- EN - English
- CN - 中文
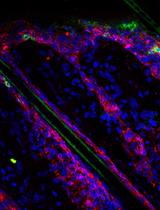
Whole-mount Enteroid Proliferation Staining
对小肠培养物进行EdU整染和增殖分析
发布: 2016年06月20日第6卷第12期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1837 浏览次数: 12113
评审: Ivan ZanoniAchille BroggiAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
使用康可藻红素刺激冷冻保存的猪外周单个核细胞进行增殖检测,并结合FCS ExpressTM 7.18软件分析
Marlene Bravo-Parra [...] Luis G. Giménez-Lirola
2025年06月05日 2599 阅读
Abstract
Small intestinal organoids, otherwise known as enteroids, have become an increasingly utilized model for intestinal biology in vitro as they recapitulate the various epithelial cells within the intestinal crypt (Mahe et al., 2013; Sato et al., 2009). Assessment of growth dynamics within these cultures is an important step to understanding how alterations in gene expression, treatment with protective and toxic agents, and genetic mutations alter properties essential for crypt growth and survival as well as the stem cell properties of the individual cells within the crypt. This protocol describes a method of visualization of proliferating cells within the crypt in three dimensions (Barrett et al., 2015). Whole-mount proliferation staining of enteroids using EdU incorporation enables the researcher to view all proliferating cells within the enteroid as opposed to obtaining growth information in thin slices as would be seen with embedding and sectioning, ensuring a true representation of proliferation from the stem cell compartment to the terminally differentiated cells of the crypt.
Materials and Reagents
- 12-well MatTek plate with 1.5 coverslip thickness (MATTEK, catalog number: P12G-1.5-14-F )
- 18 G non-flexible stainless steel oral gavage needle (Cadence, Inc., catalog number: 7906 )
- 10 ml syringe (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher ScientificTM, catalog number: 14-823-2A )
- 50 ml sterile Falcon tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 339653 )
- Sterile 12-well cell culture dish (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CLS3513 )
- 15 ml sterile Falcon tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 339651 )
- Pre-chilled sterile pipette tips
Notes:- Any tips that are sterile and can be used with the lab’s pipettors.
- These tips can be placed in a -20 °C freezer for 30 min or in a 4 °C refrigerator one hour prior to plating.
- 70 μM cell strainer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher ScientificTM, catalog number: 08-771-2 )
- C57BL/6 mouse (male or female, 6-8 weeks of age)
- Isofluorane (Allivet, catalog number: 50562 )
- Ice cold sterile 1x DPBS without calcium or magnesium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14190-235 )
- UltraPure EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15576-028 )
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0389 )
- D-Sorbitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S1876 )
- Matrigel® basement membrane matrix (Corning, catalog number: 356237 )
Note: Thaw at 4 °C the night before use. - Epidermal growth factor (EGF) (R&D Systems, catalog number: 2028-EG-200 )
- Noggin (R&D Systems, catalog number: 1967-NG-025/CF )
- R-spondin (R&D Systems, catalog number: 3474-RS-050 )
- Wnt3A (R&D Systems, catalog number: 1324-WN-010 )
- Advanced DMEM/F12 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12634-010 )
- L-glutamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 25030-081 )
- Penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140-148 )
- 1 M HEPES (pH 7.0-7.6, Sterile filtered) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H0887 )
- N2 supplement (R&D Systems, catalog number: AR003 )
- B27 supplement (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17504-044 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10437-028 )
- Click-iT EdU cell proliferation assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: C10337 )
- Paraformaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6148 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A8531 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X100 )
- TO-PRO-3 Iodide (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: T3605 )
- Chelation buffer, prepare fresh (see Recipes)
- Shaking buffer (see Recipes)
- Minigut culture media (see Recipes)
- 2% Formaldehyde (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Scissors for dissection (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-951-20 )
- Sorvall Legend X1R Centrifuge (or other large refrigerated centrifuge)
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 cell culture incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: HERAcell 150i )
- LSM 510 META Inverted (or other inverted laser scanning) confocal microscope with 647 (TO-PRO-3) and 488 (EdU) emission filters
Software
- ImageJ Image Analysis Software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Barrett, C. W., Short, S. P., Choksi, Y. A. and Williams, C. S. (2016). Whole-mount Enteroid Proliferation Staining. Bio-protocol 6(12): e1837. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1837.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫细胞分离 > 维持和分化
免疫学 > 免疫细胞功能 > 综合
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link