- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Determination of Recombinant Mannitol-1-phosphate Dehydrogenase Activity from Ectocarpus sp.
水云属中重组甘露醇-1-磷酸脱氢酶活性的测定
发布: 2016年11月05日第6卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1982 浏览次数: 8887
评审: Valentine V TrotterYanjie LiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Brown algae belong to a phylogenetic lineage distantly related to green plants and animals, and are found predominantly, but not exclusively, in the intertidal zone, a harsh and frequently changing environment. Because of their unique evolutionary history and of their habitat, brown algae feature several peculiarities in their metabolism. One of these is the mannitol cycle, which plays a central role in their physiology, as mannitol acts as carbon storage, osmoprotectant, and antioxidant. This polyol is derived directly from the photoassimilate fructose-6-phosphate via the action of a mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase (M1PDH, EC 1.1.1.17) and a mannitol-1-phosphatase (M1Pase, EC 3.1.3.22). This protocol describes the biochemical characterization of the recombinant catalytic domain of one of the three M1PDHs identified in Ectocarpus sp. This recombinant catalytic domain, named hereafter M1PDHcat, catalyzes the reversible conversion of fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) to mannitol-1-phosphate (M1P) using NAD(H) as a cofactor. M1PDHcat activity was assayed in both directions i.e., F6P reduction and M1P oxidation (Figure 1).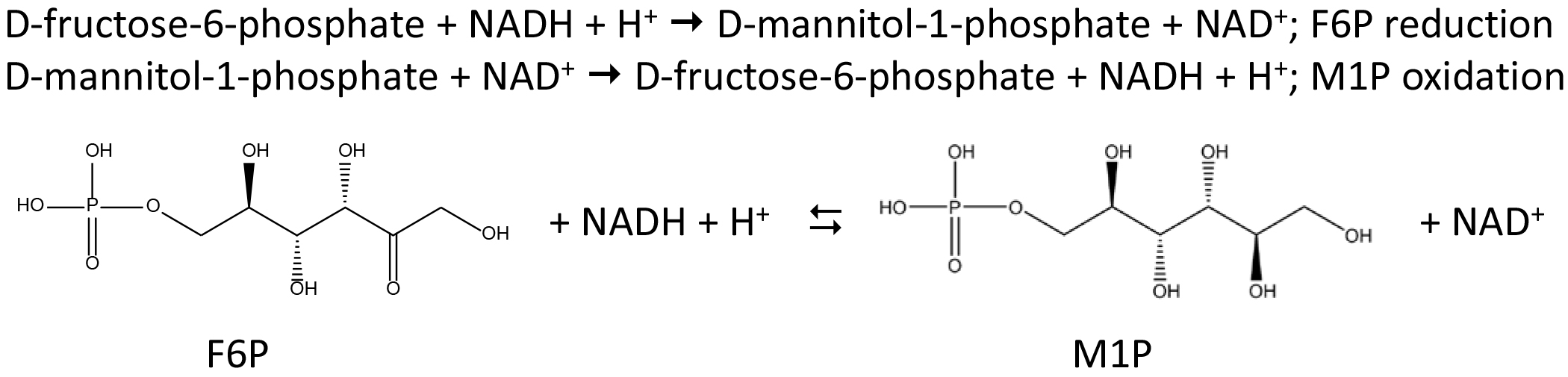
Figure 1. Reversible reaction of mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase
Materials and Reagents
- UV-Star® PS microplate (96 well) (Greiner Bio One International, catalog number: 655801 )
- 0.22 µm filter
- Purified recombinant His-tagged M1PDHcat
Note: This protein was produced in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) containing the recombinant pFO4_M1PDHcat vector, as described by Groisillier et al. (2010). This recombinant protein was purified by affinity chromatography using a HisPrep FF 16/10 column (GE Healthcare) and then by gel filtration using a Superdex 200 (GE Healthcare) onto an Äkta avant system (GE Healthcare). The complete purification protocol is described in details in Bonin et al. (2015). - MilliQ water
- Trizma® base (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503 )
- 4-morpholineethane-sulfonic acid (MES) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2933 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- Bis-Tris propane (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6755 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71380 )
- Examples of chemicals to be tested to assess substrate and co-factor specificity:
- D-mannitol-1-phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 92416 )
- D-fructose-1-phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F1127 )
- α-D-glucose-1-phosphate disodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G9380 )
- D-mannose-6-phosphate sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3655 )
- D-glucose-6-phosphate sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7879 )
- D-fructose-6-phosphate disodium salt hydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F3627 )
- β-NAD (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N1636 )
- β-NADP (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N5755 )
- β-NADH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N8129 )
- β-NADPH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N5130 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl (see Recipes)
- 5 M NaCl (see Recipes)
- 10 mM NADH (see Recipes)
- 10 mM NAD+ (see Recipes)
Equipment
- NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: NanoDrop 2000 )
- Safire2 UV spectrophotometer microplate reader (Tecan Trading)
Software
- Hyper 32 (Informer Technologies, model: hyper32)
- Microsoft Excel
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Groisillier, A. and Tonon, T. (2016). Determination of Recombinant Mannitol-1-phosphate Dehydrogenase Activity from Ectocarpus sp.. Bio-protocol 6(21): e1982. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1982.
分类
植物科学 > 藻类学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link