- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Activity-based Pull-down of Proteolytic Standard and Immunoproteasome Subunits
利用活性探针pull-down天然蛋白酶体亚基及免疫蛋白酶体亚基
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2016年12月20日第6卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2073 浏览次数: 9767
评审: Alka MehraMarielle CavroisAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

Cluster FLISA——用于比较不同细胞系蛋白表达效率及蛋白亚基聚集状态的方法
Sabrina Brockmöller and Lara Maria Molitor
2025年11月05日 1209 阅读
Abstract
Activity-based probes (ABP) are small organic molecules that irreversibly bind to the active center of a specific enzyme family and may be coupled to a fluorophore or an affinity tag (Li et al., 2013). Here, we describe a method to pull-down active catalytic standard and immunoproteasome subunits in cell lysates using the biotinylated, proteasome-specific ABP Biotin-Epoxomicin (Bio-EP). Covalent labeling of the active catalytic subunits with Bio-EP is followed by a pull-down using streptavidin-coated beads. After elution from the beads, enriched subunits may be detected via Western blot, tandem mass spectrometry (Li et al., 2013), or alternative techniques.
Keywords: Activity-based probe (基于酶活性的探针)Background
The proteasome is a barrel-shaped, multicatalytic enzyme complex that is present in the nucleus and cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is essential for protein degradation, including processing of antigenic peptides for MHC I presentation, and regulates many cellular processes (Kammerl and Meiners, 2016). In cells of hematopoietic origin, the standard (constitutive) proteasome is often replaced by the immunoproteasome (Meiners et al., 2014), which differs in the incorporation of the three distinct catalytically active β-subunits (Figure 1).
