- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Rice Root Organic Acid Efflux Measurement by Using Ion Chromatography
采用离子色谱法测定水稻根有机酸分泌
发布: 2017年02月20日第7卷第4期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2141 浏览次数: 9129
评审: Arsalan DaudiWan-Jun ZhangAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
通过在体内直接组装多个DNA片段在青蒿中异源生产青蒿素
Nur Kusaira Khairul Ikram [...] Henrik Toft Simonsen
2023年07月20日 2322 阅读
Abstract
Organic acids secreted from plant roots play important roles in various biological processes including nutrient acquisition, metal detoxification, and pathogen attraction. The secretion of organic acids may be affected by various conditions such as plant growth stage, nutrient deficiency, and abiotic stress. For example, when white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) is exposed to phosphorus (P)-deficient conditions, the secretion of citrate acid from its proteoid roots significantly increases (Neumann et al., 1999). This protocol describes a method for the collection and measurement of the efflux of organic acids (oxalate, malate, and citrate) from the roots of rice cultivar Nipponbare (‘Nip’) under different nitrogen forms (NH4+ and NO3-), together with different P supply (+P and -P) conditions.
Keywords: Organic acids (有机酸)Background
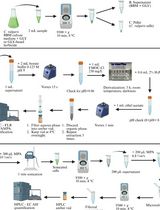
In addition to enzymatic methods (Delhaize et al., 1993) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (Chen et al., 2013), ion chromatography is another widely used method for the determination of organic acids, which has previously been employed to detect the significant increase in oxalate content in taro root exudates during Al3+ stress (Ma and Miyasaka, 1998). Compared to ion chromatography, alternative methods have their own defects. For example, enzymatic methods require the use of enzymes that can easily undergo denaturation. Moreover, it is difficult to distinguish oxalate acid from Cl- peaks by HPLC. Here, we describe a method for analyzing organic acids secreted by rice roots using ion chromatography. This method could be used in the analysis of organic acids that are secreted by other hydroponically cultivated plants.
Materials and Reagents
- 0.2 µm syringe filter (Beyotime, catalog number: FF252 )
- Rice seedlings
- Nutrient solution
- Amerlite IR-120B resin (H+ form) (Alfa Aesar, catalog number: L14285 )
- Dowex 1 x 8 resin (100-200 mesh, formate form)
- Distilled water
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258148 )
- Formic acid (HCOOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 695076 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 221465 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 223506 )
- Oxalate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 75688 )
- Malate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8304 )
- Citrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 251275 )
- 1 N HCl (see Recipes)
- 2 N HCl (see Recipes)
- 2 M HCOOH (see Recipes)
- 4 N NaOH (see Recipes)
- 0.5 mM CaCl2 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 1.25 L black plastic pot (plastic pot must be opaque, if required, wrap it in black tape)
- pH meter (Mettler Toledo, model: S40 / SG78 / SG23 / SG68 )
- Cation exchange column (16 mm x 14 cm) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: 732-1010 )
- Rotary evaporator (IKA, model: RV10 )
- Ion chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Dionex, model: ICS 3000 System )
- IonPac AS11 anion-exchange analytical column (4 x 250 mm)
- Guard column (4 x 50 mm)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Zhu, C., Zhu, X. and Shen, R. (2017). Rice Root Organic Acid Efflux Measurement by Using Ion Chromatography. Bio-protocol 7(4): e2141. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2141.
- Zhu, C. Q., Zhu, X. F., Hu, A. Y., Wang, C., Wang, B., Dong, X. Y. and Shen, R. F. (2016). Differential Effects of Nitrogen Forms on Cell Wall Phosphorus Remobilization Are Mediated by Nitric Oxide, Pectin Content, and Phosphate Transporter Expression. Plant Physiol 171(2): 1407-1417.
分类
植物科学 > 植物新陈代谢 > 其它化合物
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 其它化合物
生物化学 > 其它化合物 > 酸
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link