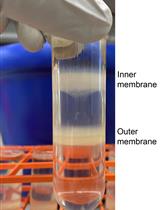
Recently, membrane vesicle (MV) production was described in Gram-positive bacteria, which harbor a variety of components such as toxins, antibiotic resistance proteins, proteases, DNA, and immune modulators. Free lipids have the ability to form micelles, thus it is important to rule out spontaneous association of lipids into vesicle-like structures and rather, that MVs are produced naturally by a metabolically active cell. Here, we describe a protocol utilizing the polysaccharide, glucuronoxylomannan (GXM) from Cryptococcus neoformans (C. neoformans) as a marker to differentiate naturally produced MVs from vesicles that form spontaneously in the Gram-positive model organism, Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis). MVs are purified from bacterial cultures grown in the presence of GXM; MVs naturally produced by cells would not contain GXM in the lumen whereas vesicular structures forming in the media could encapsulate GXM and this can be visualized via immunogold transmission electron microscopy.