- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Highly Efficient Method for Measuring Oxygen Consumption Rate in Fusarium graminearum
禾谷镰刀菌中耗氧率的高效测量法
发布: 2016年08月05日第6卷第15期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1887 浏览次数: 10888
评审: Valentine V TrotterEmilia Krypotou Jose Thekkiniath
Abstract
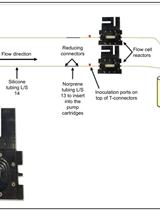
The filamentous ascomycete Fusarium graminearum is the causal agent of Fusarium head blight, a devastating disease of cereals with a worldwide distribution. Fusarium graminearum infections result in a quantitative yield reduction by impairing the growth of the kernels, and a qualitative reduction by poisoning the remaining kernels with mycotoxins toxic to animals and humans. The colonization of wheat florets by phytopathogenic fungus requires high-efficiency energy generation in the mitochondria (Bönnighausen et al., 2015). Mitochondrial activity in microorganisms can be measured using the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) method. Here we describe a method for the assessment of fungal respiration using an XF24 extracellular flux analyzer. The Seahorse XF Analyzer is a microplate-based respirometer which measures oxygen consumption by changes in the fluorescence of immobilized fluorophores (Gerencser et al., 2009). Multiple mitochondrial parameters can be measured by the application of mitochondrial substrates and inhibitors which are injected automatically during the assays via ports (Divakaruni et al., 2014). The experimental work-flow involves the inoculation with conidia and the application of specific inhibitors of mitochondrial functions. The analysis of fungal respiration represents a valuable tool that complements classical phenotypic screenings.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips
- Conidia of F. graminearum (preferably fresh, not frozen)
- Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit including oligomycin, rotenone, antimycin A and Cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl hydrazone (Seahorse Bioscience, catalog number: 103015-100 )
- Seahorse XF24 Islet FluxPak containing XF24 cartridges and Islet capture microplates (Seahorse Bioscience, catalog number: 101174-100 )
- Calibrant solution (Seahorse Bioscience, catalog number: 103059-000 )
- Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (Carl Roth, catalog number: X886.1 )
- KH2PO4 (Carl Roth, catalog number: P018.1 )
- MgSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 230391-500G )
- NaCl (Carl Roth, catalog number: 9265.1 )
- Sucrose
- H3BO3 (Carl Roth, catalog number: 6943.1 )
- CuSO4·5H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 209198-250G )
- KI (Carl Roth, catalog number: 6750.1 )
- MnSO4·H2O (Carl Roth, catalog number: 7347.2 )
- (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 09880-100G )
- ZnSO4·7H2O (Carl Roth, catalog number: 7316.1 )
- FeCl3·6H2O (Carl Roth, catalog number: 7119.1 )
- Solution A (see Recipes)
- Solution B (see Recipes)
- Suspension D (see Recipes)
- Minimal medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Multi-channel pipettes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z683930-1EA )
- XF24 extracellular flux analyzer (Seahorse Bioscience, model: Seahorse XFe24 )
- Incubator at 28 °C (Heraeus B20/UB20) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 50061005 )
- Microplate centrifuge (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022620509 )
Software
- XF24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer Software
- Spreadsheet software program [e.g., Excel (Microsoft)]
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Gebhard, D., Bönnighausen, J., Bergemann, J., Schäfer, W. and Bormann, J. (2016). A Highly Efficient Method for Measuring Oxygen Consumption Rate in Fusarium graminearum. Bio-protocol 6(15): e1887. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1887.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生理学 > 呼吸
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link