- EN - English
- CN - 中文
In vitro Autophosphorylation and Phosphotransfer Assay of Cyanobacterial Histidine Kinase 2
蓝藻组胺酸激酶2的体外自磷酸化和磷酸根传递转分析
发布: 2016年12月05日第6卷第23期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2036 浏览次数: 11687
评审: Maria SinetovaAnna A. ZorinaTatsuki Kunoh
Abstract
This is a detailed protocol of an autophosphorylation and phosphotransfer activities of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 full-length Histidine Kinase 2 (Hik2) protein described by Ibrahim et al., 2016. In this protocol, radioactively labelled ATP was used to study an autophosphorylation and phosphotransfer activity of the full-length Hik2 protein.
Keywords: Histidine Kinase 2 (组氨酸激酶2)Background
Protein phosphorylation is an important post-translational modification of proteins that takes place in every living organism. The activity of protein kinases, the enzyme that catalyses the phosphorylation of proteins, was first described by Burnett and Kennedy in 1954, where they showed phosphorylation of casein by a liver enzyme (Burnett and Kennedy, 1954). However, its significance was not appreciated until the 1970s and 1980s (Cohen, 2002). The transfer of the γ-phosphate from an ATP molecule to proteins can be studied using coupled assays or directly with radioactively labelled ATP. Kinase assays based on incorporation of 32P can easily be followed by autoradiography, whereas coupled assays require monitoring of indirect reporter enzyme-catalysed colorimetric or chemiluminescence signals. The work presented here was conducted using radioactive ATP. Serine/threonine-type protein kinases dominate in eukaryotes, while in prokaryotes histidine kinases are the primary protein kinases involved in signal transduction. A histidine kinase catalyses the transfer of only γ-phosphate from an ATP molecule to its conserved histidine residue and transfers phosphoryl group to its response regulator (see Figure 1), but cannot catalyse the transfer of α-phosphate of ATP (Pernestig et al., 2001). Therefore [α-32P]ATP can be used as a negative control when characterising the autophosphorylation activity of putative histidine kinases.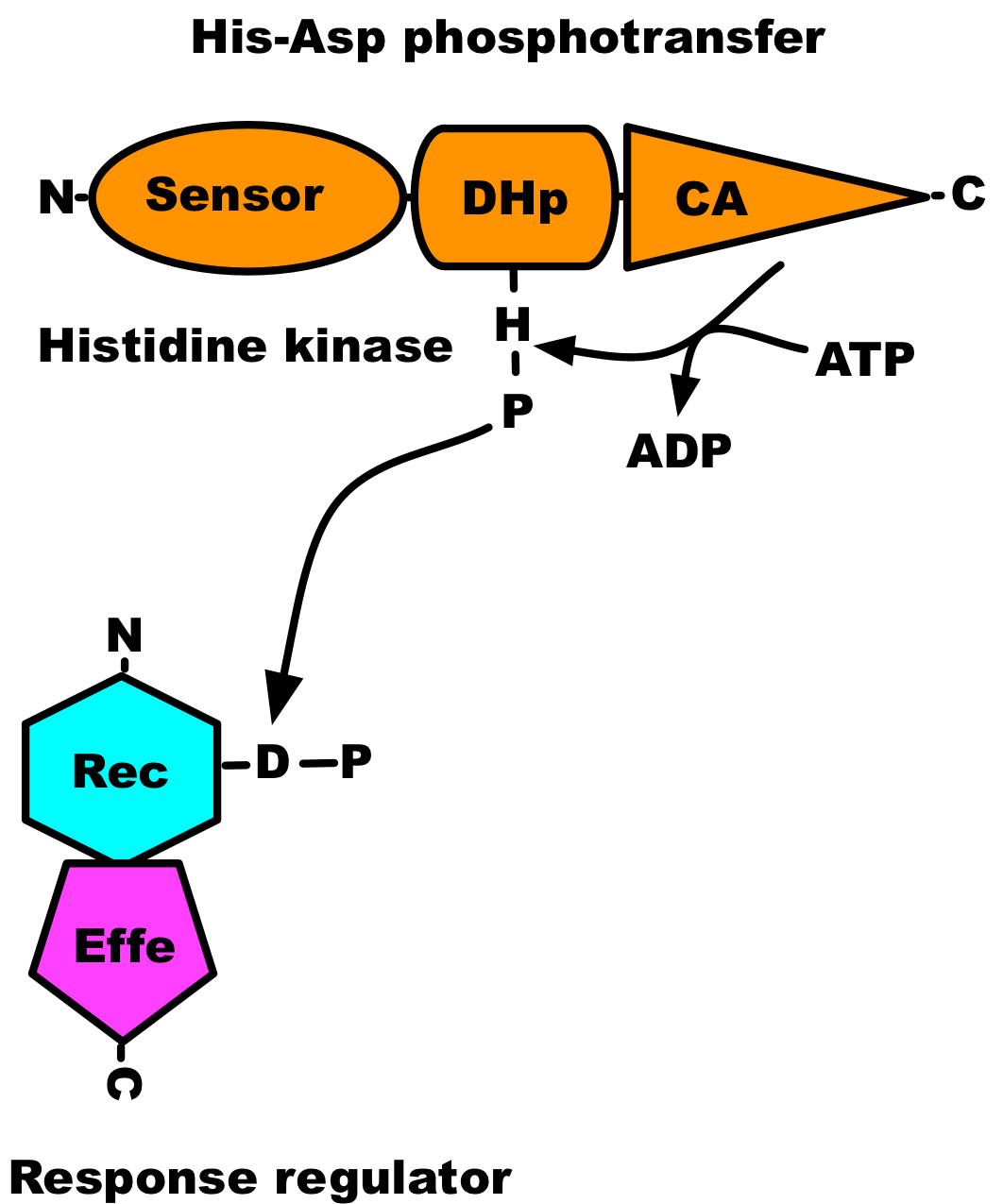
Figure 1. Domain architecture of two-component system. The sensor domain is indicated by oval, the dimerisation and phosphoaccepting (DHp) domain by a cylinder, and the catalytic and ATP-binding (CA) domain by a triangle; receiver (Rec) domain by a hexagon; effector (Effe) domain by a pentagon.
