- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Genome-Wide siRNA Screen for Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Adherent Cell Lines
全基因组siRNA法筛选粘附细胞系中的耐(抗癌)药物基因
发布: 2015年05月20日第5卷第10期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1474 浏览次数: 13535
评审: HongLok LungMichael EnosAgnieszka Pastula
Abstract
The expression of genes is frequently manipulated in cell lines to study their cellular functions. The use of exogenous small Interfering RNAs (siRNAs) is a very efficient technique to temporarily downregulate the expression of genes of interest [reviewed by Hannon and Rossi (2004)]. A genome-wide siRNA library allows the user to study both the effect of each individual gene on a particular cell phenotype in a high throughput manner and also assess its phenotypic effect relative to all other genes targeted. Several factors that potentially influence the outcome of a screen need to be considered when performing a large siRNA screen (Jiang et al., 2011). Here we present a detailed protocol for a genome-wide screen to identify genes involved in anti-cancer drug resistance using the human siGENOME library from Dharmacon. In this protocol, we focus on resistance to treatment with the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) erlotinib in the lung cancer cell line PC9, which is exquisitely sensitive to EGFR-TKIs (de Bruin et al., 2014). This protocol can be used for other cell lines and other drug treatments, as we expand in the Notes below.
Materials and Reagents
- Human lung adenocarcinoma cell line PC9 (RIKEN BioResource Center, catalog number: RCB4455 )
- RPMI 1640 Medium containing L-Glutamine (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: A10491-01 )
Note: For cell culture, the medium is supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% Penicillin Streptomycin (see details FBS and Pen/Strep below). - Penicillin streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15070-063 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (PAA Laboratories GmbH, catalog number: A15-101 )
- Opti-MEM® I Reduced Serum Medium (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 31985-047 )
- 384-well tissue culture plates, black with clear F-bottom (4titude, Anachem, catalog number: 4TI-0201 were used for our screen; currently plates from Greiner bio-one (catalog number: 781091 ) are used
- Adhesive foil plate seal (Brandle Plate Sealer, Alpha Biotech)
- 5x siRNA buffer (GE Healthcare, catalog number: B-002000-UB-100 )
- Human siGENOME SMARTpool siRNA library (GE Healthcare, catalog number: G-005005 )
Note: We used an older version (from 2005) for our study (de Bruin et al., 2014) that is no longer available. Updated versions will contain other siRNA sequences as well as annotations, which will impact results. We therefore strongly recommend validating identified genes using other approaches. - siRNA controls (see Note 1)
Negative controls:Human siGENOME non-targeting siRNA 2 (GE Healthcare, catalog number: D-001210-02 ), RISC-Free control siRNA (catalog number: D-001220-01 ), ON-Targetplus non-targeting (catalog number: D-001810-10 )
Positive controls: Human siGENOME SMARTpool UBB (GE Healthcare, catalog number: M-013382-01 ) and PLK1 (Dharmacon, catalog number: M-003290-01 ) - DharmaFECT 2 siRNA transfection reagent (GE Healthcare, catalog number: T-2002-01 ) (see Note 2)
- DAPI (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10236276001 )
- siGENOME LaminA/C control siRNA (GE Healthcare, catalog number: D-001050-01-05 ) (see Note 3)
- Human LaminA/C antibody (catalog number: SC-7292 ) (see Note 3)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7.0, made in-house)
- Erlotinib (Enzo Life Sciences, catalog number: BML-DL279 )
Equipment
- Acumen (TTP LABTECH, mode: eX3 )
- ArrayscanVTi HCS microscope (Cellomics)
- Biomek FX Liquid handling platform (Beckman Coulter)
- Countess Cell counter (Life Technologies)
- Liquid dispensor8-channel [for our screen the WellMate (Matrix) was used, currently the FluidX (Xrd-384) is used]
- Cytomat 24 °C CO2 incubator 37 °C and 5% CO2
Note: The Cytomat is a cell culture incubator that has racks built in holding ~500 plates, and the racks rotate to minimize plate edge effects. - Plate washer (BioTek Instruments, model: ELx405 Select CW , Figure 1)
- Plate sealer (Brandel Plate Sealer, Alpha Biotech)
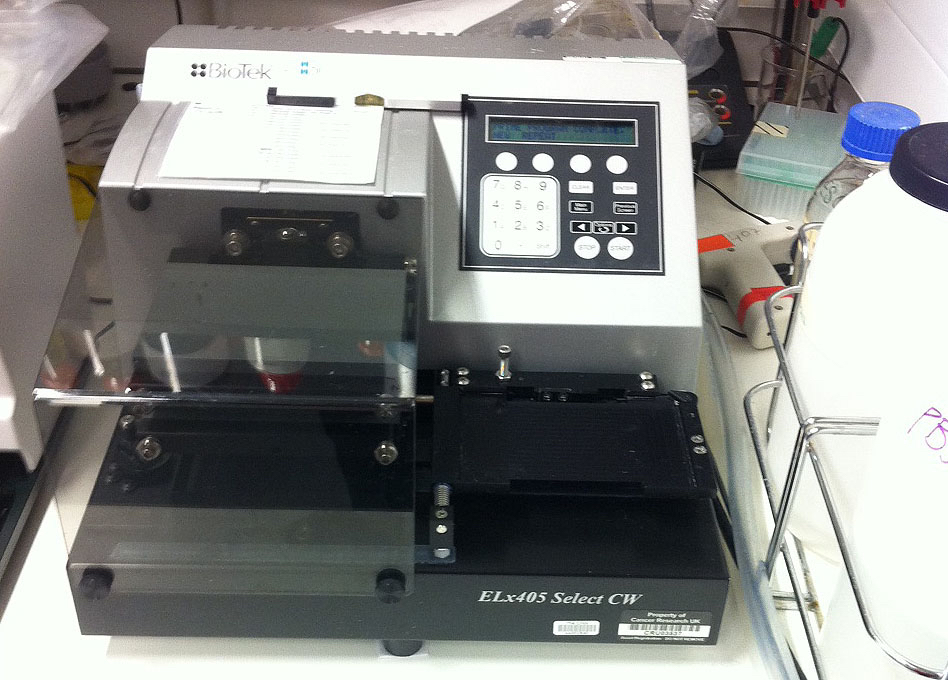

Figure 1. Picture of plate washer
Important considerations
Before performing a large-scale siRNA screen, there are a few crucial points to consider and to optimize in order to obtain the best results (Jiang et al., 2011). These include:
- Optimization of the siRNA transfection: Reagent, cell number, siRNA concentration.
- Optimization of the drug dose, treatment time length in combination with the siRNA transfection for drug resistant/sensitizing screens.
Details of these optimization steps are provided in the Notes section at the end of this protocol. We recommend performing, if possible, a pilot screen with a range of random siRNAs and selected control RNAs to determine the feasibility and screen read-out prior to the genome-wide screen.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
de Bruin, E. C., Jiang, M., Howell, M. and Downward, J. (2015). Genome-Wide siRNA Screen for Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Adherent Cell Lines. Bio-protocol 5(10): e1474. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1474.
分类
癌症生物学 > 通用技术 > 癌症治疗 > 全基因组分析
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
分子生物学 > DNA > 基因表达
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link