- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Antibiotic Disc Assay for Synechocystis sp. PCC6803
采用抗生素纸盘试验法测定集胞藻PCC6803的细胞壁功能
发布: 2016年12月20日第6卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2071 浏览次数: 11108
评审: Maria SinetovaElizabeth LibbyLaura Molina-García
Abstract
This protocol describes how to investigate the integrity of the outer cell wall in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 using antibiotics. It is adapted to the agar diffusion test (Bauer et al., 1966), in which filter paper discs impregnated with specified concentrations of antibiotics were placed on agar plates inoculated with bacteria. The antibiotics we tested, interfering with the biosynthesis/function of bacterial cell walls, will diffuse into the agar and produce a zone of cyanobacterial growth inhibition around the disc(s). The size of the inhibition zone reflects the sensitivity of the strain to the action of antibiotics, e.g., a mutation in a protein functioning within the cell wall or its construction would render the mutant strain more sensitive to the respective antibiotic. The method has proven to be useful for phenotyping a mutant of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 lacking all three genes encoding Deg proteases. Deletion of these ATP-independent serine proteases was shown to have impact on the outer cell layers of Synechocystis cells (Cheregi et al., 2015).
Keywords: Cyanobacteria (蓝细菌)Background
The cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 (hereafter, Synechocystis 6803) is a model organism for studying the process of photosynthesis. While its genome was sequenced already in 1996, still more than 50% of its genes encode proteins with hypothetical or unknown function. The three genes slr1204 (htrA), sll1679 (hhoA) and sll1427 (hhoB) encode serine proteases of the Deg (degradation of periplasmic proteins) family; despite detailed analyses (see Cheregi et al., 2016 and references therein) their exact subcellular localization and substrates still are enigmatic. Previous proteomic and metabolomic characterizations of single and triple deg deletion mutants performed in our lab have shown altered expression of proteins with functions in or on the outer cell layers of Synechocystis 6803 (Miranda et al., 2013; Tam et al., 2015; Cheregi et al., 2015).
The antibiotics carbenicillin, colistin and polymyxin inhibit or disrupt the bacterial cell wall and therefore can be used to test the integrity of this cellular component in mutants: polymyxin acts on the outermost lipopolysaccharide layer surrounding the cyanobacterial S-layer, carbenicillin interferes with the peptidoglycan layer and colistin acts on the plasma membrane of gram-negative bacteria (Table 1). An agar diffusion test has been developed (Bauer et al., 1966) in which filter paper discs impregnated with specified concentrations of antibiotics are placed on agar plates inoculated with bacteria. The antibiotics will diffuse from the disc into the agar and inhibit cyanobacterial growth around it. The size of this inhibition zone then reflects the sensitivity of the strain to the antibiotic. The antibiotic disc assay method was used to characterize a triple deg protease mutant, and could be used for the characterization of any cyanobacterial mutant. However, the reader should be aware of the limitations of this assay. Despite the Sll1951 protein being the main component of the outermost cell layer of cyanobacteria, called S-layer, the antibiotic disc assay only had limited effect on a sll1951 deletion mutant (Trautner and Vermaas, 2013). Though the S-layer is compromised in the sll1951 deletion mutant, the underlying layers are still intact, preventing Carbenicillin and Polymyxin B, due to their relatively high molecular masses, to penetrate into the cell.
Table 1 describes the molecular weight, the mode of action and the ordering information for the above mentioned antibiotic discs.
