- EN - English
- CN - 中文
In vivo Mitophagy Monitoring in Caenorhabditis elegans to Determine Mitochondrial Homeostasis
秀丽隐杆线虫中的体内线粒体自噬监测以确定线粒体稳态
发布: 2017年04月05日第7卷第7期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2215 浏览次数: 11429
评审: Jyotiska ChaudhuriPia GiovannelliAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Perturbation of mitochondrial function is a major hallmark of several pathological conditions and ageing, underlining the essential role of fine-tuned mitochondrial activity (Lopez-Otin et al., 2013). Mitochondrial selective autophagy, known as mitophagy, mediates the removal of dysfunctional and/or superfluous organelles, preserving cellular and organismal homeostasis (Palikaras and Tavernarakis, 2014; Pickrell and Youle, 2015; Scheibye-Knudsen et al., 2015). In this protocol, we describe a method for assessing mitophagy in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
Keywords: Ageing (衰老)Background
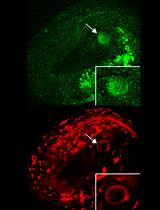
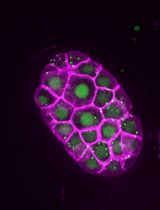
Mitochondria are characterized as cellular powerhouses of eukaryotic cells, since they are the major energy providers through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and ATP generation. Moreover, their pivotal role in cellular homeostasis is highlighted by their contribution in the regulation of several fundamental cellular processes including calcium buffering, metabolite synthesis and apoptosis, among others. Deregulation of mitochondrial function is associated with the onset of several pathological conditions including ageing and age-related neurodegenerative diseases (Vafai and Mootha, 2012; Palikaras and Tavernarakis, 2014). Thus, eukaryotic organisms have evolved several complex and highly specialized molecular pathways to guard energy homeostasis (Pickrell and Youle, 2015; Scheibye-Knudsen et al., 2015). Mitophagy is a selective type of autophagy promoting the elimination of impaired mitochondria, and the major degradation pathway by which cells regulate mitochondrial content in response to intracellular and environmental signals (Palikaras et al., 2015; Schiavi et al., 2015; Fang et al., 2016). In this protocol, we describe two methods for monitoring mitophagy in C. elegans. We developed two composites, in vivo imaging systems to asses mitophagy based, first, on the Rosella biosensor (Rosado et al., 2008), which combines a fast-maturing pH-insensitive DsRed fused to a pH-sensitive GFP variant, and second, on a custom, dual-fluorescence reporter system that involves a mitochondria-targeted GFP, together with the autophagosomal marker LGG-1/LC3 fused to DsRed. These protocols facilitate non-invasive monitoring of mitophagy in live specimens.
Materials and Reagents
- Greiner Petri dishes (60 x 15 mm) (Greiner Bio One International, catalog number: 628161 )
- Microscope slides 75 x 25 x 1 mm (Marienfeld-Superior, catalog number: 10 006 12 )
- Microscope cover glass 18 x 18 mm (Marienfeld-Superior, catalog number: 01 010 30 )
- Use the following transgenic nematodes to monitor mitophagy: IR1631: N2;Ex003 [pmyo-3TOMM-20::Rosella; pRF4], R1284: N2;Is [pmyo-3mtGFP];Ex011 [plgg-1DsRed::LGG-1; pmyo-2GFP])
- Escherichia coli OP50 strain (obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center)
- 70% of EtOH
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 104873 )
- di-Potassium hydrogen phosphate (K2HPO4) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 137010 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106404 )
- Peptone (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 211677 )
- Streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6501 )
- Agar (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 05040 )
- Cholesterol stock solution (SERVA Electrophoresis, catalog number: 17101.01 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C5080 )
- Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M7506 )
- Nystatin stock solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N3503 )
- di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106586 )
- Levamisole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L9756 )
- Paraquat (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 856177 )
- Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C2759 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide cell culture grade BC (DMSO) (AppliChem, catalog number: A3672,0250 )
- Phosphate buffer (1 M; sterile, see Recipes)
- Nematode growth medium (NGM) agar plates (see Recipes)
- M9 buffer (see Recipes)
- Levamisole (0.5 M, see Recipes)
- M9-levamisole solution (20 mM solution, see Recipes)
- Paraquat (0.5 M, see Recipes)
- Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (49 mM; CCCP, see Recipes)
Equipment
- UV crosslinker (Vilber Lourmat, model: BIO-LINK – BLX-E365 )
- Zeiss AxioImager Z2 epifluorescence microscope (Zeiss, model: Zeiss AxioImager Z2 )
- Olympus DP71 CCD camera (Olympus, model: Olympus DP71 )
- Zeiss AxioObserver Z1 confocal microscope (Zeiss, model: Zeiss AxioObserver Z1 )
- Dissecting stereomicroscope (Olympus, model: SMZ645 )
- Incubators for stable temperature (AQUA®LYTIC incubator 20 °C)
Software
- Olympus CELL-A software
- Zeiss ZEN 2012 software
- Image J (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/)
- Microsoft Office 2011 Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, USA)
- GraphPad Prism software package (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, USA)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Palikaras, K. and Tavernarakis, N. (2017). In vivo Mitophagy Monitoring in Caenorhabditis elegans to Determine Mitochondrial Homeostasis. Bio-protocol 7(7): e2215. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2215.
分类
发育生物学 > 细胞信号传导 > 能量平衡
发育生物学 > 细胞信号传导 > 线粒体自噬
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 活细胞成像
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link