- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Ribosomal RNA N-glycosylase Activity Assay of Ribosome-inactivating Proteins
核糖体灭活蛋白的核糖体RNA N-糖基化酶活性测定
发布: 2017年03月20日第7卷第6期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2180 浏览次数: 12268
评审: Zhaohui LiuTzvetina BrumbarovaFeng Li
Abstract
Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) are enzymes that irreversibly inactivate ribosomes as a consequence of their N-glycosylase (EC 3.2.2.22) activity. The enzyme cleaves the N-glycosidic bond between the adenine No. 4324 from the 28S rRNA and its ribose in rat ribosomes (or the equivalent adenine in sensitive ribosomes from other organisms). This adenine is located in the α-sarcin-ricin loop (SRL) that is crucial for anchoring the elongation factor (EF) G and EF2 on the ribosome during mRNA-tRNA translocation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, respectively. RIPs have been isolated mainly from plants and examples of these proteins are ricin or Pokeweed Antiviral Protein (PAP). These proteins, either alone or as a part of immunotoxins, are useful tools for cancer therapy. The following protocol describes a method to detect the RNA fragment released when the RIP-treated apurinic RNA from rabbit reticulocyte lysate is incubated in the presence of acid aniline by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels. The fragment released (Endo’s fragment) is diagnostic of the action of RIPs.
Keywords: Ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) (核糖体灭活蛋白(RIP))Background
N-glycosylase activity of RIPs on the eukaryotic 28S rRNA was first described by Endo and Tsurugi for ricin (Endo and Tsurugi, 1988) in rat ribosomes; subsequently it was shown that some RIPs can also depurinate ribosomes from plants, bacteria and fungi. The result of this effect, upon treatment with aniline, is the release of an RNA fragment of between 240 and 500 nucleotides (depending on species) from the rRNA of the large subunit (Figure 1). Most RIPs depurinate ribosomes at one site (the adenine 4,324), whereas other RIPs such as saporins, PAP-R and trichokirin depurinate the rRNA at multiple sites. The protocol described here uses rabbit reticulocyte lysate, a eukaryotic cell-free model system very sensitive to the action of RIPs, which shows high rates of depurination for most RIPs. This allows obtaining a large amount of fragment which facilitates its detection by electrophoresis. In this procedure we use denaturing polyacrylamide minigels which require small quantities of sample and have higher resolution than the agarose gels when staining with fluorescent dyes.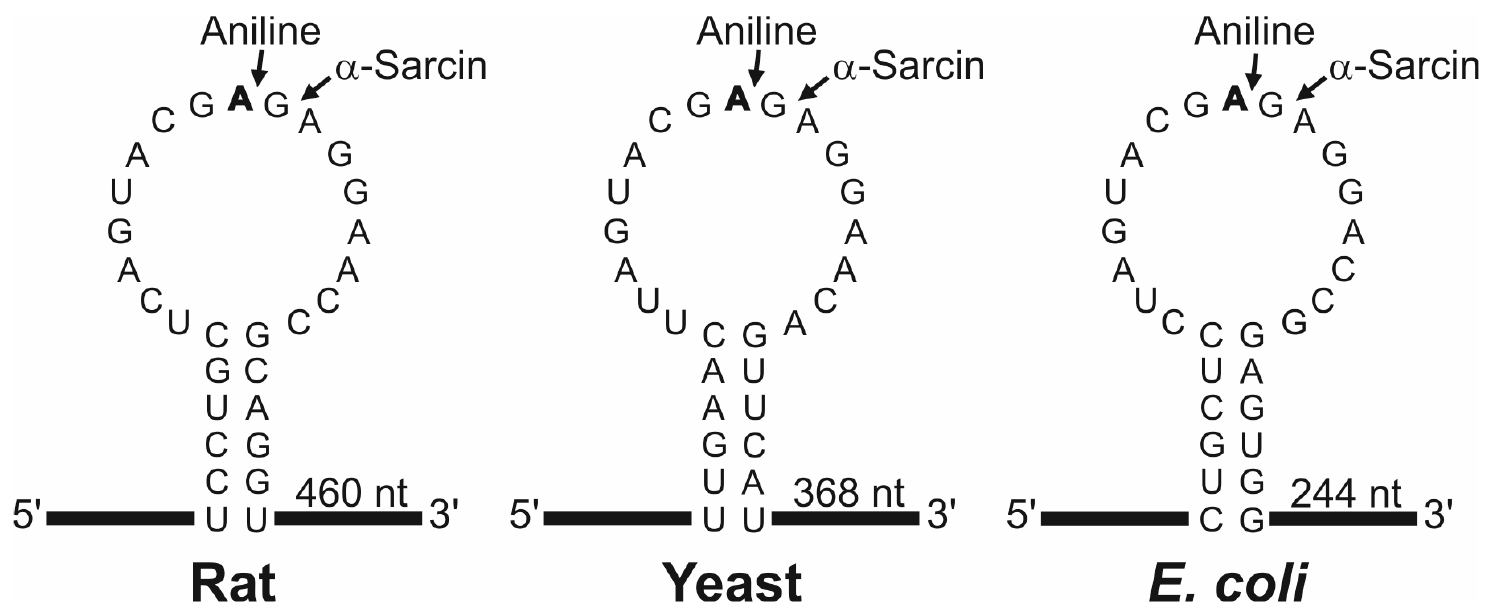
Figure 1. Sarcin Ricin Loop of the large rRNA from rat, yeast and Escherichia coli. The sequences (accession numbers NR_046246, J01355 and AB035926) were downloaded from the NCBI sequence database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/). The adenine released by the RIP action (boldfaced), the site of splitting by either the aniline or α-sarcin (arrows) and the size of the generated fragment are also indicated. Partial sequence of rabbit 28S rRNA (AF460236) indicates that rat and rabbit share the same SRL sequence.
