- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Spectrophotometric Determination of Glutamine Synthetase Activity in Cultured Cells
分光光度测定培养细胞的谷氨酰胺合成酶的活性
发布: 2016年10月05日第6卷第19期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1959 浏览次数: 13940
评审: Masahiro MoritaRaghuveer KavarthapuAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Glutamine synthetase (GS), which catalyzes the conversion of glutamate and ammonia to glutamine, is widely distributed in animal tissues and cell culture lines. The importance of this enzyme is suggested by the fact that glutamine, the product of GS-catalyzed de novo synthesis reaction, is the most abundant free amino acid in blood (Smith and Wilmore, 1990). Glutamine is involved in many biological processes including serving as the nitrogen donor for biosynthesis, as an exchanger for the import of essential amino acids, as a means to detoxifying intracellular ammonia and glutamate, and as a bioenergetics nutrient to fuel the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (Bott et al., 2015). The method for the assay of GS enzymatic activity relies on its γ-glutamyl transferase reaction by measuring γ-glutamylhydroxamate synthesized from glutamine and hydroxylamine, and the chromatographic separation of the reaction product from the reactants (Deuel et al., 1978). An overview of the GS glutamyl transferase reaction can be found in Figure 1. GS activity was measured by a spectrophotometric assay at a specific wavelength of 560 nm using a microplate reader. The method is simple, and has a comparable sensitivity with those methods applying radioactively labelled substrates. This modified procedure has been applied to assay/determine GS activity in cultured cell lines including the human mammary epithelial MCF10A cells and the murine pre-B FL5.12 cells, and could be used to measure GS activity in other cell lines.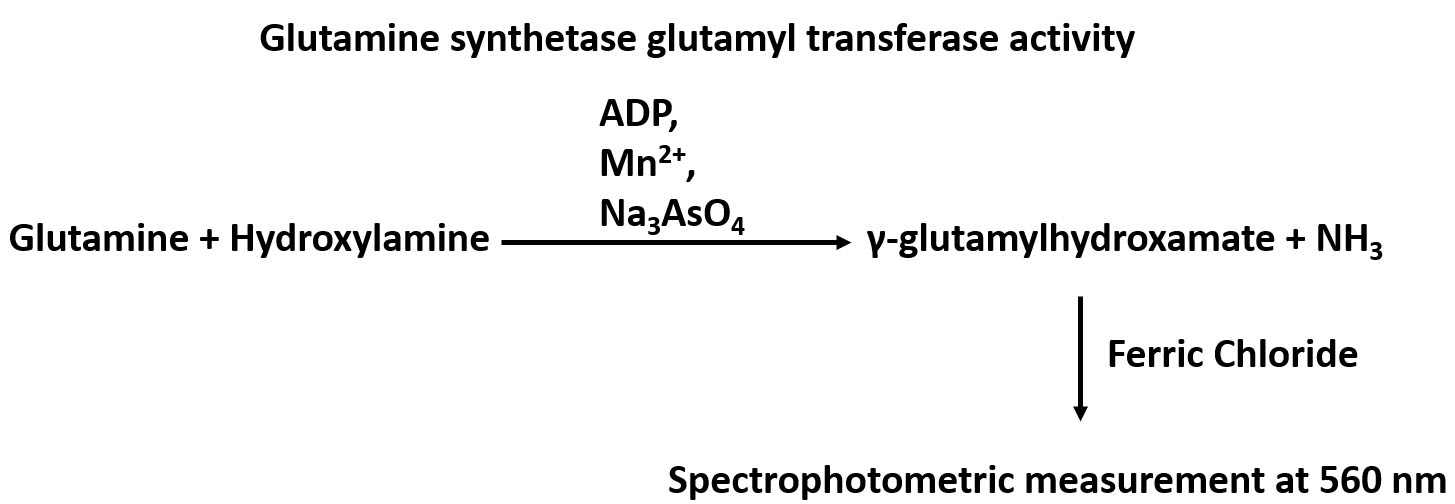
Figure 1. An overview of the GS glutamyl transferase reaction
Materials and Reagents
- 0.05% trypsin-EDTA (1x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 25300-054 )
- PBS (1x) (Corning, catalog number: 21-031-CV )
- Imidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I0250 )
- L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G3126 )
- Hydroxylamine hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 55459 )
- Sodium arsenate dibasic heptahydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9663 )
- Manganese(II) chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 221279 )
- Adenosine 5’-diphosphate sodium salt (ADP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2754 )
- Iron(III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 31232 )
- Trichloroacetic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 522082 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258148 )
- L-glutamic acid γ-monohydroxamate (γ-glutamylhydroxamate) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G2253 )
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- 1x assay buffer (see Recipes)
- 1x stop buffer (see Recipes)
- γ-glutamylhydroxamate standard stock (see Recipes)
Equipment
- AccumetTM AB15 Basic and BioBasicTM pH/mV/°C Meters (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 13-636-AB15B )
- Sonicator (model: CL-18/120 ) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher ScientificTM, catalog number: FB120110 )
- -80 °C freezer
- 37 °C incubator
- Microcentrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5418 )
- Microplate (96-well plate clear bottom) reader (Molecular Devices, model: SpectraMax M5 )
Software
- SoftMaxPro software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Peng, I., Bott, A. J. and Zong, W. (2016). Spectrophotometric Determination of Glutamine Synthetase Activity in Cultured Cells. Bio-protocol 6(19): e1959. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1959.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
癌症生物学 > 细胞能量学 > 生物化学试验
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 检测
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link