- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Extraction and Measurement of Abscisic Acid in a Unicellular Red Alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae
单细胞红藻Cyanidioschyzon merolae中脱落酸的提取和测定
发布: 2016年12月05日第6卷第23期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2033 浏览次数: 11849
评审: Maria SinetovaSriema L. WalawageScott A M McAdam
Abstract
Abscisic acid (ABA) has been known as a phytohormone of land plants, which is synthesized in response to abiotic stresses and induces various physiological responses, but is also found from eukaryotic algae. Recently, we reported that a unicellular red alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae produced ABA, which prevented cell growth and enhanced salt stress tolerance (Kobayashi et al., 2016). This report describes the detailed method for the extraction and quantification of ABA in the model red alga C. merolae.
Keywords: Abscisic acid (脱落酸)Background
The phytohormone ABA has been found in divergent photosynthetic eukaryotes, but the function in unicellular algae remained unclear. In a recent study, we showed that a unicellular red alga C. melorae accumulates ABA in response to salt stress by the present protocol. This is the detail of the first published protocol for the extraction and quantification of ABA from C. merolae. This protocol is optimized for C. merolae based on the land plant protocol.
Materials and Reagents
- 500 ml centrifuge bottle (Hitachi, model: S305830A )
- Membrane filters Millex-GV syringe filter unit 0.22 μm (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SLGV033RS )
- Wild type C. merolae 10D cells (National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan)
- Abscisic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A4906-250UG )
- NaCl (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 195-15975 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- Acetic acid (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 017-00256 )
- Diethyl ether (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 052-01165 )
- Methanol (HPLC grade) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 132-06471 )
- Boric acid (H3BO3) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 021-15645 )
- Manganese(II) chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 133-00725 )
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 265-00415 )
- Sodium molybdate dehydrate (Na2MoO4·2H2O) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 514-30001 )
- Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 034-20065 )
- Cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate (Co[NO3]2·6H2O) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 031-03752 )
- Ammonium sulfate ([NH4]2SO4) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 016-03445 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 138-00415 )
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 195-04706 )
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 166-04255 )
- Calcium chloride (CaCl2) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 036-00485 )
- Iron(III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 090-02802 )
- Na2EDTA (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 345-01865 )
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 28314-82 )
- 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol (Tokyo chemical industry, catalog number: D0228 )
- MA2 medium (see Recipes)
- Extraction solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, model: DU730 )
- Refrigerated centrifuge (Hitachi, model: CF16RXII )
- Angle rotor (Hitachi, model: R10A3 )
- Mortar and pestle
- Vortex mixer (M & S Instruments, model: VORTEX-GENIE 2 Mixer )
- Microcentrifuge (TOMY DIGITAL BIOLOGY, model: MX150 )
- Vacuum centrifugal evaporator with low temperature trapper (TOMY DIGITAL BIOLOGY, model: CC-105 system )
- pH meter (As One, model: KR5E )
- HPLC system (Shimadzu, model: X2 HPLC system ) equipped with a photodiode array detector (PDA) and column (5 μm, 4.6 x 250 mm) (Senshu Scientific, model: ODS SP100 )
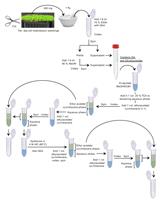
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Kobayashi, Y. and Tanaka, K. (2016). Extraction and Measurement of Abscisic Acid in a Unicellular Red Alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae. Bio-protocol 6(23): e2033. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2033.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 植物激素
生物化学 > 其它化合物 > 植物激素
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link