To study the molecular function of single catalytic subunits and to modulate physiological processes, the development of subunit-specific proteasome inhibitors is indispensable. Large progress has recently been made in this area by de Bruin et al. (2014). Specific immunoproteasome inhibitors have proven as potential drug candidates for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune disease. The inhibition of the immunoproteasome subunit β5i may alter cytokine production by activated monocytes and lymphocytes. In a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis, this reversed signs of the disease (Muchamuel et al., 2009).
The protocol was developed in the context of a study that investigated the effects of selective inhibition of β5i on the polarization of alveolar macrophages (Chen et al., 2016). The activity-based pull-down of catalytic standard and immunoproteasome subunits using the pan-reactive ABP Bio-EP allowed us to confirm the specific inhibition of β5i by the inhibitor ONX-0914, previously developed by ONYX Pharmaceuticals.
The use of ABPs with alternative specificity may allow for activity-based pull-down of other enzyme families in a similar experimental approach.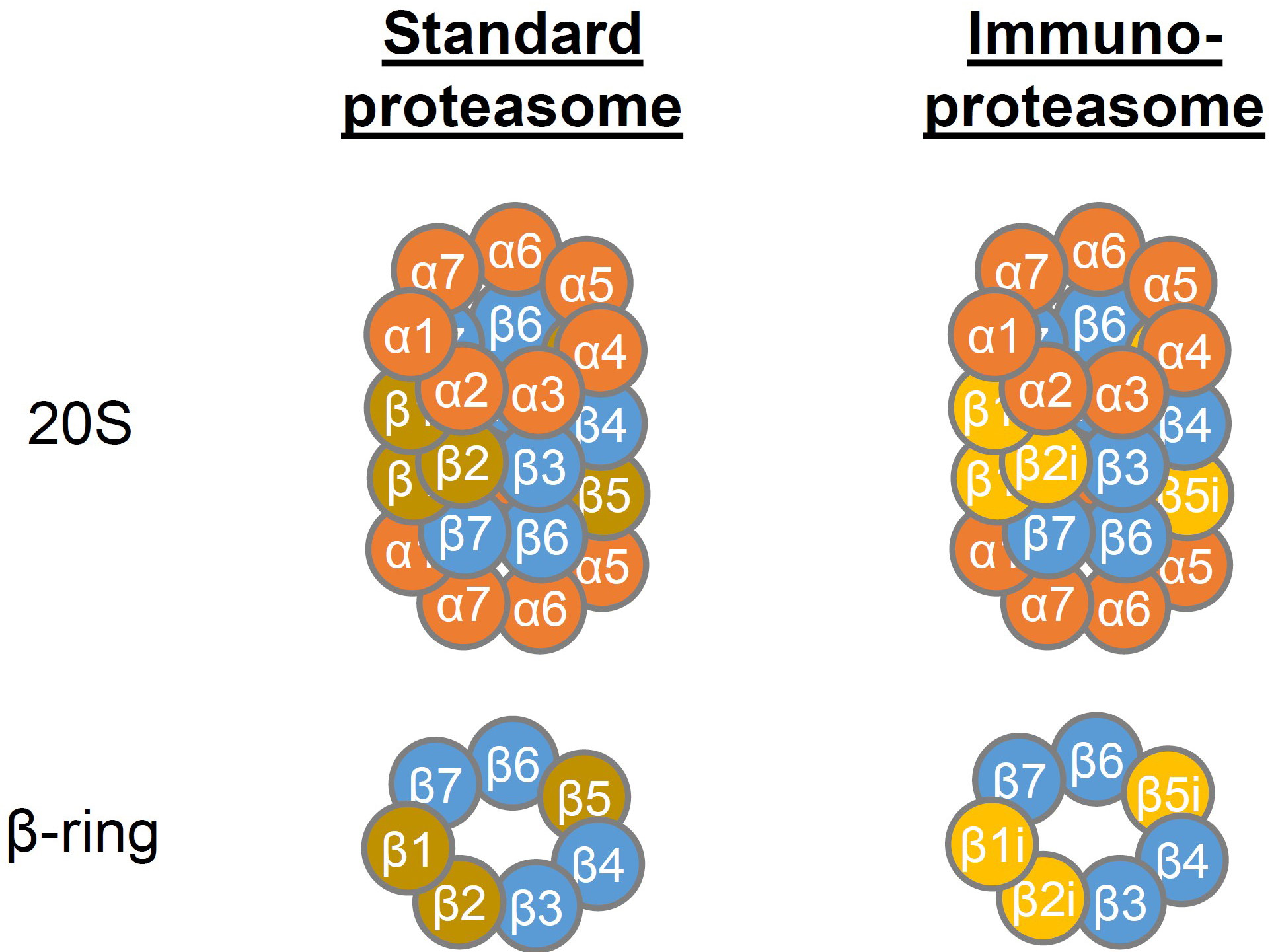
Figure 1. Structure of the 20S standard and immunoproteasome. The 20S core particle of the proteasome consists of two stacked inner rings containing the β-subunits 1-7 of which β1, β2 and β5 exhibit proteolytic activity. The β-rings are flanked by two α-rings containing the α-subunits 1-7. In the immunoproteasome β1, β2 and β5 are replaced by β1i, β2i and β5i, respectively, which leads to altered proteolytic activity.
