- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
莱茵衣藻的间接免疫荧光测定
发布: 2016年07月05日第6卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1864 浏览次数: 13281
评审: Maria SinetovaCindy AstAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
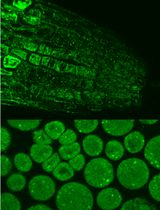
Determining the protein localization is essential to elucidate its in vivo function. Fluorescence-tagged proteins are widely used for it, but it is sometimes difficult to express tagged proteins in Chlamydomonas. Alternatively, indirect immunofluorescence assay is also one of the widely used methods and many reports determining the localization of Chlamydomonas proteins using this method are published. Here, we introduce a protocol of indirect immunofluorescence assay adapted from our papers reporting LCIB (CO2-recycling factor in the vicinity of pyrenoid; Yamano et al., 2010), LCI1 (plasma membrane-localized inorganic carbon transporter; Ohnishi et al., 2010), HLA3 (plasma membrane-localized ABC-type bicarbonate transporter; Yamano et al., 2015), and LCIA (chloroplast envelope anion channel; Yamano et al., 2015) in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The protocol described here could be useful for observing the protein of interest in other algae cells.
Keywords: Chloroplast membrane (叶绿体膜)Materials and Reagents
- Poly-L-lysine-treated glass slide (Poly-Prep Slides) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0425-72EA )
- Coverslips (Matsunami Glass, catalog number: C218181 )
- Dako Pen (Dako, catalog number: S2002 )
- Plastic box (9 cm x 19 cm x 4 cm)
Note: In this experiment, but any size is OK. - Kimwipes® paper (Kimberly Clark)
- Chlamydomonas cells of interest
- Hematocytometer (Erma, catalog number: 03-303-6 )
- Phosphate-buffered Saline (PBS)
- Tween-20 (Santa Cruz, catalog number: sc-29113 )
- PBS-T (PBS with 0.1% Tween-20)
- Paraformaldehyde (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 26126-54 )
- Methanol (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 21915-64 )
- Globulin-free Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 01281-26 )
- Affinity-purified rabbit primary antibody against LCIB (Yamano et al., 2010)
- Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: A-11001 )
- Mounting medium (Vectorshield, catalog number: H-1300 )
- 4% formaldehyde (see Recipes)
- PBS (see Recipes)
- PBS-T (see Recipes)
- Blocking solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Coplin jar (50 ml size)
- Fluorescence microscopy Axioscope2 (Zeiss) with a specific filter set (excitation bandpass
480/40 and emission band pass 527/30) or laser scanning confocal microscopy TCS SP8
(Leica) with a 488 nm laser line
Note: these were the instruments used throughout our experiments, but any company is OK.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Yamano, T. and Fukuzawa, H. (2016). Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bio-protocol 6(13): e1864. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1864.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 标记
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 免疫检测 > 免疫染色法
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 荧光
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link