Table 1. Antibiotic discs used in this protocol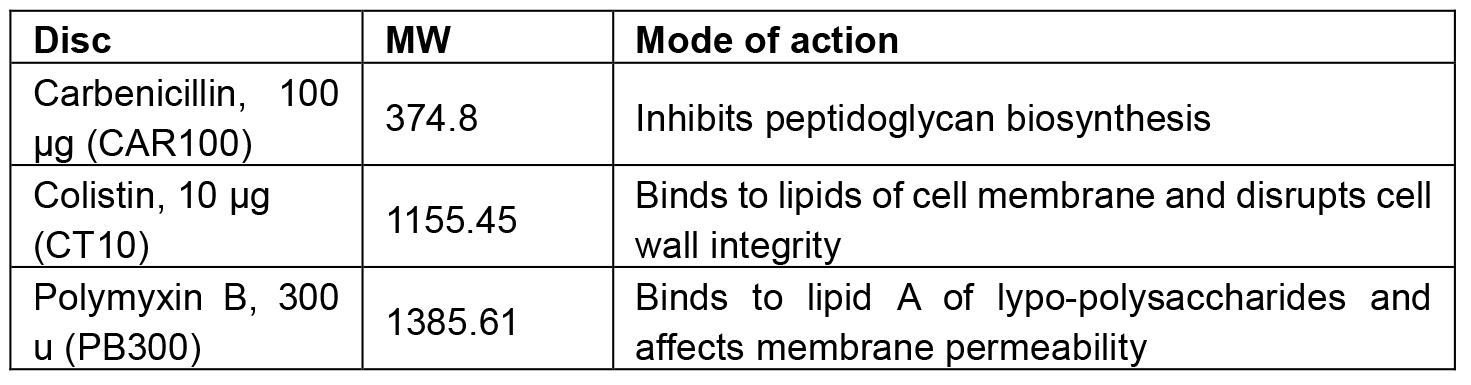
Materials and Reagents
- RemelTM plastic Petri dishes (85 mm diameter) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: R80085 )
- Sterile polystyrene spreading rods (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 86.1569.005 )
- Carbenicillin (CAR100) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: CT0006B )
- Colistin (CT10) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: CT0017B )
- Polymyxin (PB300) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: CT0044B )
- Dispenser for discs (included in the kit of each of the above mentioned test discs)
- Cyanobacterial cultures of WT control and mutants to be tested
- Boric acid, H3BO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6768 )
- Manganese(II) chloride tetrahydrate, MnCl2·4H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 221279 )
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrate, ZnSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z1001 )
- Sodium molybdate dehydrate, Na2MoO4·2H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 331058 )
- Cupric sulfate pentahydrate, CuSO4·5H2O (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fischer Scientific, catalog number: C493-500 )
- Cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate, Co(NO3)2·6H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 239267 )
- Sodium nitrate, NaNO3 (Scharlab, catalog number: SO05010500 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, MgSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 63138 )
- CaCl2·2H2O (Scharlab, catalog number: CA01981000 )
- Citric acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 251275 )
- Na2-EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 27285 )
- Ferric ammonium citrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F5879 )
- Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3(Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71345 )
- di-potassium hydrogen phosphate, K2HPO4 (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 105104 )
- Na-thiosulfate (solid) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 217263 )
- Difco Bacto-agar (BD, catalog number: 214530 )
- TES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6541 )
- 100x BG11 without Fe, phosphate, carbonate (see Recipes)
- 1,000x ferric ammonium citrate (see Recipes)
- 1,000x Na2CO3 (see Recipes)
- 1,000x K2HPO4 (see Recipes)
- BG11 solid agar plates (see Recipes)
- 1 M TES/NaOH buffer, pH 8.2 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Cell culture flasks (50-250 ml) with vented caps (TC flask T25) (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 83.3910.002 )
- UV/VIS spectrophotometer (GlobalMarket, PG Instruments, model: T90+ ) for measuring the absorption of cell culture (OD730).
- MultisizerTM Coulter Counter for counting cells (Beckman Coulter, model: Z Series Coulter Counter )
- Laminar hood (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: HeraguardTM Eco Clean Bench )
- Shaking incubator (80-120 rotations/min) with light (IVIS ~60-100 µE m-2 s-1) and temperature adjusted to 30 °C (Eppendorf, model: New BrunswickTM Innova® 43 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Cheregi, O. and Funk, C. (2016). Antibiotic Disc Assay for Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Bio-protocol 6(24): e2071. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2071.
分类
微生物学 > 抗微生物试验 > 抗细菌试验
微生物学 > 微生物新陈代谢 > 其它化合物
细胞生物学 > 细胞新陈代谢 > 其它化合物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