Materials and Reagents
- Eppendorf tubes
- 50 ml Falcon tubes
- Pipette tips
- Chelating Sepharose Fast Flow (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17057501 )
- PD-10 desalting columns (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17085101 )
- 1 ml cuvette
- Polyethylene bags (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 01817200 )
- BL21-DE3 E.coli cells containing Hik2, Rre1, and RppA clones. Each protein should be prepared fresh for each assay.
- pET-21b vector (Invitrogen)
- One Shot® TOP10 chemically competent E. coli (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: C404006 )
- BL21-(DE3) chemical competent cells
- NdeI endonuclease (New England BioLabs, catalog number: R0111S )
- XhoI endonuclease (New England BioLabs, catalog number: R0146S )
- KpnI
- Primers were purchased from Eurofins MWG Operon, Germany.
- Deoxynucleoside triphosphate set (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: DNTP-RO )
- Phusion® high-fidelity DNA polymerase (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0530S )
- RNase/DNase free water
- GeneJET Gel Extraction Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: K0691 )
- Tris-HCl
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (New England BioLabs, catalog number: B9000S )
- DNA loading dye (6x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: R0611 )
- Agarose
- Fermentas Gel Extraction Kit
- T4-ligase (New England BioLabs, catalog number: M0202S )
- Ampicillin sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9518-25G )
- Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Melford Laboratories, catalog number: MB1008 )
- Imidazole
- Bradford reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6916-500ML )
- 500 μCi [γ-32P]-ATP (6,000 Ci mmol-1) (PerkinElmer, catalog number: NEG502Z500UC )
- Adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2383-5G )
- Luria broth (LB), low salt, granulated (Melford Laboratories, catalog number: GL1703 )
- KCl
- MgSO4
- MgCl2
- Glucose
- NaCl
- PMSF
- Glycerol
- SDS
- β-2-mercaptoethanol
- 30% acrylamide/bis-acrylamide
- APS
- TEMED
- Precision Plus Protein All Blue Standards (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-0373 )
- LB medium (see Recipes)
- Super optimal broth with catabolic repressor (SOC) (see Recipes)
- Lysis buffer/wash buffer 1 (see Recipes)
- Wash buffer 2 (see Recipes)
- Wash buffer 3 (see Recipes)
- Elution buffer (see Recipes)
- PD-10 desalting column equilibration buffer (see Recipes)
- 5x kinase reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- 5x ATP mix (see Recipes)
- SDS-PAGE Laemmli sample buffer (see Recipes)
- SDS-PAGE (see Recipes)
- 1x SDS-PAGE running buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- PCR machine
- Pipette shield
- 2 L Erlenmeyer flask
- Bottle assembly, J-Lite PC-1000, polycarbonate (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 363676 )
- Backment Coulter AvantiTM J-30I centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Avanti J-30I )
- EmulsiFlex-C3 homogenizer (Abestin, model: EmulsiFlex-C3 )
- Bottle assembly, polycarbonate, 50 ml (Beckman Coulter, order number: 357000 )
- Heating block
- Phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics)
- Fume-hood
- GM counters
- Perspex Eppendorf holders
- JA-30.5 Ti rotor (Beckman Coulter, model: JA-30.5 Ti Rotor )
- JLA-9.1000 rotor, fixed angle (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 366754 )
- Gilson pipettes
- Plexiglas shielding
- Mini-PROTEAN® Electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1658000EDU )
- Bio-Rad PowerPac (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1645050 )
- Phosphor cassette (Molecular Dynamics)
- Phosphor plate (Molecular Dynamics)
- Image Eraser (Molecular Dynamics)
Software
- ImageQuant software (Molecular Dynamics)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Ibrahim, I. M. (2016). In vitro Autophosphorylation and Phosphotransfer Assay of Cyanobacterial Histidine Kinase 2. Bio-protocol 6(23): e2036. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2036.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物信号传导 > 磷酸化
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 磷酸化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