Materials and Reagents
Note: All the reagents used in preparing buffers should be of molecular biology grade purity (RNase, DNase-free). Water and solutions should be autoclaved at 120 °C for 15 min (except of aniline and ethanol).
- Disposable gloves
- Pipettes and tips (either RNase, DNase-free or autoclaved)
- Eppendorf tubes (1.5 ml polypropylene microcentrifuge tubes, either RNase, DNase-free or autoclaved)
- Paper towels
- Corning 50 ml PP centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430291 )
- Pasteur pipettes
- Cotton swabs
- Rabbit reticulocyte lysate, untreated with micrococcal nuclease, either obtained as indicated by Pelham and Jackson (1976) or purchased from a biochemical supplier (for example: Promega, catalog number: L4151 )
- RIP either obtained as indicated by Barbieri et al. (2001) or purchased from a biochemical supplier (for example Ricin A chain: Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L9514 )
- Crushed ice
- Phenol/TRIS saturated sol., for molecular biology, stabilized, DNAse, RNAase and Protease free (ACROS Organics, catalog number: 327125000 )
- Ethanol absolute (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 100983 )
- Deionized, RNase and DNase-free water
Note: For example, Millipore Elix 5 (UV) water autoclaved 120 °C 15 min. - Aniline (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 242284 )
- Urea (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Affymetrix, catalog number: 75826 )
- Ammonium persulfate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A3678 )
- N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9281 )
- Acrylamide bis-acrylamide 19:1, 40% (w/v) solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Affymetrix, catalog number: 75848 )
- Either ethidium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E7637 ) or GelRed (Biotium, catalog number: 41003 )
- EDTA·2H2O
- NaOH pellets
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 100317 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Affymetrix, catalog number: 75819 )
- Sodium acetate trihydrate (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106267 )
- Glacial acetic acid (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 100063 )
- Diethyl pyrocarbonate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5758 )
- Diethyl ether (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 100921 )
- Trimethylol aminomethane (Tris base) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP154-1 )
- Boric acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6768 )
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 84097 )
- RNA markers (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 1062 638 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. Can be replaced by Low Range ssRNA Ladder (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N0364S ) - Bromophenol blue (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-0404 )
- 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) (see Recipes)
- 50 mM Tris/0.5% SDS (pH 7.8) (see Recipes)
- 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.2) (see Recipes)
- 70% ethanol (see Recipes)
- 2 M aniline (pH 4.5) (see Recipes)
- Water saturated ether (see Recipes)
- 10x TBE buffer (see Recipes)
- 2x gel loading buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Deep freezer (-80 °C freezer) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: TSE Series , catalog number: TSE400SSV)
- Fume hood (BURDINOLA, model: V21-Space BAJA ST 1500 )
- Two microcentrifuges (DJB Labcare, model: Heraeus Biofuge Pico , catalog number: 75003235), one of them kept at 4 °C
- 30 °C water bath (JP SELECTA, catalog number: 6000140 )
- Vortex mixer for test tubes (IKA, catalog number: 0003617000 )
- BECKMAN DU-640 spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, model: DU-640 )
- Quartz cuvette (Hellma Analytics, model: 104-QS , catalog number: 104-10-40)
- Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 80-6418-77 )
- Power supply (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 18-1130-01 )
- Molecular Imager® Gel DocTM XR+ System with Image LabTM Software (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1708195 )
- Gel staining tray
- Magnetic stirrer
- Autoclave (JP SELECTA, catalog number: 4002516 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Iglesias, R., Citores, L. and Ferreras, J. M. (2017). Ribosomal RNA N-glycosylase Activity Assay of Ribosome-inactivating Proteins. Bio-protocol 7(6): e2180. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2180.
分类
植物科学 > 植物分子生物学 > 蛋白质
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 抗微生物分析
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link