Materials and Reagents
- 15 cm cell culture dishes
- Protein LoBind® tubes (1.7 ml tubes; OMNILAB-LABORZENTRUM, catalog number: 5409327 )
- 50 ml Falcon tube (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352070 )
- Pipette tips
- Fine Dosage Syringe Omnifix-F (1 ml) (OMNILAB-LABORZENTRUM, catalog number: 5421736 )
- 15 ml Falcon tube (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352096 )
- Immun-Blot® PVDF membrane (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 162-0177 )
- PD MidiTrap G-25 (store at RT) (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 28-9180-08 )
- Filter 0.2 µm (Sartorius, catalog number 16534-K )
- Fuji X-ray films RX, 18 x 24 cm (Kisker Biotech, model: RX1824 )
- Whatman blotting paper (Laborbedarf Lammel, catalog number: 3030690 )
- Murine alveolar macrophage cell line MH-S (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-2019 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 23225 )
- Biotin-Epoxomicin (Bio-EP; dissolved in DMSO, stable for at least 12 months at -20 °C; Hermen Overkleeft Lab, synthesis described in Florea et al., 2010)
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Carl Roth, catalog number: A994.2 )
- HEPES (Molecular biology grade) (AppliChem, catalog number: A3724,1000 )
- Ultrapure water (e.g., MilliQ)
- Streptavidin beads (Strep-Tactin® Superflow® 50% suspension; store at 4 °C) (IBA, catalog number: 2-1206-010 )
- Methanol (AppliChem, catalog number: A3493.1000 )
- Roti®-Block blocking solution (store at RT) (Carl Roth, catalog number: A151.3 )
- Anti-β5 antibody (store at -20 °C) (Abcam, catalog number: 90867 )
- Anti-β5i antibody (store at -20 °C) (Abcam, catalog number: 3329 )
- Anti-Rabbit IgG, HRP-linked antibody (store at -20 °C) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: 7074S )
- Amersham ECL prime Western blotting detection reagent (store at 4 °C) (GE Healthcare, catalog number: RPN2232 )
- RPMI-1640 cell culture medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number 11875093 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Biochrom, catalog number S 0615 )
- β-mercaptoethanol (Molecular biology grade) (AppliChem, catalog number A1108-100 )
- Penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number 15140122 )
- Tris (buffer grade) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1379,1000 )
- Magnesium chloride 6-hydrate (MgCl2.6H2O) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1036,0500 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (AppliChem, catalog number: A2942,1000 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (AppliChem, catalog number: A2937,1000 )
- Sodium azide (NaN3) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1430,0100 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (molecular biology grade) (AppliChem, catalog number: A2948,0025 )
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), disodium salt (10 g) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10127531001 )
- Glycerol (87%) (molecular biology grade) (AppliChem, catalog number: A3739,1000 )
- cOmpleteTM protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11697498001 )
- PhosSTOPTM (phosphatase inhibitor) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 4906845001 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (pure) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1502,1000 )
- Bromophenol blue (AppliChem, catalog number: A2331,0025 )
- Hydrochloric acid (fuming) (37%) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258148-2.5L )
- Rotiphorese® Gel 30 (37.5:1) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 3029.2 )
- Ammonium peroxodisulfate (APS) (AppliChem, catalog number: A0834,0250 )
- Tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) (AppliChem, catalog number: A1148,0100 )
- Tween 20 (Moleculare biology grade) (AppliChem, catalog number: A4974,1000 )
- Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (1x DPBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14190-144 )
- Complete growth medium for MH-S cells (see Recipes)
- TSDG buffer (see Recipes)
- 500 µM Bio-EP in DMSO (see Recipes)
- 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) (see Recipes)
- 10% SDS (see Recipes)
- 6x Laemmli buffer (see Recipes)
- 4x SDS-PAGE resolving buffer (pH 8.8) (see Recipes)
- 4x SDS-PAGE stacking buffer (pH 6.8) (see Recipes)
- Stacking gel (see Recipes)
- Resolving gel (15% acrylamide) (see Recipes)
- PBST (0.1% Tween) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Falcon tube centrifuge (Hettich Instruments, model: Rotina 420R )
- Table centrifuge (Hettich Instruments, model: MIKRO 200R )
- Water bath (LAUDA, model: Aqualine AL12 LCB 0725 )
- Thermomixer (Eppendorf, model: Thermomixer comfort )
- Forceps
- Pipettes
- Scissors
- Intelli-mixer rotator (ELMI, model: RM 2M )
- Western blot chambers (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: Mini PROTEAN Tetra Cell )
- Power supply (PowerPacTM Basic Power supply) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: 1645050 )
- Western blot developer (Agfa-Gevaert, model: Curix60 )
- Fume hood
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Baumann, T., Vosyka, O., Florea, B. I., Overkleeft, H. S., Meiners, S. and Kammerl, I. E. (2016). Activity-based Pull-down of Proteolytic Standard and Immunoproteasome Subunits. Bio-protocol 6(24): e2073. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2073.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 免疫检测
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link