- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Secretion Rates of Single Cells
单细胞外泌体分泌速率的定量分析
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2017年02月20日第7卷第4期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2143 浏览次数: 13445
评审: Gal HaimovichShalini Low-NamMarco Di Gioia
Abstract
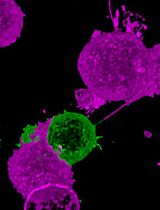
To study the inhomogeneity within a cell population including exosomes properties such as exosome secretion rate of cells and surface markers carried by exosomes, we need to quantify and characterize those exosomes secreted by each individual cell. Here we develop a method to collect and analyze exosomes secreted by an array of single cells using antibody-modified glass slides that are position-registered to each single cell. After each collection, antibody-conjugated quantum dots are used to label exosomes to allow counting and analysis of exosome surface proteins. Detailed studies of exosome properties related to cell behaviors such as responses to drugs and stress at single cell resolution can be found in the publication (Chiu et al., 2016).
Keywords: Single cell (单细胞)Background
Exosomes have been found to play an essential role in tumorigenesis, cell-cell signaling, organotropic metastasis, drug resistance, and many crucial biological processes involving cell-cell communications. Most exosome isolation methods developed to date use ultracentrifugation at 100,000 x g (Théry et al., 2006) and require a large amount of samples. Combinations of microfluidics with immunological separation or physical trap have been reported (Liga et al., 2015) as simpler exosome isolation methods requiring a relatively small amount of sample. However, most microfluidic platforms have difficulties in integration of standard cell culture protocols, while cell culture in microfluidic environments can introduce new variables and unintended stresses to cells and change their behaviors and gene expressions. Above all, all existing approaches collect exosomes from cells without distinction, so it is extremely difficult to trace exosomes to the cells that secrete them. However, given the high diversity and inhomogeneity of biological samples, it is of great value to correlate the exosomes to the cell source. Furthermore, it is highly desirable to quantify the exosome analysis at a single cell level by finding the changes in exosome properties and secretion rates when cells are affected by stimuli, stresses and/or environmental changes. Here we provide a culture friendly, high-throughput, and versatile single-cell assay that enables quantitative analysis of exosomes secreted by individual cells.
Materials and Reagents
- 35 mm Petri dish (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 351008 )
- Cover glass (Ted Pella, catalog number: 260364 )
- Glass slides
- Silicon wafer (4” test grade) (University Wafer, catalog number: 452 )
- Acrylic (PMMA, 2 mm thick) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: GF10188996 )
- 35 mm cell culture dish (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D7804 )
- Parafilm (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7793 )
- Aluminum foil
- 0.22 µm filter
- Cells
Note: Our protocol can be used for both adherent and non-adherent cells. For examples, MCF7, MB-MDA-231, MCF10A, Neuronspheres, etc. - Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) (Dow Corning, catalog number: SYLGARD® 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit )
- Pure ethanol (Decon Labs, catalog number: V1001 )
- (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPS) (Gelest, catalog number: 4420-74-0 )
- Sulfo-GMBS, N-[γ-maleimidobutyryloxy]sulfosuccinimide ester (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 22324 )
- Phosphate-buffered salines (PBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10010023 )
- Monoclonal anti-human CD63 antibody (Ancell, catalog number: 215-820 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA power) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A8531 )
- Paraformaldehyde solution (4% in PBS) (Affymetrix, catalog number: 19943 1 LT )
- Biotinylated anti-CD63 (Ancell, catalog number: 215-030 )
- Qdot® incubation buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: Q20001MP )
- Quantum dots (Qdot® 545 ITKTM) streptavidin conjugate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: Q10091MP )
- Tris buffered saline with Tween® 20 (TBST-10x) (Cell Signaling Technology, catalog number: 9997 )
- DI water
- Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
- Blocking buffer for Qdot (see Recipes)
- 1x TBST (see Recipes)
Equipment
- CNC (Computer Numeric Control) micro milling machine (Minitech Machinery, model: Mini/Mill/1 )
- Disco automatic dicing saw 3220 (Nano3, model: 3220)
- Plasma Etch system (for cleaning) (Plasma Etch, model: PE-100 )
- Soda Lime Silica glass Petri dish (Corning, catalog number: 70165-152 )
- Standard biosafety cabinet
- Shaker (VWR, model: VWR Mini shaker )
- Oven
- 1 ml pipet
- Microscope (KEYENCE, model: BZ-9000 , similar to BZ-X700 )
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: CL2 )
- Tweezers
- Cell counter
Notes
- Equipment 1-3 can be found in core facility such as micro/nano fab. Please see Nano3 facility of UCSD as an example. Equipment 1 can also be found in most machine shop as a service.
- Centrifuge is chosen to fit 35 mm dishes. If you have a centrifuge that suit 6-well plate, 35 mm dishes can be replaced with a 6-well plate.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Chiu, Y., Cai, W., Lee, T., Kraimer, J. and Lo, Y. (2017). Quantitative Analysis of Exosome Secretion Rates of Single Cells. Bio-protocol 7(4): e2143. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2143.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞器分离 > 外来体
细胞生物学 > 单细胞分析 > 微流体
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 活细胞成像
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link