- EN - English
- CN - 中文
RNase H Polymerase-independent Cleavage Assay for Evaluation of RNase H Activity of Reverse Transcriptase Enzymes
RNase H 聚合酶依赖性分裂试验评估逆转录酶中Rnase H的活性
发布: 2015年08月20日第5卷第16期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1561 浏览次数: 13635
评审: Modesto Redrejo-RodriguezToshitsugu FujitaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The ribonuclease H (RNase H) polymerase-independent cleavage assay allows detection and quantification of RNase H activity of reverse transcriptase (RT) enzymes with a hybrid substrate formed by a fluorescein labeled RNA annealed with Dabcyl DNA (Figure 1). Here we describe a protocol that we have adapted for HIV-1 RT expressed from a p(His)6-tagged p66/p51 HIV-1HXB2 RT-prot plasmid and for RT of the prototype foamy virus (PFV RT). 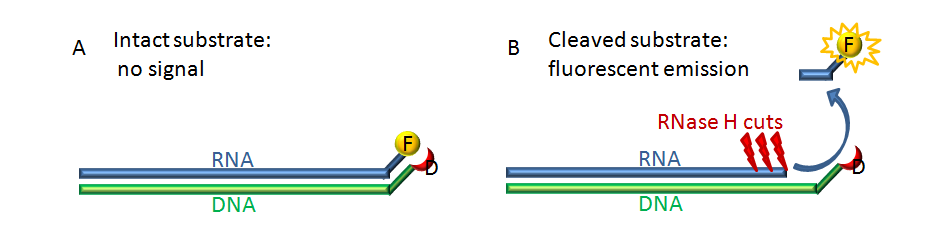
Figure 1. Scheme of the principle of the experiment. The RNA substrate (blue) labeled with the fluorophore fluorescein (F, yellow) is annealed with complementary DNA strand (green) labeled with a quencher molecule Dabcyl (D, red). Panel A. In the intact substrate the quencher is so close to the fluorophore that it can quench the fluorescence emitted after excitation. Panel B. After the RNA substrate is cut by the RNase H a few ribonucleotides oligo labeled with the fluorescein is free to escape from the quencher, and to release fluorescence after excitation.
Materials and Reagents
- Reverse transcriptase enzyme (HIV-1 RT or PFV RT). HIV-1 RT expressed and purified from p(His)6-tagged p66/p51 HIV-1HXB2 RT-prot plasmid (Corona et al., 2014a), PFV RT provided by Birgitta M. Wöhrl from Universität Bayreuth, Lehrstuhl Biopolymere, Bayreuth, Germany (Corona et al., 2014b).
- Distilled water (DNase/RNase-free UltraPureTM) (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 10977-015 )
- 5'-GAUCUGAGCCUGGGAGCU-FLUORESCEIN-3' (HPLC, dry, QC: Mass Check) (Metabion)
- 5'-DABCYL-AGCTCCCAGGCTCAGATC-3' (HPLC, dry, QC: Mass Check) (Metabion)
- 1 M KCl solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 60142-100ML-F )
- 1 M MgCl2 solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 63069-100ML )
- 1 M Dithiothreitol (DTT) solution (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: P2375 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl Solution (pH 7.8) prepared from Trizma base® (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number 93352 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl Solution (pH 8.1) prepared from Trizma base® (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93352)
- 5 M NaCl solution (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9760G )
- EDTA (0.5 M, pH 8.0) UltraPureTM (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15575-020 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) >=99.5% (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5879-1 L )
- Microcentrifuge tubes, extended capacity, volume 0.65 ml, graduated, siliconized polypropylene (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T3406-250EA )
- OPTIPLATE-96 F /50B (PerkinElmer, catalog number: 6005270 )
- HIV-1 RT reaction mix (1.25x) (see Recipes)
- PFV RT reaction mix (1.25x) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Thermal cycler
- Refrigerated tabletop microcentrifuge
- Sonicator Bath (Elma Ultrasonic bath Transonic T 310)
- Vortex mixer
- Multi Thermo-Shaker for microplates (Bionics)
- Multilabel counter plate reader Victor 3 (PerkinElmer, model: 1420-051 ) equipped with filters for fluorescein fluorophore 490/528 nm (excitation/emission wavelength)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Corona, A. and Tramontano, E. (2015). RNase H Polymerase-independent Cleavage Assay for Evaluation of RNase H Activity of Reverse Transcriptase Enzymes. Bio-protocol 5(16): e1561. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1561.
分类
微生物学 > 抗微生物试验 > 抗病毒试验
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 蛋白质
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link














