- EN - English
- CN - 中文
In vitro Colorimetric Method to Measure Plant Glutamate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Activity
体外比色法测定植物谷氨酸脱氢酶的活性
发布: 2015年08月20日第5卷第16期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1560 浏览次数: 12048
评审: Arsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) is an NAD(H) dependent enzyme that catalyzes, in vitro, the reversible amination of glutamate. Here we describe how to determine spectrophotometrically GDH activity monitoring NADH evolution. This protocol is described here for Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana) although it is also valid for other plant species. GDH protein is a hexamer composed, in the case of Arabidopsis, of a combination of GDHα, GDHβ and GDHγ subunits. Every combination of subunits is possible; however, it is still barely known whether different combinations affect the enzymatic properties of the hexamers. In other species, hexamers are a combination of GDHα and GDHβ but it cannot be discarded the existence of other genes since for instance GDHγ subunit in Arabidopsis was described in Fontaine et al. (2012).
Glutamate + NAD+ + H+ → 2-Oxoglutarate + NADH + NH4+
Materials and Reagents
- 4-weak old Arabidopsis thaliana leaves and roots
- Ultrapure water
- Liquid N2
- Ice
- Flat bottom microplates (Deltalab, catalog number: 900011.1 )
- 4 mm diameter glass beads (Glaswarenfabrik Karl Hecht) (VWR International, catalog number: 201-0278 )
- 1.2 ml deep well storage plate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AB-0564 )
- EVA Capband for capping 8 tubes (Micronic, catalog number: MP227B1 )
- Bio-Rad Protein Assay Dye Reagent Concentrate (Bio-Rad Laboratories, AbD Serotec®, catalog number: 500-006 )
- NADH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 43420 )
- PVPP (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 77627 )
- Glycerol (EMD Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 104092 )
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7906 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-9284 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- KOH (EMD Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 105029 )
- MnCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8266 )
- EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: ED255 )
- EGTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E4378 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632 )
- PMSF (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- Delta-aminocaproic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2504 )
- Leupeptin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L2884 )
- Tricine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0377 )
- CaCl2 (Panreac Applichem, catalog number: 131232 )
- 2-Oxogutarate (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 5194 )
- (NH4)2SO4 (Panreac Applichem, catalog number: 131140 )
- Extraction buffer (see Recipes)
- Reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- Bradford solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- TissueLyser (RETSCH, model: MM400 )
- Plate centrifuge (Sigma, model: 2-16K )
- Absorbance microplate reader (Biotek Powerwave X 384 Microplate spectrophotometer)
- TissueLyser Adapter Set 2 x 96 (QIAGEN, catalog number: 69984 )
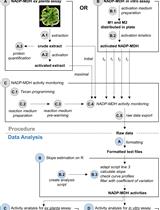
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Sarasketa, A., Vega-Mas, I. and Marino, D. (2015). In vitro Colorimetric Method to Measure Plant Glutamate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Activity. Bio-protocol 5(16): e1560. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1560.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
植物科学 > 植物新陈代谢 > 氮
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link