- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Infection Experiments (Hepatitis C Virus)
感染实验(丙型肝炎病毒)
发布: 2015年02月05日第5卷第3期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1392 浏览次数: 9963
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
诱导型HIV-1库削减检测(HIVRRA):用于评估外周血单个核细胞中HIV-1潜伏库清除策略毒性与效力的快速敏感方法
Jade Jansen [...] Neeltje A. Kootstra
2025年07月20日 2393 阅读
Abstract
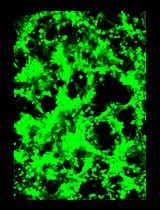
The establishment of a cell culture system for hepatitis C virus based on the JFH-1 strain and human hepatoma cell lines has been instrumental for the study of the viral replication cycle. The robustness of the JFH1-based cell culture models enabled many laboratories around the world to perform HCV infections in cell culture, accelerating the identification of cellular and viral targets to develop novel antiviral compounds. Although other robust infection systems based on different molecular clones and different cell lines have been developed since then, here we describe the protocols corresponding to infections with JFH-1 and JFH1-derived viruses carried out in our laboratory to produce virus stocks and persistently infected cell cultures. We also describe the experimental setups used to determine virus spreading capacity (multiple cycle infections) as well as to dissect early and late aspects of HCV infection (single cycle infections).
Materials and Reagents
- Biological materials
- Human hepatoma cells Huh-7 (Nakabayashi et al., 1982) and derived subclone Huh-7.5.1 clone 2, hereafter clone 2 (Pedersen et al., 2007)
- Viruses: Genotype 2a JFH-1 strain (Zhong et al., 2005) and a cell culture-adapted JFH1 variant D183 (Zhong et al., 2006)
- Human monoclonal anti-E2 (AR3A) (antibody provided by Mansun Law, The Scripps Research Institute) (Law et al., 2008)
- Alexa Fluor 555 Goat Anti-Human IgG (H+L) (Alexa 555-conjugated antibody) (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: A21433 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (LINUS, catalog number: 501805 )
- BSA (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10 735 086 001 )
- Human hepatoma cells Huh-7 (Nakabayashi et al., 1982) and derived subclone Huh-7.5.1 clone 2, hereafter clone 2 (Pedersen et al., 2007)
- Reagents
- 1 M HEPES (pH 7.4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375-500G )
- 100x MEM nonessential amino acids (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11140-050 )
- Penicillin/streptomycin (10,000 U/ ml) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15140-122 )
- 0.5% trypsin/EDTA solution (10x) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15400-054 )
- Prolong (Life Technologies, catalog number: P-36930 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-8787 )
- Formaldehyde solution (37% wt% in H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 252549 )
- 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 32670 )
- Dulbecco´s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 41965-039 ) (see Recipes)
- 10x phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
- Immunofluorescence (IF) buffer (see Recipes)
- 4% formaldehyde solution (see Recipes)
- 1 M HEPES (pH 7.4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375-500G )
Equipment
- CO2 incubator
- 1.5 ml safe-lock PCR clean microtubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030 123 328 )
- Falcon 50 ml tubes (Falcon®, catalog number: 352098 )
- 75 cm2 cell culture flask (canted neck, 0.2 µM vent cap) (Corning, catalog number: 430641 )
- 162 cm2 traditional straight neck cell culture flask with vent cap (corning, catalog number: 3151 )
- 6 well culture cluster (flat bottom) (Corning, Costar®, catalog number 3506 )
- 12 well culture cluster (flat bottom) (Corning, Costar®, catalog number 3513 )
- 24 well culture cluster (flat bottom) (Corning, Costar®, catalog number 3527 )
- 96 well culture cluster (flat bottom) (Corning, Costar®, catalog number 3599 )
- 5 ml stripette (Corning, Costar®, catalog number 4487 )
- 10 ml stripette (Corning, Costar®, catalog number 4488 )
- 25 ml stripette(Corning, Costar®, catalog number 4489 )
- Pipet aid (IBS INTEGRA Biosciences, catalog number: 155000 )
- Pipetman p200 micropipette (GILSON®, catalog number: F123601 )
- Pipetman p1000 micropipette (GILSON®, catalog number: F123602 )
- Centrifuges (Hettich Zentrifugen, catalog number: EBA 12R )
- -20 °C freezer
- -80 °C freezer
- Fluorescence microscope (inverted fluorescence microscope with long distance objectives)
- Microscope slides and coverslips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 5425508 )
- Filter tips 10 µl (Sorenson Bioscience, catalog number: 35200 )
- Filter tips 20 µl (Sorenson Bioscience, catalog number: 35220 )
- Filter tips 200 µl (Sorenson Bioscience, catalog number: 35230 )
- Filter tips 1,000 µl (Sorenson Bioscience, catalog number: 35260 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Mingorance, L., Vasallo, C., Friesland, M. and Gastaminza, P. (2015). Infection Experiments (Hepatitis C Virus). Bio-protocol 5(3): e1392. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1392.
分类
微生物学 > 抗微生物试验 > 抗病毒试验
微生物学 > 微生物-宿主相互作用 > 病毒
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link