bath (Fine, catalog number: FWB-21B )
- Centrifuge (KUBOTA, catalog number: 040-000 )
- Hemocytometer (SANSYO, SLGC, catalog number: A103 )
- Reservoir (BM Equipment, catalog number: BM-0850-2 )
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) incubator (SANYO, catalog number: MCO-18AIC UV )
- IN Cell Analyzer 1000 (GE Healthcare, model: IN Cell Analyzer 1000 ) equipped with a Plan Fluor ELWD 40x/0.6 objective lens (Nikon Instruments, model: CFI Plan Fluor 40x ). Excitation filters for DAPI (D360/40x) and Venus (S475/20x) and emission filters for DAPI (HQ460/40M) and Venus (HD535/50M) were used. Acquisition and processing of the images were done using IN Cell Analyzer 1000 Software (GE Healthcare, version 3.0)
Software
- IN Cell Analyzer 1000 Software (GE Healthcare, version 3.0)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Mannen, T. and Hirose, T. (2017). RNase Sensitivity Screening for Nuclear Bodies with RNA Scaffolds in Mammalian Cells. Bio-protocol 7(8): e2232. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2232.
-
Mannen, T., Yamashita, S., Tomita, K., Goshima, N. and Hirose, T. (2016). The Sam68 nuclear body is composed of two RNase-sensitive substructures joined by the adaptor HNRNPL. J Cell Biol 214(1): 45-59.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 固定细胞成像
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










